Overview
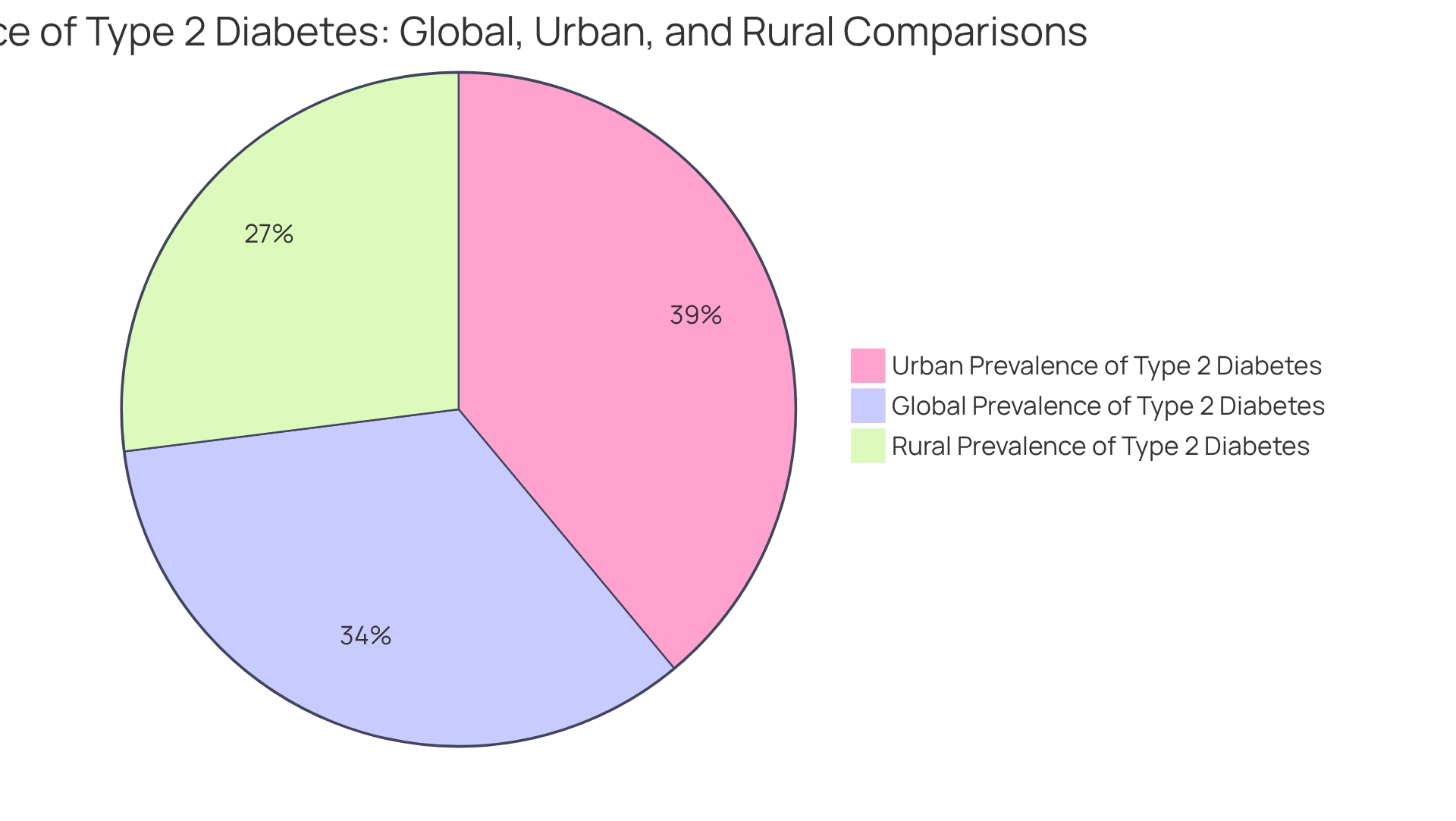
In today’s world, type 2 diabetes affects many lives, and it’s crucial to understand its prevalence. Did you know that urban areas experience a higher rate of this condition, with a prevalence of 12.7% compared to 8.8% in rural regions? This difference is not just a statistic; it reflects the real challenges that individuals face every day. It’s important to recognize that access to healthcare, nutrition education, and lifestyle choices play significant roles in this disparity.
