Overview
This article discusses the essential ICD-10 codes and guidelines for screening diabetes, and it truly understands the challenges faced by patients. It emphasizes the importance of accurate coding in patient management and healthcare reimbursement, recognizing how these factors can significantly impact lives. The primary code for screening, Z13.1, is highlighted as vital for early detection and intervention. Many patients find that early diagnosis can lead to more effective management of their condition.
However, it’s important to recognize that coding errors can have serious consequences, such as delayed treatment and financial losses for healthcare providers. This underscores the critical role of precise documentation in diabetes care. By ensuring accurate coding, we can help facilitate timely interventions that make a real difference in patients’ lives. Together, we can work towards a healthier future, emphasizing the need for careful attention to detail in every aspect of diabetes management.
Introduction
In the complex landscape of diabetes management, accurate coding is more than just a bureaucratic necessity; it is a cornerstone of effective patient care. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, it’s important to recognize that understanding the intricacies of ICD-10 codes is crucial for healthcare providers who want to deliver timely and appropriate interventions. The primary code for diabetes screening, Z13.1, serves as a vital tool in identifying at-risk patients, but it represents just one part of a larger puzzle.
Many patients find that navigating these complexities can be overwhelming. This article delves into the essential ICD-10 codes, highlighting the importance of precise coding for reimbursement and patient outcomes. We will also explore best practices for screening and the serious consequences that can arise from coding errors. As healthcare continues to evolve, staying informed about these coding practices is imperative for both providers and patients in the fight against diabetes. Together, we can foster a supportive environment that encourages healthy living and proactive management.
ICD-10 Codes for Diabetes Screening: Key Identifiers
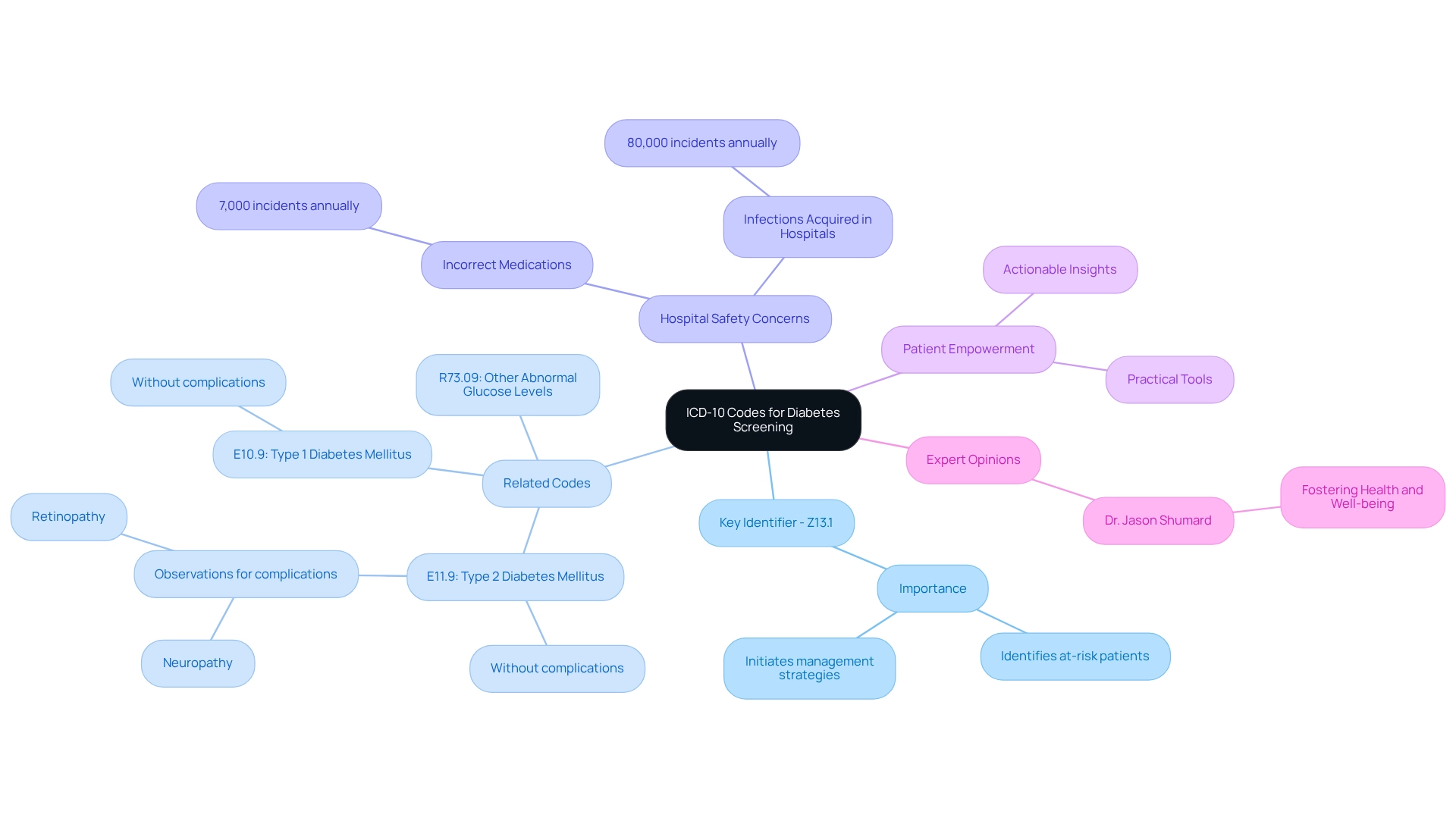
