Overview:
The article focuses on how to effectively use an A1C glucose equivalent chart to enhance diabetes management. It explains that by understanding A1C percentages and their corresponding average blood sugar levels, patients can make informed decisions regarding their treatment plans, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and reduced risks of complications.
Introduction
Understanding A1C levels is essential for anyone managing diabetes, as it serves as a key indicator of long-term blood glucose control. The A1C test, reflecting average glucose levels over the preceding months, plays a pivotal role in guiding treatment decisions and preventing complications.
With a recommended target of below 7% for many patients, the significance of regular monitoring cannot be overstated. This article delves into the intricacies of A1C testing, its relationship with average blood glucose, and effective strategies for maintaining optimal levels.
By exploring the latest guidelines and personal success stories, readers will gain valuable insights into proactive diabetes management and the transformative potential of a holistic approach.
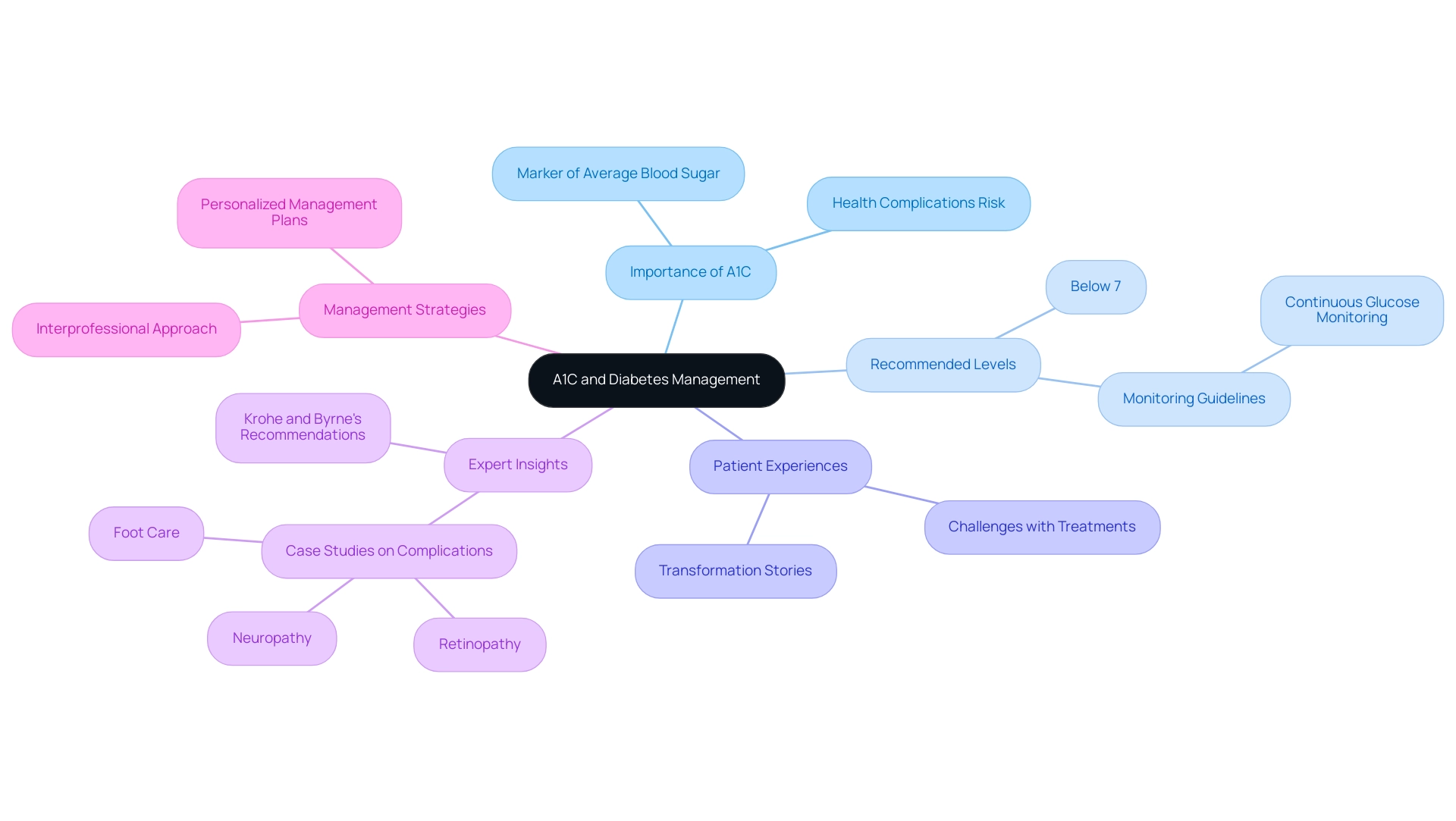
Understanding A1C: The Key to Diabetes Management
The A1C test, referred to as glycated hemoglobin, acts as an important marker of average blood sugar concentrations over the past two to three months and can be interpreted using the A1C glucose equivalent chart presented as a percentage. A higher percentage signifies elevated blood glucose concentrations, which can lead to serious health complications. For individuals managing blood sugar levels, it is typically recommended to maintain an A1C level below 7%, as indicated by the A1C glucose equivalent chart, since this threshold is associated with a reduced risk of complications.