Many patients find that these factors can make a profound impact on their health journey. This highlights the urgent need for tailored public health interventions that address the unique challenges faced by each community. We must come together to foster understanding and support for those navigating these struggles. By focusing on compassionate solutions, we can encourage healthier choices and empower individuals to take charge of their health.
Let’s work towards a future where everyone has the resources and guidance they need to thrive. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of those affected by type 2 diabetes.
Introduction
In a world increasingly touched by chronic health conditions, type 2 diabetes emerges as a significant concern, with its prevalence rising at an alarming rate. Have you noticed the growing disparity in diabetes rates between urban and rural populations? This striking difference invites us to explore the underlying factors that contribute to this divide. It’s important to recognize that as healthcare systems strive to address these challenges, understanding the unique needs of each community becomes essential.
With projections indicating a nearly 60% increase in diabetes cases by 2025, the urgency for targeted interventions and innovative management strategies has never been greater. Many patients find that tailored public health initiatives can make a transformative difference in their lives. This article delves into the complexities of type 2 diabetes prevalence, exploring the critical differences in care and outcomes across diverse environments. Together, we can uncover paths to better health and well-being.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes Prevalence: Key Definitions and Statistics
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that can feel overwhelming, marked by insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels. It’s important to recognize that around 11.1% of the adult population globally is affected by type 2 diabetes prevalence, according to the 2025 IDF Diabetes Atlas. Many patients find that significant differences exist between urban and rural areas. In urban environments, the type 2 diabetes prevalence can soar to 12.7%, while in rural regions, the type 2 diabetes prevalence averages around 8.8%. This stark contrast underscores the necessity for targeted interventions tailored to the unique challenges faced in both settings, particularly as the worldwide burden of diabetes intensifies, with forecasts suggesting a remarkable 59.7% rise in type 2 diabetes prevalence by 2025. This highlights the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to tackle this escalating medical crisis.