The main ICD-10 code for screening diabetes, Z13.1, indicates an encounter specifically for testing for diabetes mellitus. This code is crucial as it helps healthcare providers identify patients at risk and initiate appropriate management strategies. Other relevant codes include:
- E11.9: Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications.
- E10.9: Type 1 diabetes mellitus without complications.
- R73.09: Other abnormal glucose levels.
These codes are essential for precise documentation of patient encounters, ensuring that medical providers can deliver appropriate care and navigate reimbursement processes effectively. It’s important to recognize that recent statistics indicate approximately 75% of healthcare providers utilize the Z13.1 code for screening diabetes, highlighting its significance in clinical practice.
Many patients find that incorporating expert opinions can be beneficial. The use of Z13.1 is highlighted as a key identifier in managing blood sugar conditions, allowing for early detection and intervention. Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where they can reclaim their health and well-being.” This emphasizes the importance of individual empowerment in managing blood sugar levels.
However, it is essential to consider the broader context of hospital safety concerns. For instance, there are about 7,000 incorrect medications and 80,000 infections acquired in hospitals each year, which can significantly impact the management of blood sugar conditions. Individuals with blood sugar issues may face an increased risk for complications if they receive erroneous medications or encounter infections. This highlights the significance of precise documentation and record-keeping in providing safe and effective care.
Real-world instances of E11.9 classification involve situations where individuals with type 2 diabetes are observed for complications like neuropathy or retinopathy. This illustrates how accurate classification can lead to improved outcomes for individuals. Overall, comprehending these ICD-10 codes, especially screening diabetes ICD 10, is vital for both medical providers and individuals. They play a crucial role in the management and treatment of blood sugar conditions, particularly concerning hospital safety matters.
Importance of Accurate Coding in Diabetes Management
Managing blood sugar conditions can be challenging, and precise classification plays a crucial role in addressing these difficulties for several important reasons.