Recent statistics indicate that 93.0% of individuals with this condition have had their cholesterol checked, highlighting a growing awareness of comprehensive health management among this population. Engaging in regular discussions with healthcare providers about A1C results and referencing an A1C glucose equivalent chart is vital, as these conversations facilitate the development of personalized management strategies that can ultimately enhance patient outcomes. Furthermore, the latest guidelines, including Recommendation 7.33, advocate for the continuation of personal continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in hospitalized patients when appropriate, underscoring the dynamic nature of managing blood sugar.
One patient shared their experience of feeling lost and overwhelmed by ineffective treatments, stating,
‘I was depressed, no energy, and had insomnia. I hated how I felt and looked. I was on 2 different meds that weren’t working and was told that I needed insulin.’
However, after joining the Integrative Wellness Center, they experienced a profound transformation, declaring,
‘If you have the opportunity to join this family, DO IT! It will be the most important choice you will ever make in your life.’
This highlights the important transition from conventional methods to a holistic care model that enables patients to find peace and remove concerns about complications.
Ms. Krohe and Ms. Byrne from Novo Nordisk Inc. emphasize the importance of understanding A1C results by using the A1C glucose equivalent chart, stating,
‘Effective management of A1C levels is essential for preventing complications and ensuring a better quality of life for individuals with diabetes-related conditions.’
Additionally, integrating insights from case studies on retinopathy, neuropathy, and foot care can provide real-world examples of managing diabetes complications. By understanding A1C results and their implications, patients can refer to the A1C glucose equivalent chart to empower themselves to make informed decisions regarding their treatment plans, leading to improved overall management of their condition.
