Overview
An A1C level of 5.5% is generally considered good for individuals without diabetes, indicating effective blood glucose control; however, for those diagnosed with diabetes, its appropriateness depends on individual health conditions and treatment goals. The article emphasizes that personalized assessments are crucial, as factors such as age, overall health, and the presence of comorbidities can significantly influence whether a 5.5 A1C is suitable for a patient, underscoring the importance of tailored management strategies.
Introduction
The A1C test, a vital tool in diabetes management, provides insights into average blood glucose levels over a two to three-month period, represented as a percentage. Understanding this test is crucial, as elevated A1C levels can signal inadequate blood sugar control and increase the risk of severe complications such as:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Kidney failure
This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, the implications of various A1C levels, and the multifaceted strategies necessary for maintaining optimal levels. Through a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Dietary adjustments
- Physical activity
- Stress management
Individuals can better navigate their diabetes care. Additionally, the importance of personalized targets and professional guidance is emphasized, ensuring that patients are equipped with the knowledge and support needed to manage their health effectively.
Understanding the A1C Test: Importance and Implications
The A1C test, officially referred to as the glycated hemoglobin test, acts as an essential indicator of average blood glucose quantities over the prior two to three months, represented as a percentage. Elevated A1C levels indicate inadequate blood sugar control, significantly heightening the risk for various diabetes-related complications, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Kidney failure
- Neuropathy
Emphasizing a holistic approach, individuals at the Integrative Wellness Center are guided to address the root causes of their condition through personalized strategies such as:
- Dietary adjustments
- Stress management techniques
- Regular physical activity
These strategies can help alleviate anxiety regarding potential complications.
Regular A1C monitoring is essential for individuals with this condition, as it informs crucial lifestyle choices regarding:
- Diet
- Physical activity
- Medication adherence
The American Diabetes Association advises that individuals with the condition consider if 5.5 A1C is good, aiming for a level below 7%. However, determining if 5.5 A1C is good may differ based on individual health conditions and treatment goals.
Recent statistics reveal that in 2021, approximately 97.6 million U.S. adults aged 18 years or older were estimated to have prediabetes, highlighting the pressing need for enhanced awareness and screening efforts. Furthermore, 2020 recorded approximately 202,000 emergency department visits linked to hypoglycemia, equating to 8.6 visits per 1,000 adults with the condition, highlighting the importance of effective A1C oversight to avert such acute complications. As Roopa Naik observes, ‘Effective management of this condition is crucial in preventing complications that can arise from poor blood sugar control.’
By adopting a holistic regimen, patients can find new peace in life, eliminating worry about developing traumatic and debilitating complications from blood sugar issues. As the landscape of metabolic condition management evolves, ongoing updates to recommendations and monitoring practices remain imperative for optimal patient outcomes, reinforcing the importance of a comprehensive, integrative approach.
Is an A1C Level of 5.5 Considered Healthy? Insights and Considerations
An A1C measurement of 5.5% is often asked whether 5.5 A1C is good, as it is usually regarded as typical for individuals without the condition, signifying effective blood glucose control. However, for patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus, this figure requires a more nuanced evaluation. Individual factors such as age, overall health, and the presence of comorbidities are crucial in determining if an A1C of 5.5 is good.
For instance, research indicates that older individuals or those with specific health issues may require modified target thresholds for effective blood sugar control. The Integrative Wellness Center has seen transformative patient success stories, such as one patient who, through personalized care, was able to lower their A1C from 7.5% to 5.4% in just six months, emphasizing the importance of tailored approaches. Significantly, the anticipated prevalence of men with an A1C ≥5.5% varies considerably according to iron status, emphasizing the varied implications of these measurements.
Catherine Kim, MD, MPH, points out that reproductive-age women are particularly susceptible to iron deficiency, making it essential for healthcare professionals to assess what it means when they ask, “is 5.5 A1C good” for each individual. Establishing personalized management goals is vital, particularly given the serious health risks associated with diabetes, including ischemic heart disease and stroke, which are leading causes of hospitalization. Moreover, ongoing observation, combined with lifestyle changes like a balanced diet and regular exercise, is crucial for sustaining or enhancing A1C values.
The Integrative Wellness Center offers various treatment options, including nutritional counseling and exercise programs, ultimately contributing to better overall health outcomes at the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego.