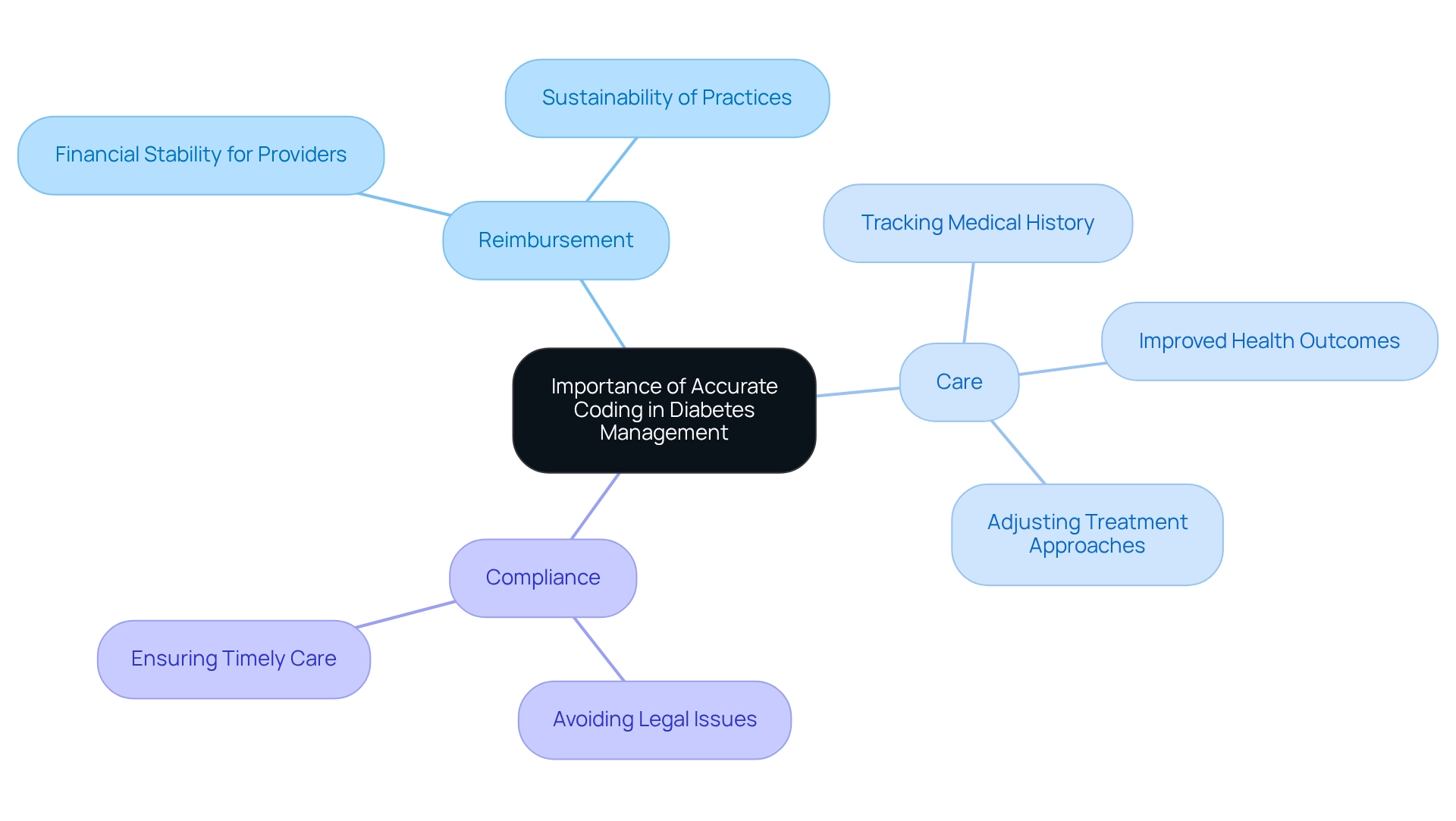
- Reimbursement: It’s essential to ensure that medical providers receive appropriate compensation for their services. This financial stability is vital for the sustainability of practices, especially in diabetes management, where ongoing care is often necessary.
- Care: Accurate documentation allows for efficient tracking of medical history and treatment plans, which directly contributes to improved health outcomes. When providers use precise codes, they can better monitor individual progress and adjust treatment approaches as needed.
- Compliance: Adhering to established guidelines is essential to avoid legal issues and penalties related to incorrect billing practices. This not only protects medical practitioners but also ensures that individuals receive the care they need without unnecessary delays.
