Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, the A1C test stands out as a pivotal tool for assessing blood glucose control over time. This test not only provides a snapshot of average glucose levels but also plays a critical role in shaping personalized management strategies for individuals living with diabetes.
With the rising prevalence of diabetes, particularly among diverse populations, understanding the significance of A1C results has never been more crucial. This article delves into the intricacies of the A1C test, offering insights on how to:
- Interpret results
- Utilize conversion charts
- Implement effective monitoring practices
By fostering a comprehensive approach to diabetes care that addresses both physiological and psychological aspects, individuals can take proactive steps towards better health outcomes and reduced anxiety about potential complications.
Understanding the A1C Test: Importance for Diabetics
The A1C test is essential in blood sugar control, as it measures the percentage of hemoglobin in your blood that has combined with glucose, and this information can be displayed on an A1C and glucose chart. This test is especially important for people with blood sugar issues, as it offers a dependable representation of average blood glucose readings over the prior two to three months, which can be visualized in an A1C and glucose chart. By understanding your A1C results through the A1C and glucose chart, you and your healthcare team can formulate effective strategies for your management plan within a holistic framework, aiming to eliminate worry about developing traumatic and debilitating complications.
A commonly accepted standard is that an A1C level of 7% or lower signifies good control for most adults with blood sugar issues; however, it is crucial to acknowledge that individual targets may differ depending on specific health conditions, as noted in the A1C and glucose chart and tailored advice from your healthcare provider. Recent studies emphasize that the A1C test, illustrated in the A1C and glucose chart, captures chronic hyperglycemia more effectively than two fasting assessments or the 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test, underscoring its importance in monitoring blood sugar levels. With the rising occurrence of identified health conditions related to blood sugar, especially among Hispanic individuals—representing 5.0 million recognized and 1.9 million undetected cases—customized treatment strategies are essential.
The Integrative Wellness Center advocates for a comprehensive strategy that includes monitoring through an A1C and glucose chart while also addressing underlying factors contributing to insulin resistance. Furthermore, a recent study titled ‘International Comparison of Continuous Glucose Monitoring’ provided insights into the effectiveness of continuous glucose monitoring in youth with type 1 condition, which may also inform strategies for managing A1C levels. As noted by healthcare professionals, it is crucial that patients communicate any factors impacting their condition management with their doctors, as highlighted by the statement, ‘Let your doctor know if any of these factors apply to you.’
This collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers can lead to more tailored and effective treatment plans, ultimately empowering patients to mitigate anxiety about diabetes complications and focus on their health.
How to Read and Utilize the A1C to Glucose Conversion Chart
To effectively utilize the a1c and glucose chart, begin by locating your A1C percentage along the left side of the chart. The corresponding average blood glucose amount is indicated on the right side. For instance, an A1C of 6.0% correlates to an average blood glucose concentration of approximately 126 mg/dL.
This a1c and glucose chart is a valuable tool for tracking how fluctuations in your A1C levels can influence your average glucose readings. By understanding this relationship, you can make informed adjustments to your diet, exercise regimen, and medication as necessary, aligning with a holistic approach to health that addresses root causes and empowers your well-being. Regular consultation of the a1c and glucose chart is recommended to improve your understanding of blood sugar control, thereby supporting better health outcomes.
Significantly, recent statistics show that:
- 94.2% of individuals receive A1C tests
- 96.8% have their blood pressure examined
- 93.0% have their cholesterol assessed
This highlights the chart’s importance in ongoing care for the condition. Furthermore, as highlighted in transformative patient success stories from the Integrative Wellness Center, such as M.L. ‘s experience of losing 55 lbs and reducing their A1C from 9.1 to 5.7, monitoring A1C levels is crucial given the rising trend in blood sugar conditions, which increased from 6.3% in 2004 to 8.3% in 2021.