Have you ever felt like you’re facing this alone? One patient shared, ‘If you have the opportunity to join this family, DO IT! It will be the most important choice you will ever make in your life.’ Transformative patient experiences, like those from Dr. Jason Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, demonstrate the potential for considerable wellness improvements.
Patients have reported remarkable changes, including substantial weight loss and improved blood sugar levels. It’s encouraging to see how lives can be transformed through supportive programs. To discover more about how you can restore your well-being, reach out to the Integrative Wellness Center today. You deserve to feel your best, and support is available to help you on this journey.
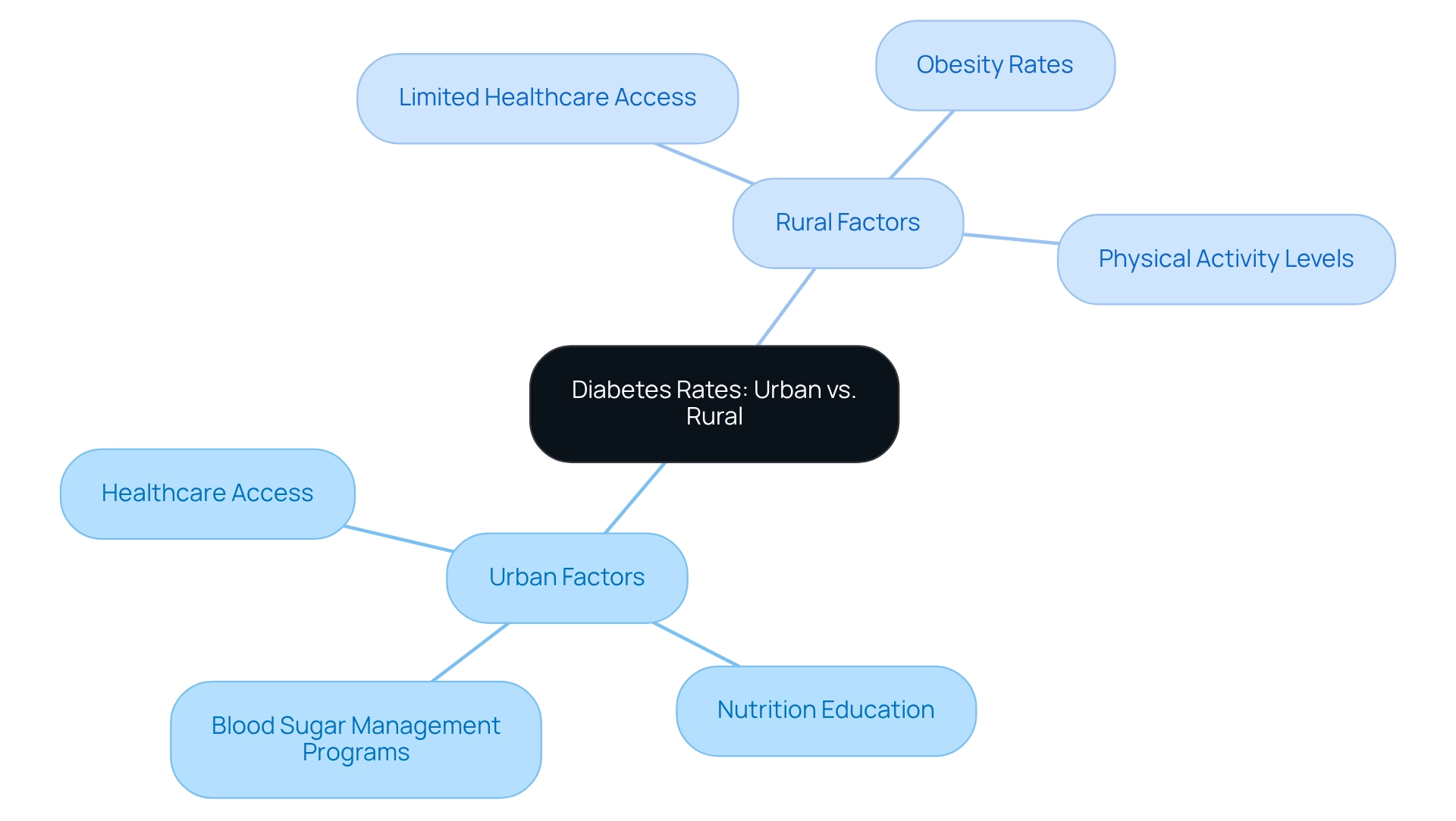
Analyzing Contributing Factors: Urban vs. Rural Diabetes Rates
It’s important to recognize that differences in blood sugar conditions between urban and countryside regions are influenced by various factors. City dwellers typically enjoy better access to healthcare services, nutrition education, and blood sugar management programs, leading to improved health outcomes. In contrast, many countryside communities face significant challenges, including limited healthcare access, higher obesity rates, and lower levels of physical activity. Studies reveal that the type 2 diabetes prevalence in rural areas can be 9% to 17% greater compared to other regions. Contributing risk factors such as age, income, and education level play critical roles in these disparities. Many patients find that understanding these issues is the first step toward seeking help.
These disparities highlight the urgent need for tailored public health strategies that truly address the unique challenges each community faces. By ensuring that interventions are relevant and impactful, we can foster healthier lives for everyone. Together, we can create a supportive environment that nurtures well-being and encourages positive change.