It’s important to recognize that incorrect labeling can lead to serious consequences, such as treatment delays and financial challenges for medical providers. Research indicates that effective long-term care management can significantly reduce medical expenses among Medicare recipients, underscoring the importance of precise classification in facilitating effective blood sugar management.
Real-life experiences highlight the challenges that arise from classification errors, which can disrupt reimbursement processes and ultimately affect patient care. Many patients find that the need for precise programming is further emphasized by recent findings supporting the exploration of innovative care models, like the NFFCCM, aimed at enhancing blood sugar management through improved programming practices and modern technologies. As Lizheng Shi, PhD, noted, ‘Our findings provide evidence to support NFFCCM as an effective tool for managing blood sugar conditions.’ Additionally, the final evaluation of IBT guidelines in October 2015 serves as a reminder of the evolving nature of classification practices and their significance in the contemporary management of blood sugar conditions.
As we look towards 2025, the importance of precise classification in managing blood sugar conditions remains critical—not just for ensuring compliance and reimbursement, but also for fostering better individual outcomes and overall medical efficiency. Understanding how coding accuracy influences patient perceptions of care is vital, as it shapes their views on treatment and the healthcare system as a whole.
Guidelines for Screening Diabetes: Best Practices
Best practices for diabetes screening encompass several key strategies that can truly make a difference in your health journey:
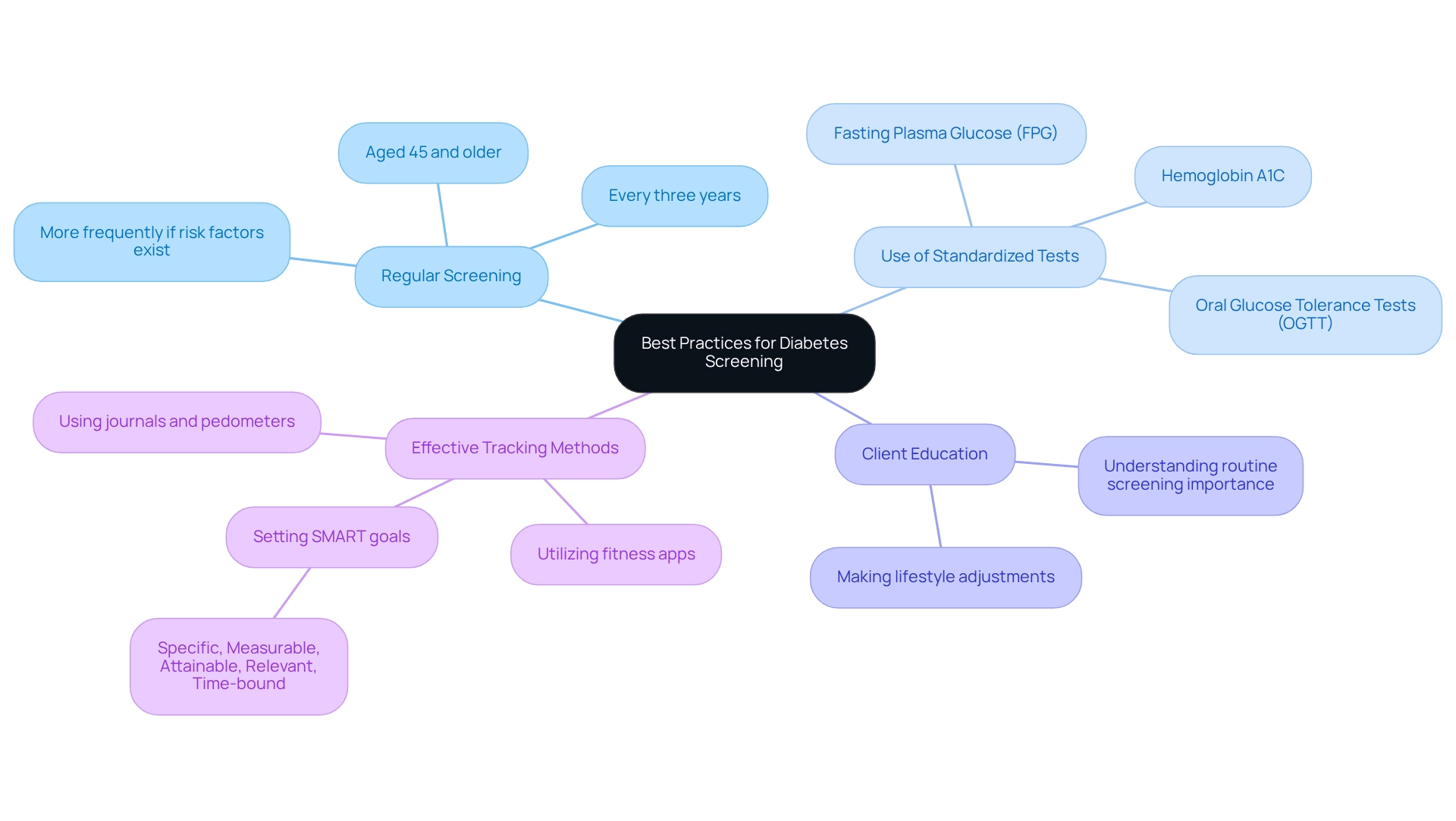
- Regular Screening: It’s important to recognize that adults aged 45 and older should undergo diabetes screening every three years. If you have additional risk factors, such as obesity or a family history of blood sugar issues, consider having screenings more frequently. Early detection can lead to timely intervention, which is crucial for your well-being.
- Use of Standardized Tests: Accurate diagnosis relies on standardized tests, including fasting plasma glucose (FPG), hemoglobin A1C, and oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT). These tests provide dependable measurements for evaluating blood sugar levels and identifying potential concerns.