This success story exemplifies how a personalized, holistic approach can alleviate the anxiety surrounding complications related to blood sugar management. According to Qiuping Gu from the National Center for Health Statistics, understanding the prevalence of total, diagnosed, and undiagnosed conditions related to blood sugar is essential for effective oversight, reinforcing the value of a comprehensive, integrative approach.
The Connection Between A1C Levels and Average Blood Glucose
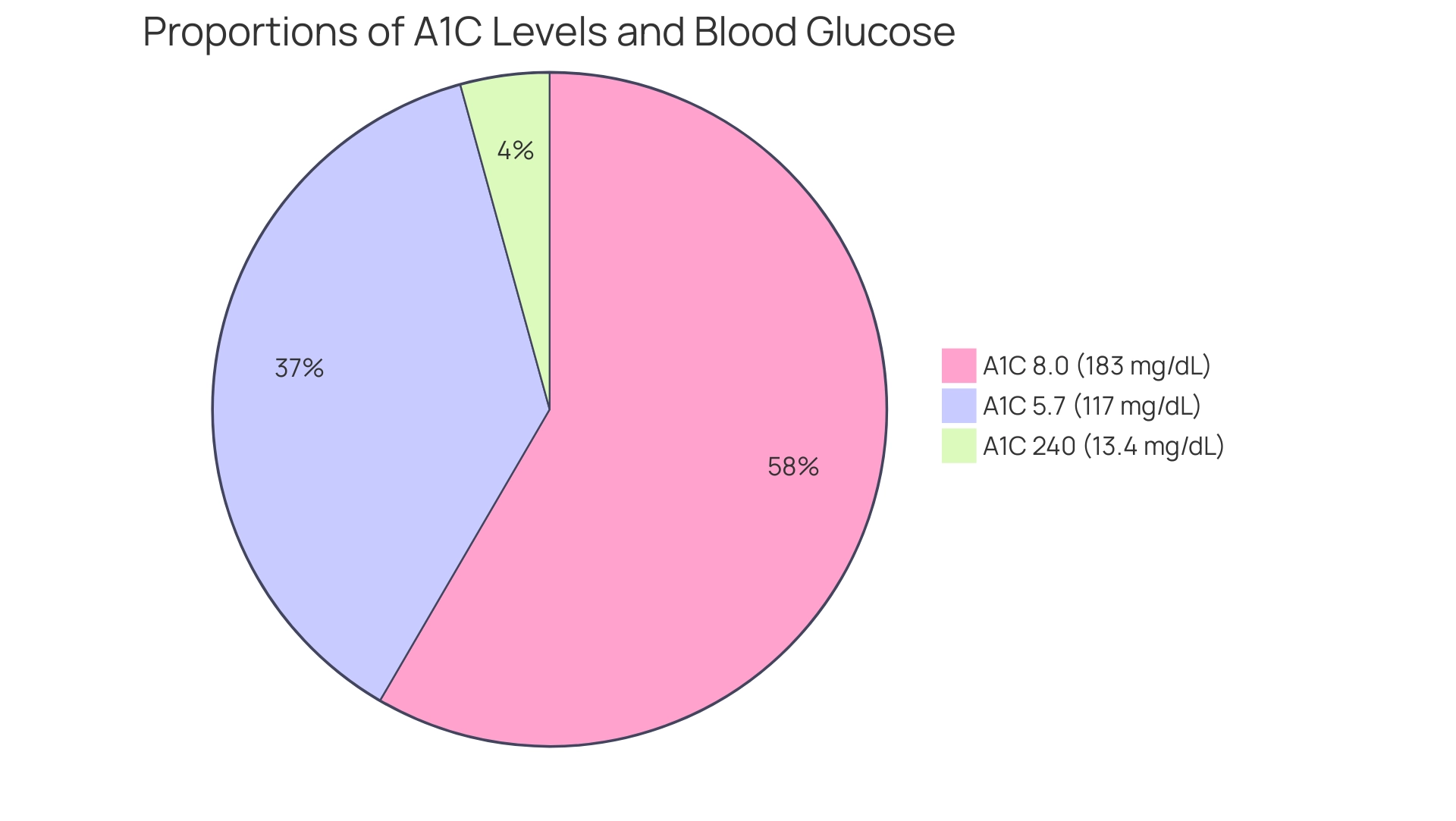
A1C levels serve as a crucial indicator of average blood glucose levels, which can be clearly seen in the a1c and glucose chart that illustrates the relationship between the two metrics. For instance, according to the a1c and glucose chart:
- An A1C of 5.7% correlates with an average blood glucose of approximately 117 mg/dL.