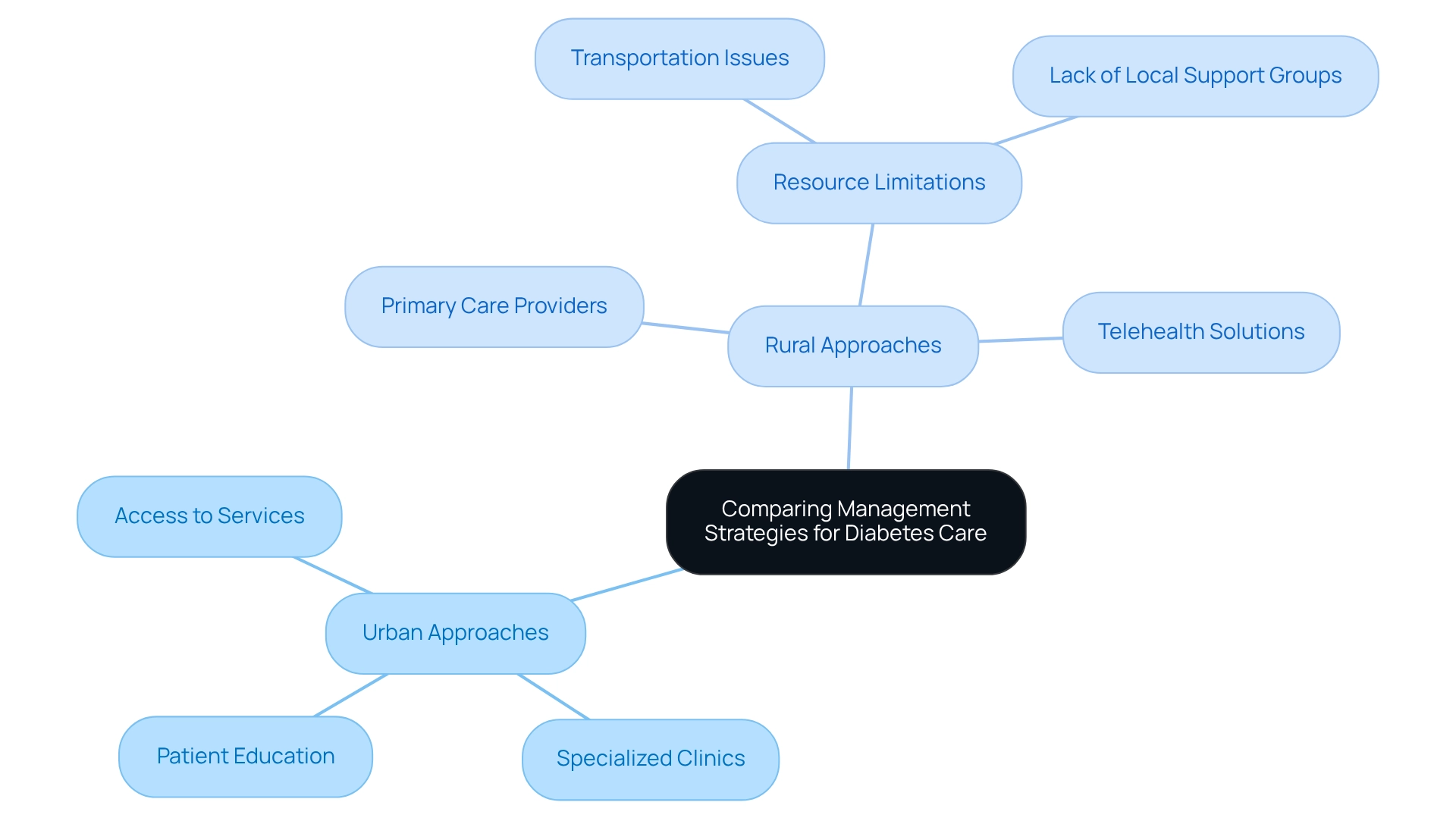
Comparing Management Strategies: Urban and Rural Approaches to Diabetes Care
Management strategies for addressing type 2 diabetes prevalence can vary significantly between urban and rural environments, and it’s important to recognize how these differences impact patient care. In urban centers, individuals often benefit from a wider range of healthcare services, including specialized clinics dedicated to blood sugar management and access to endocrinologists. This supportive environment facilitates comprehensive education and guidance for managing blood sugar levels, which can greatly enhance patient outcomes.
Conversely, many patients in remote areas find themselves relying on primary care providers who may not have the necessary resources or specialized training to effectively manage blood sugar conditions. This limitation can lead to poorer well-being outcomes for those in rural settings, compounded by challenges such as transportation difficulties and a lack of local support groups. Many patients find that these barriers can feel overwhelming, making it crucial for healthcare systems to address these disparities.