- Client Education: Many patients find that understanding the importance of routine screening and making lifestyle adjustments can empower them to prevent or postpone diabetes. Knowledge is a powerful tool in promoting proactive health management, which is essential for effectively managing blood sugar conditions.
In addition to these guidelines, consider implementing effective tracking methods for your health management. Utilizing fitness apps, journals, and pedometers can help you monitor your progress in lifestyle changes. Setting SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—can significantly enhance your focus and motivation. For example, aiming to achieve 10,000 steps daily or gradually increasing your exercise duration can lead to better health outcomes. Research indicates that goal-setting persistence scores can positively impact performance, demonstrating the effectiveness of structured goal-setting. Regularly reviewing your progress not only fosters accountability but also allows for the adaptation of goals as your fitness levels change. By prioritizing goal-setting and consistent progress tracking, you can cultivate a sense of achievement and maintain engagement in your health management efforts.
Adhering to these guidelines not only enhances your diabetes screening practices but also contributes to improved health outcomes. For instance, a study revealed that only 46.2% of adults meeting the American Diabetes Association criteria reported being screened for diabetes, highlighting the need for improved rates, particularly among high-risk populations. This research also highlighted considerable undiagnosed blood sugar conditions and prediabetes rates, with elevated screening rates noted among African American and Hispanic participants. Furthermore, average medical costs for individuals with diagnosed conditions related to blood sugar are 2.6 times greater than those without, emphasizing the financial consequences of postponed diagnosis and treatment. As Dr. Karin M Nelson, M.D., M.S.H.S. stated, “This report characterizes national screening patterns by risk status and other sociodemographic factors, and examines the relationship between nonwhite ethnicity and disease screening.” By prioritizing regular screening and educating individuals, healthcare providers can significantly influence the management of blood sugar levels and enhance overall well-being.
For more information on managing your condition and to receive personalized support, please contact the Integrative Wellness Center. Additionally, remember to stay informed about heat wave preparedness tips to ensure your health and safety during extreme weather conditions.