- An A1C of 8.0% translates to an average of 183 mg/dL.
- An A1C of 240 corresponds to an estimated average glucose (eAG) of 13.4 mg/dL.
This direct correlation underscores the necessity of regular monitoring for individuals managing diabetes, particularly in light of the potential complications that can arise from traditional treatments, which can sometimes lead to severe outcomes. Grasping this relationship not only assists in understanding the long-term effects of glucose management but also highlights the significance of using the A1C and glucose chart to keep A1C values within the target ranges set by healthcare experts.
As noted by H.C.G., who contributed to and researched this topic, such diligence is vital, as higher A1C levels indicated in the a1c and glucose chart have been statistically linked to an increased risk of diabetes-related complications, which can induce significant anxiety for patients.
This emphasizes the necessity for effective management strategies, including a holistic approach that tackles the root causes of the condition. Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of A1C as a diagnostic tool, as highlighted in the research titled ‘Limitations of A1C in diagnosis.’ While A1C can be useful for screening, glucose measures remain essential for accurate diagnosis of the condition, particularly for individuals recently diagnosed.
By re-evaluating the origin of your condition, we can more effectively tackle health at the foundational aspect using a holistic approach.
Practical Steps for Monitoring Your A1C Levels
To ensure effective monitoring of your A1C levels and alleviate the anxiety that often accompanies concerns about potential complications related to this condition, it is essential to schedule regular testing with your healthcare provider, typically every three to six months. According to the latest recommendations, maintaining a log of your A1C results in conjunction with an A1C and glucose chart and corresponding changes in your diet, exercise, or medication can provide valuable insights into your health management. Counseling regarding the risk and symptoms of blood sugar disorders is crucial, especially for individuals testing positive for autoantibodies.
Moreover, comprehending insulin resistance is crucial; conventional therapies may carry risks, highlighting the necessity to investigate integrative methods that tackle the underlying factors of this condition. This includes re-examining the source of your diabetes to develop a holistic regimen tailored to your needs. The integration of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices is highly beneficial, as these tools offer real-time data on blood glucose levels, allowing you to correlate daily fluctuations with your A1C results using the A1C and glucose chart.
ACOG suggests thresholds of 130, 135, or 140 mg/dL for the 1-hour 50-g glucose load test, which can assist in shaping your strategies. Participating in regular consultations with your healthcare team is essential; these discussions will enable necessary modifications to your care plan based on the A1C and glucose chart results. As one expert in blood sugar regulation observed, ‘Effective monitoring strategies are pivotal for achieving optimal glycemic control and minimizing long-term complications.’
The different diagnostic criteria will identify varying degrees of maternal hyperglycemia and maternal/fetal risk, highlighting the importance of the A1C and glucose chart for accurate monitoring. By following these practices and adopting a comprehensive view of your health, including tackling anxiety and reassessing the origin of your condition, you can sustain a proactive position in your care.
Common Questions About A1C Testing and Management
Understanding the a1c and glucose chart is essential for effective control of blood sugar levels, particularly given that 26 states and territories have a prevalence of the condition exceeding the national average. According to the a1c and glucose chart, a normal A1C value is generally regarded as being below 5.7%. Levels ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes, signaling the need for proactive health changes.
It is advised that the majority of people with diabetes use the a1c and glucose chart to have A1C testing every three months; however, healthcare providers may propose an alternate schedule customized to personal health conditions and care plans. As Amy Richter, a Medical Reviewer with a Master’s degree in Nutrition Diagnostics, emphasizes, consulting with healthcare professionals is vital for personalized guidance regarding A1C testing. Importantly, A1C readings can be positively influenced through holistic lifestyle modifications.