Research indicates that urban-rural differences in health education regarding glucose conditions are influenced by various factors, including education level and overall health status. This highlights the necessity for targeted interventions that cater specifically to the needs of rural populations. Creative solutions, such as telehealth services, are emerging to bridge these gaps, offering remote access to care and education for managing blood sugar conditions. However, challenges persist, underscoring the need for ongoing efforts to improve infrastructure and outreach in remote communities.
By understanding these dynamics, healthcare providers can better customize their strategies to meet the unique needs of both urban and rural patients with blood sugar issues. Together, we can work towards a healthier future, ensuring that every individual has the support they need to thrive.
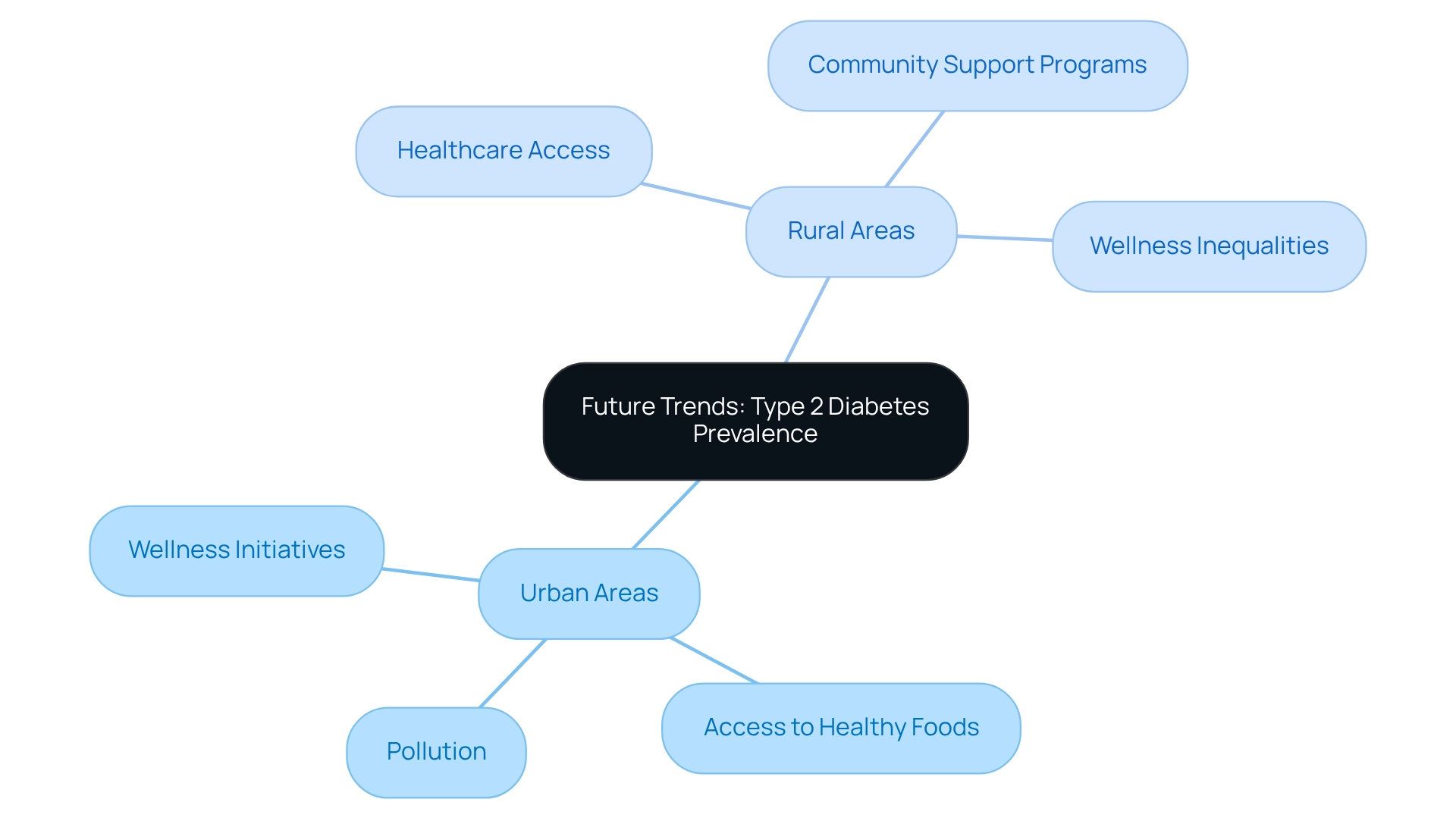
Future Trends: Projecting Type 2 Diabetes Prevalence in Urban and Rural Areas
Looking ahead, it’s important to recognize that the occurrence of type 2 conditions is expected to grow significantly in both metropolitan and rural areas. This increase is driven by factors such as rising obesity levels and an aging population. Many patients find that forecasts suggest that by 2025, the number of individuals facing blood sugar issues could rise by nearly 60%. Rural regions may experience an even steeper increase due to existing wellness inequalities.