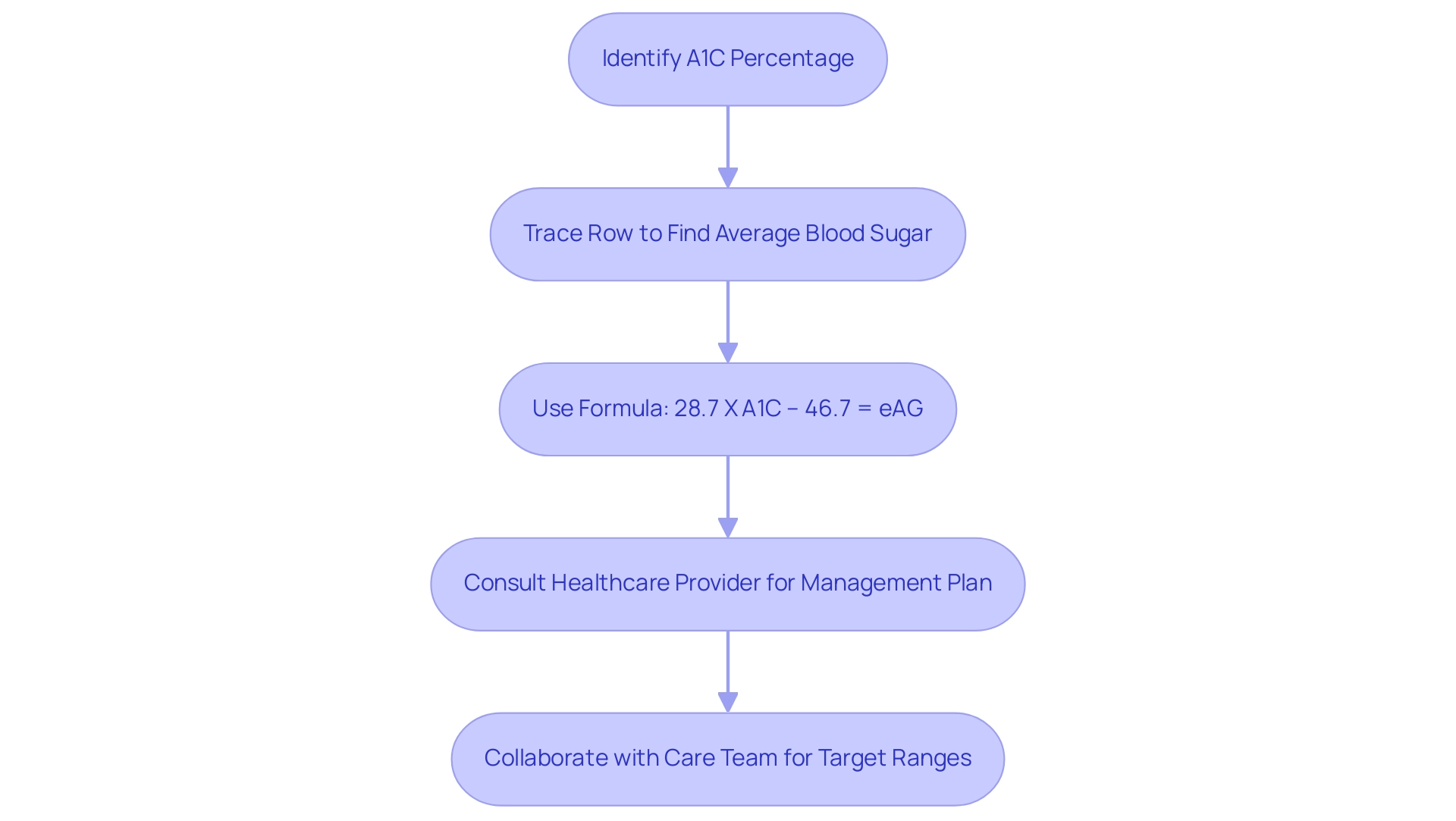
How to Effectively Use the A1C Glucose Equivalent Chart
To effectively utilize the a1c glucose equivalent chart, start by identifying your A1C percentage in the leftmost column of the chart. Then, trace horizontally across the corresponding row to determine the average blood sugar concentration associated with your A1C value. For example, an A1C of 6.0% generally aligns with an average blood sugar concentration of about 126 mg/dL.
This relationship is further illustrated by the formula from the ADAG study: 28.7 X A1C – 46.7 = eAG, which aids in converting A1C values into estimated average blood sugar (eAG) levels. Understanding this conversion is crucial for interpreting your daily glucose monitoring results. Consistently exceeding the average indicated by your A1C may signal underlying insulin resistance, which traditional treatments may not adequately address and could potentially lead to severe health complications, even life-threatening situations.
Therefore, it is advisable to consult your healthcare provider to discuss potential adjustments to your blood sugar management plan. Garner emphasizes the importance of collaborating with a care team to establish specific blood sugar target ranges tailored to your individual needs. Acknowledging the anxiety that frequently comes with worries about complications related to blood sugar, a comprehensive approach can assist in reducing these fears by tackling health at the fundamental basis.
Consistently consulting the a1c glucose equivalent chart not only enhances your understanding of blood sugar management but also serves as a motivating resource for making informed lifestyle changes, especially during pregnancy, to prevent gestational conditions and promote overall well-being.