Enhancements in diet, heightened physical activity, and efficient stress management are crucial elements that help reduce A1C readings. Additionally, addressing the anxiety and worry surrounding potential complications of this condition is important for overall well-being. Incorporating strategies such as mindfulness practices and support groups can significantly reduce stress levels.
Moreover, a case study titled ‘Impact of Education on Diabetes Incidence’ highlights how individuals with less than a high school education have higher incidence rates of diagnosed conditions, underscoring the influence of educational attainment on health outcomes. By empowering patients through education and community wellness initiatives, individuals can improve their health care strategies. Always consult with your healthcare provider prior to implementing significant changes to your diabetes management strategy, as personalized guidance is key to successful outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is essential for effective diabetes management, providing a reliable measure of average blood glucose levels over time. By interpreting A1C results accurately, individuals can collaborate with healthcare professionals to create tailored management strategies that address both physiological and psychological aspects of diabetes care. Regular A1C testing, typically every three to six months, paired with a holistic approach that includes lifestyle modifications, can significantly improve health outcomes and reduce anxiety about potential complications.
Utilizing conversion charts enhances the ability to track changes in A1C levels and their correlation with average blood glucose, empowering individuals to make informed adjustments to their diabetes management plans. The relationship between A1C levels and average glucose underscores the importance of consistent monitoring and proactive management strategies. Furthermore, integrating tools like continuous glucose monitoring can provide real-time insights, allowing for timely interventions.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the A1C test and its implications is vital for individuals managing diabetes. By prioritizing regular testing, leveraging educational resources, and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, patients can take significant steps toward achieving optimal glycemic control. This proactive approach not only alleviates concerns about diabetes complications but also fosters a greater sense of empowerment in one’s health journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test measures the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has combined with glucose, providing a reliable representation of average blood glucose levels over the previous two to three months. It is especially important for individuals with blood sugar issues as it helps in managing their condition effectively.
What does an A1C level of 7% signify?
An A1C level of 7% or lower is generally accepted as indicating good control for most adults with blood sugar issues. However, individual targets may vary based on specific health conditions.
How does the A1C test compare to other blood sugar assessments?
The A1C test is more effective in capturing chronic hyperglycemia than two fasting assessments or a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test, making it a crucial tool for monitoring blood sugar levels.
What does the A1C and glucose chart represent?
The A1C and glucose chart shows the correlation between A1C percentages and average blood glucose levels, allowing individuals to track how their A1C levels affect their average glucose readings.
How can individuals use the A1C and glucose chart?
To use the A1C and glucose chart, locate your A1C percentage on the left side and find the corresponding average blood glucose amount on the right side. For example, an A1C of 6.0% correlates to an average blood glucose of approximately 126 mg/dL.
Why is regular consultation of the A1C and glucose chart recommended?
Regularly consulting the A1C and glucose chart helps individuals understand their blood sugar control, enabling them to make informed adjustments to their diet, exercise, and medication, ultimately supporting better health outcomes.
What are some statistics regarding A1C testing and health monitoring?
Recent statistics indicate that 94.2% of individuals receive A1C tests, 96.8% have their blood pressure examined, and 93.0% have their cholesterol assessed, highlighting the importance of ongoing care for blood sugar management.
Can you provide an example of a success story related to A1C monitoring?
One success story from the Integrative Wellness Center involves an individual named M.L., who lost 55 lbs and reduced their A1C from 9.1 to 5.7, demonstrating the effectiveness of monitoring A1C levels in managing blood sugar conditions.
What is the overall approach advocated by the Integrative Wellness Center?
The Integrative Wellness Center advocates for a comprehensive strategy that includes monitoring A1C levels while addressing underlying factors contributing to insulin resistance, promoting a holistic approach to health management.