Consequences of Coding Errors in Diabetes Screening
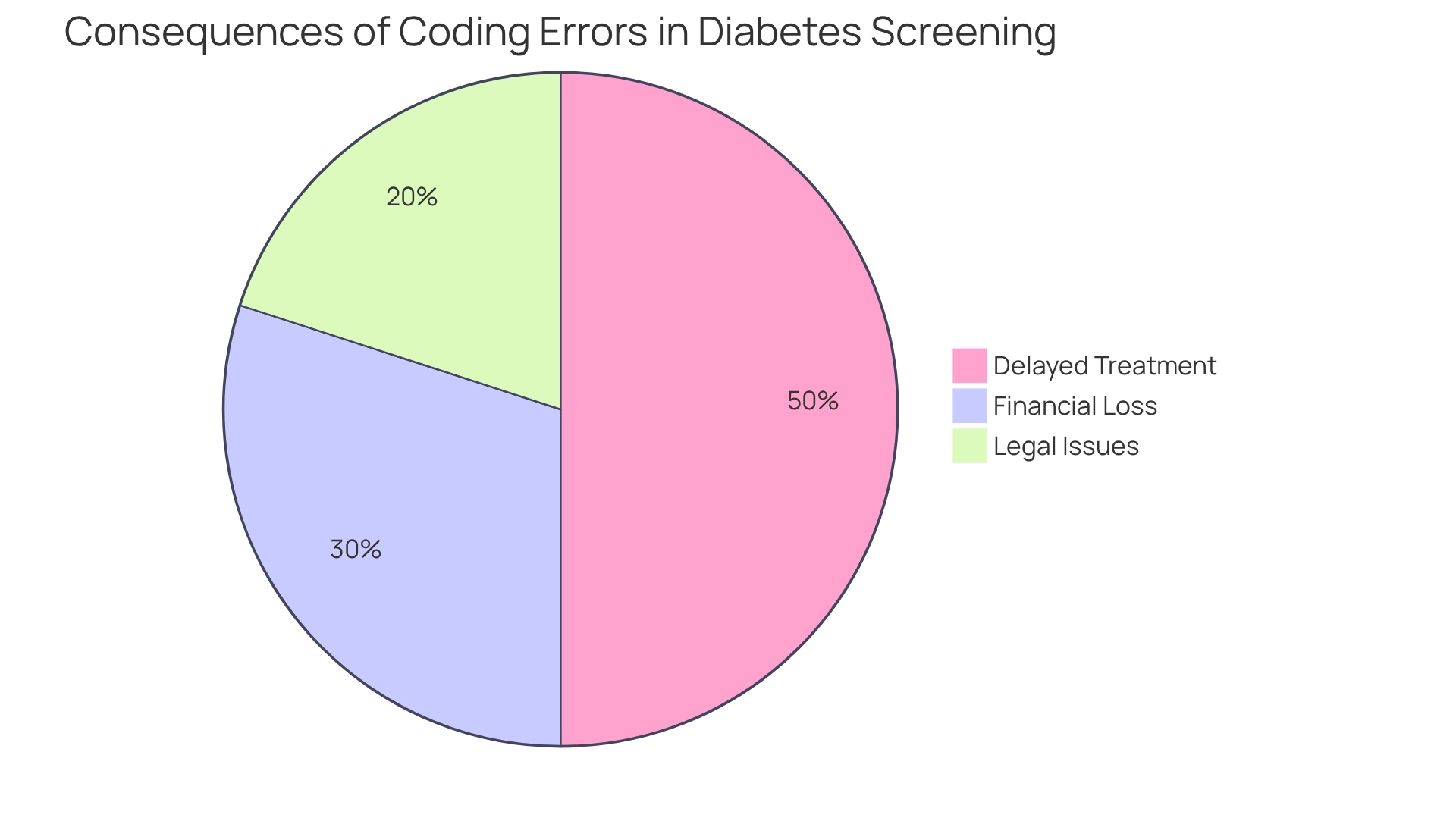
Coding errors in diabetes screening can have profound consequences that impact patients’ lives significantly. It’s important to recognize that these errors can lead to:
-
Delayed Treatment: Inaccurate coding can result in misdiagnosis or delays in necessary interventions, ultimately exacerbating health issues for patients. Many patients find that documentation discrepancies can lead to a startling 30% rise in hospital readmissions due to delayed care. This highlights the essential need for precise documentation practices to ensure timely and effective treatment.