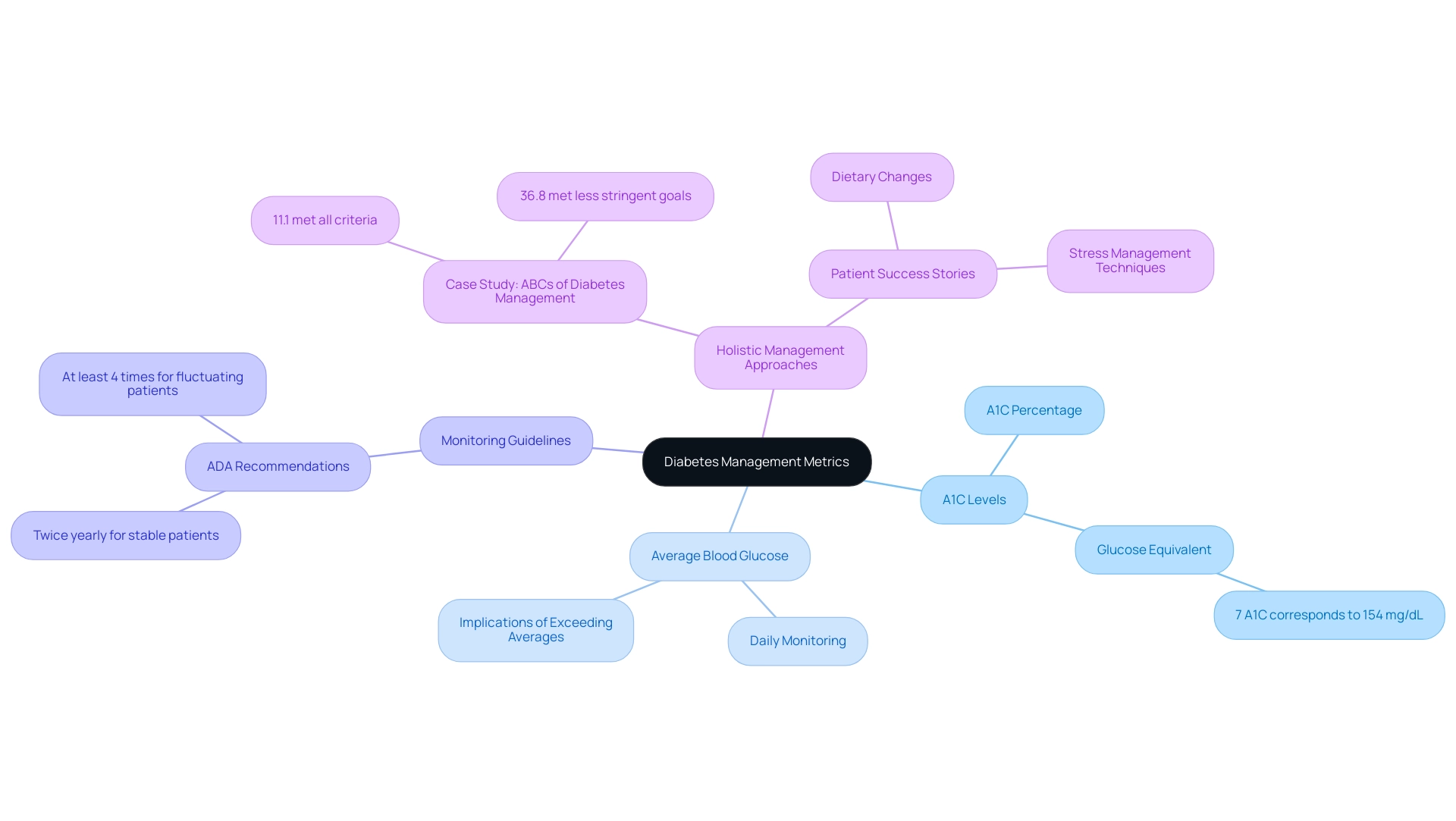
The Connection Between A1C Levels and Average Blood Glucose
The A1C test is essential for assessing your average blood sugar readings over time, while daily blood sugar monitoring provides immediate insights into your current condition. As per ADA guidelines, HbA1c readings should be assessed biannually in stable individuals and no fewer than four times in patients with fluctuations in blood sugar, emphasizing the importance of consistent monitoring in managing blood sugar conditions. Understanding the interplay between these two measures and the A1C glucose equivalent chart is vital.
For instance, an A1C level of 7% is typically indicated on the A1C glucose equivalent chart as corresponding to an average blood sugar concentration of about 154 mg/dL. If daily blood sugar readings consistently surpass this average, it may suggest the necessity for modifications in your management strategy. This understanding fosters a more comprehensive interpretation of daily glucose results when utilizing the A1C glucose equivalent chart in the context of long-term control, enabling more productive discussions with healthcare providers regarding your management plan.
Through the Integrative Wellness Center’s holistic approach, patients have successfully reversed type 2 conditions by addressing root causes and empowering their health. For example, one patient, after engaging in a personalized program that included dietary changes and stress management techniques, reported a significant reduction in A1C values and improvements in overall well-being. A case study titled ‘ABCs of Diabetes Management’ found that only 11.1% of adults met all criteria for A1C, blood pressure, cholesterol, and smoking, underscoring the challenges in achieving optimal management of the condition.