In Saudi Arabia, for example, the Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALY) count was reported at 391 (thousands), which highlights the global implications of diabetes prevalence. Public wellness initiatives must focus on prevention and education tailored to the unique challenges of each environment. For urban areas, addressing environmental factors like pollution and access to healthy foods will be crucial. In contrast, rural areas may benefit from improved healthcare access and community-based support programs.
As Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the Integrative Wellness Center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.”
It’s also important to note that the analysis did not estimate gestational conditions or rarer forms of the disease due to a lack of relevant data, which presents additional challenges in understanding the full landscape of the condition. These tailored strategies are vital for effectively managing the unique challenges each setting presents, ultimately aiming to alleviate the growing burden of diabetes.
Conclusion
The exploration of type 2 diabetes prevalence reveals significant disparities between urban and rural populations, deeply influenced by various social, economic, and healthcare access factors. It’s important to recognize that urban areas often report higher rates of diabetes, largely due to better healthcare facilities and resources. In contrast, rural communities grapple with challenges such as limited access to care and higher obesity rates. These differences highlight the urgent need for tailored public health interventions that truly address the unique circumstances of each community.
As we look ahead, diabetes cases are projected to rise dramatically in the coming years. This reality makes it increasingly crucial to implement effective management strategies that cater to the specific needs of both urban and rural patients. Many patients find that innovations like telehealth services show promise in bridging the gap in care. However, there remains a pressing need for ongoing efforts to enhance healthcare infrastructure and outreach in rural areas.
In summary, tackling the diabetes epidemic requires a multifaceted approach that considers the distinct challenges faced by different populations. By prioritizing targeted education and support initiatives, healthcare systems can empower individuals to take charge of their health. This empowerment ultimately leads to improved outcomes and a reduction in the burden of this chronic condition. The time to act is now, as the health of our communities hangs in the balance. Together, we can make a difference and foster healthier futures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels.
What percentage of the global adult population is affected by type 2 diabetes?
Approximately 11.1% of the adult population globally is affected by type 2 diabetes, according to the 2025 IDF Diabetes Atlas.
How does type 2 diabetes prevalence differ between urban and rural areas?
In urban environments, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes can reach 12.7%, while in rural regions, it averages around 8.8%.
What is the forecast for type 2 diabetes prevalence by 2025?
The forecast suggests a significant 59.7% rise in type 2 diabetes prevalence by 2025.
Why is there a need for targeted interventions for type 2 diabetes?
The stark contrast in prevalence between urban and rural areas highlights the necessity for tailored interventions that address the unique challenges faced in both settings.
What kind of support is available for patients with type 2 diabetes?
Supportive programs, such as Dr. Jason Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, have shown potential for considerable wellness improvements, including weight loss and improved blood sugar levels.
How can individuals seeking support for type 2 diabetes improve their well-being?
Individuals can reach out to the Integrative Wellness Center to discover more about programs and support available to help restore their well-being.