-
Financial Loss: Healthcare providers may face denied claims or decreased reimbursements as a result of inaccurate billing. This situation not only jeopardizes their financial stability but can also lead to significant revenue losses. Reports indicate that programming mistakes in diabetes management alone can result in millions of dollars in lost income each year for medical facilities, underscoring the financial stakes involved.
-
Legal Issues: Ongoing inaccuracies in documentation can expose service providers to audits, penalties, or even legal actions for fraudulent billing practices. The repercussions of such errors can tarnish a provider’s reputation and lead to costly legal battles. As one specialist remarked, “I have to say, though, programming errors can really mess things up,” emphasizing the real-world implications of these mistakes.
To alleviate these risks, it is essential for healthcare professionals to engage in continuous training and strictly follow the screening diabetes ICD-10 guidelines. Utilizing advanced technologies, like AI and automation, can improve programming precision. This enables providers to focus more on client care while reducing administrative responsibilities. A case study on the integration of AI in medical coding illustrates how technology can analyze coding patterns and recommend corrections, ultimately improving overall coding accuracy and patient outcomes. By embracing these practices, we can foster a more supportive environment for both patients and providers.
Conclusion
The importance of accurate coding in diabetes management truly cannot be overstated. It’s important to recognize that the primary ICD-10 code for diabetes screening, Z13.1, plays a pivotal role in identifying at-risk patients and enabling timely interventions. Additionally, understanding other relevant codes, such as E11.9 and E10.9, is essential for comprehensive patient care. Accurate coding not only facilitates appropriate reimbursement for healthcare providers but also ensures that patients receive the necessary attention and treatment, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
Many patients find that best practices in diabetes screening, including regular assessments and patient education, are critical in fostering proactive health management. By empowering patients with knowledge and resources, healthcare providers can help them take charge of their health, thereby reducing the prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes and its complications. The significance of accurate coding extends beyond individual patient care; it impacts the entire healthcare system, influencing financial stability, compliance, and overall efficiency.
In summary, the intersection of precise coding, effective screening practices, and patient empowerment creates a robust framework for managing diabetes. As healthcare continues to evolve, prioritizing these elements will be essential in ensuring that both providers and patients can navigate the complexities of diabetes management effectively. By fostering a culture of accuracy and education, the healthcare community can significantly enhance the quality of care and improve health outcomes for individuals living with diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main ICD-10 code for screening diabetes?
The main ICD-10 code for screening diabetes is Z13.1, which indicates an encounter specifically for testing for diabetes mellitus.
Why is the Z13.1 code important?
The Z13.1 code is crucial as it helps healthcare providers identify patients at risk for diabetes and initiate appropriate management strategies.
What are some other relevant ICD-10 codes related to diabetes?
Other relevant codes include E11.9 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications, E10.9 for Type 1 diabetes mellitus without complications, and R73.09 for other abnormal glucose levels.
How does accurate documentation of these codes benefit healthcare providers?
Accurate documentation of these codes ensures that medical providers can deliver appropriate care and navigate reimbursement processes effectively.
What percentage of healthcare providers use the Z13.1 code for screening diabetes?
Approximately 75% of healthcare providers utilize the Z13.1 code for screening diabetes.
How does the Z13.1 code aid in managing blood sugar conditions?
The Z13.1 code serves as a key identifier in managing blood sugar conditions, allowing for early detection and intervention.
What safety concerns are associated with managing blood sugar conditions in hospitals?
There are concerns regarding incorrect medications and infections acquired in hospitals, which can significantly impact the management of blood sugar conditions and increase the risk for complications.
Can you provide an example of how the E11.9 classification is used in practice?
An example of E11.9 classification involves observing individuals with type 2 diabetes for complications such as neuropathy or retinopathy, illustrating how accurate classification can lead to improved outcomes.
Why is it important for individuals to understand these ICD-10 codes?
Understanding these ICD-10 codes is vital for both medical providers and individuals as they play a crucial role in the management and treatment of blood sugar conditions, particularly concerning hospital safety matters.