Moreover, Cheryl D. Fryar observes that the age-adjusted prevalence of total and diagnosed diabetes has risen from 1999–2000 to August 2021–August 2023, highlighting the increasing significance of tracking both A1C and blood sugar measurements in the pursuit of better health and diminished anxiety regarding diabetes complications.
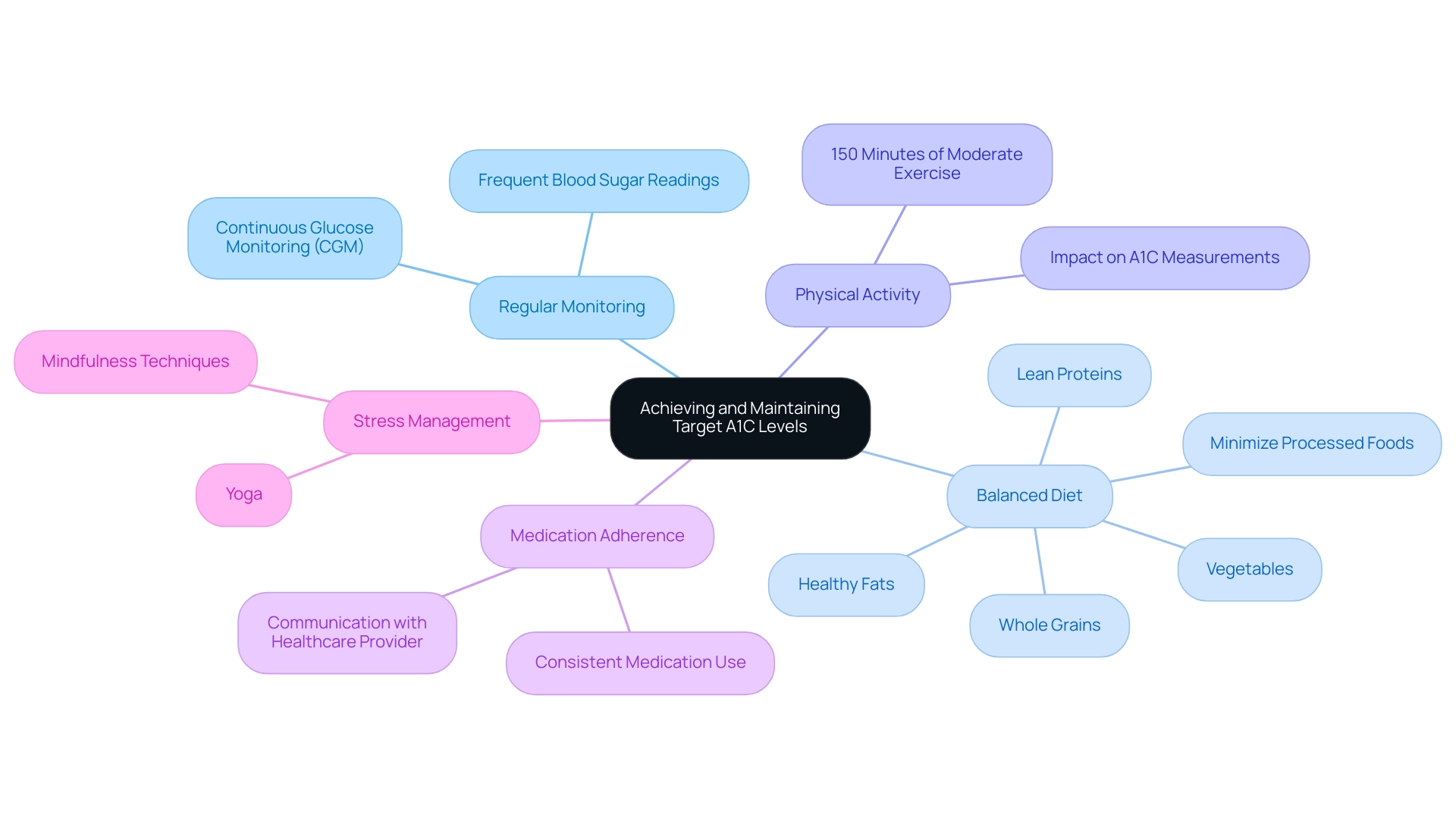
Strategies for Achieving and Maintaining Target A1C Levels
To effectively achieve and maintain target A1C values through a holistic approach, refer to the a1c glucose equivalent chart and consider the following strategies:
-
Regular Monitoring: Frequent observation of blood sugar readings is essential for recognizing patterns and making informed dietary and activity adjustments. The ongoing use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is particularly recommended in hospitalized patients when clinically appropriate, as emphasized in Recommendation 7.33.
-
Balanced Diet: Emphasize a diet abundant in whole grains, lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats, while minimizing the intake of processed foods and sugars. This dietary approach not only supports blood glucose control but is also crucial in managing overall health.
-
Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity is vital; aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Physical activity has a profound effect on A1C measurements and overall well-being, as noted by specialists who utilize the a1c glucose equivalent chart in promoting active lifestyles.
-
Medication Adherence: Consistently taking prescribed medications as directed is key. Open communication with your healthcare provider about any concerns regarding your treatment plan is essential to ensure optimal management of the condition.
-
Stress Management: Utilizing stress-reduction methods, such as mindfulness or yoga, can significantly enhance blood sugar readings, as stress is recognized to negatively impact blood sugar regulation. By incorporating these evidence-based strategies into your daily routine, you can work toward achieving your target A1C levels, which can be monitored using the a1c glucose equivalent chart, and enhancing your overall health.
Recent case studies, including the one titled ‘Impact of Lifestyle and Environment on Diabetes,’ emphasize the effectiveness of lifestyle interventions in managing the condition, reinforcing the significance of preventive measures and public health campaigns aimed at promoting awareness and healthy behaviors. As MD Rabiul Islam from the School of Pharmacy, BRAC University, states, ‘Diabetes mellitus, the fastest growing global public health concern: early detection should be focused.’ This quote highlights the necessity of proactive measures in managing blood sugar issues and the potential for transformative patient experiences through an integrative wellness approach.
Our patients have shared their success stories, stating that re-examining the source of their condition has been pivotal in their journey towards health. One patient remarked, ‘Understanding the root causes of my condition changed everything for me; it empowered me to take control of my health.’ Such testimonials highlight the significance of tackling the condition at its source for effective management.
The Importance of Regular A1C Testing for Effective Diabetes Management
Regular A1C testing is fundamental to effective management of blood sugar levels and is a key component of a holistic approach to patient health at the Integrative Wellness Center. Current guidelines indicate that individuals with blood sugar issues should undergo A1C testing a minimum of twice annually, with more frequent testing advised if treatment strategies alter or if target goals are not met. This testing provides critical insights into the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies, helping to eliminate anxiety over complications and contributing to a sense of peace in managing diabetes.
A1C measurements can assess average blood sugar amounts over time, and the A1C glucose equivalent chart equips patients with understanding about their condition. The American Diabetes Association’s ‘Standards of Care in Diabetes–2024’ emphasizes the necessity of regular monitoring with an A1C glucose equivalent chart to help patients understand their average blood sugar levels and inform necessary adjustments in lifestyle and medication. For instance, case studies on Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) demonstrate that A1C testing is particularly significant for managing this condition, where specific genetic factors influence treatment decisions.
Furthermore, the hospitalization rate for hypoglycemia was reported at 2.5 per 1,000 adults with the condition in 2019, highlighting the potential risks associated with inadequate glucose management. Unlike conventional therapies that may neglect individual patient needs, prioritizing regular A1C testing is crucial for maintaining optimal health and effectively preventing complications associated with the condition. This approach supports our commitment to a breakthrough strategy for reversing Type 2 diabetes and addressing the root causes of insulin resistance, ultimately helping patients find new peace in their lives.
Conclusion
Understanding A1C levels is crucial for anyone managing diabetes, as they serve as a vital indicator of long-term blood glucose control. The A1C test not only reflects average glucose levels over the preceding months but also guides treatment decisions and helps prevent serious complications. Regular monitoring, ideally aiming for an A1C level below 7%, is essential for effective diabetes management.
This article explored the intricacies of A1C testing, the relationship between A1C levels and average blood glucose, and strategies for maintaining optimal levels. The importance of personalized management strategies, as highlighted through patient testimonials and case studies, underscores the shift towards a holistic approach in diabetes care. Furthermore, effective use of the A1C glucose equivalent chart and regular discussions with healthcare providers empower patients to make informed decisions regarding their treatment plans.
In conclusion, prioritizing regular A1C testing and understanding its implications can lead to better health outcomes and a significant reduction in anxiety related to diabetes management. By integrating lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and stress management techniques, individuals can take proactive steps toward achieving and maintaining their target A1C levels. Embracing this comprehensive approach not only enhances overall health but also fosters a sense of control and peace in the journey of living with diabetes.