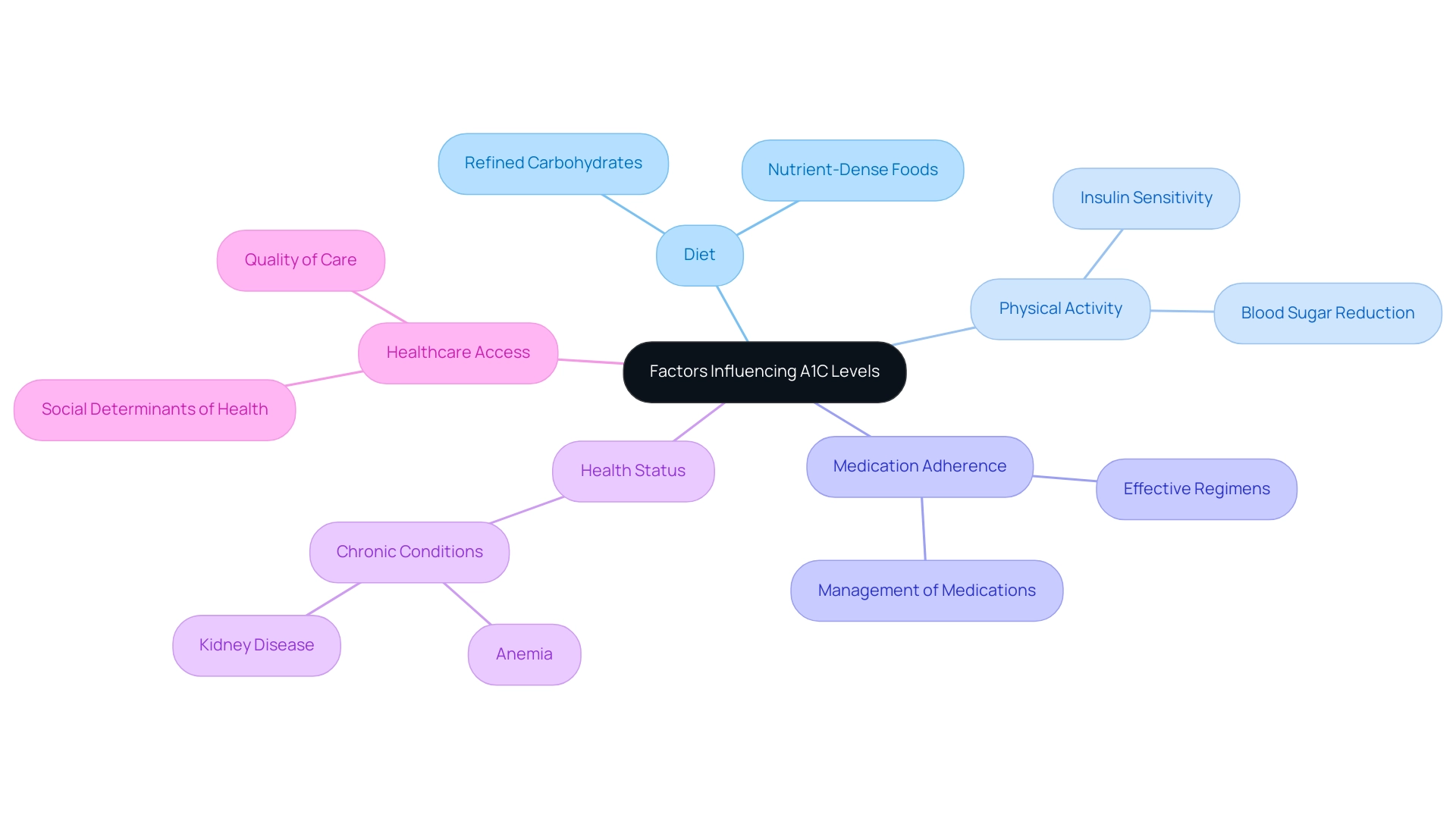
Factors Influencing A1C Levels: What You Need to Know
Numerous factors significantly influence hemoglobin A1C values, including diet, physical activity, medication adherence, and overall health status. A diet high in refined carbohydrates and sugars can lead to increased blood glucose readings, which in turn raises A1C. Recent findings emphasize the critical link between dietary choices and A1C results, underscoring the necessity for patients to prioritize nutrient-dense foods.
Consistent physical activity is another essential element, as it not only helps in reducing blood sugar amounts but also improves insulin sensitivity, thereby positively affecting A1C results. Furthermore, the effectiveness of blood sugar medications is crucial; poorly managed medication regimens can hinder A1C targets. Additional health conditions, such as anemia or kidney disease, can also skew A1C readings, complicating diabetes control.
According to the American Diabetes Association, it is recommended that A1C levels be assessed at least twice a year for stable patients and four times for those experiencing fluctuations or changes in treatment. This emphasizes the significance of ongoing monitoring and collaboration with healthcare providers to customize care plans appropriately. A holistic approach to managing this condition considers not only these physiological factors but also the underlying causes of insulin resistance and the potential dangers of relying solely on traditional treatments.
Additionally, differences in healthcare access significantly influence A1C values, emphasizing the necessity to take into account social determinants of health in the care of individuals with diabetes. The insights from the T1DX-QI Collaborative, while concentrated on Type 1 conditions, illustrate the value of data-sharing and quality enhancement techniques that could be adapted for Type 2 care as well. As Roopa Naik indicates, ‘Grasping the complex factors affecting A1C values is crucial for efficient control of the condition,’ emphasizing the necessity for a thorough and holistic method to care.
We begin by reassessing the origin of your condition to tackle these issues at their core, which can assist in reducing the stress linked to handling possible complications of the illness.
Strategies for Maintaining a Healthy A1C Level
To achieve and sustain a healthy A1C level, it is essential to implement a multifaceted approach that encompasses dietary choices, physical activity, medication adherence, and stress management, and to evaluate if 5.5 A1C is good. This holistic regimen reflects the Integrative Wellness Center’s philosophy of addressing the root causes of the condition, which can help alleviate the anxiety that often accompanies concerns about potential complications. We start by re-examining the source of your diabetes, allowing us to tailor our approach effectively.
Here are several key strategies:
-
Balanced Diet: Prioritize a diet that incorporates whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables. It is essential to track carbohydrate consumption, emphasizing complex carbohydrates that digest slowly, thus supporting stable blood sugar.
A healthcare professional will advise each person on their dietary needs, emphasizing the importance of individualized dietary plans tailored to their unique requirements.
-
Regular Physical Activity: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly. Activities such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling can significantly enhance insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic health.
Real-world evidence demonstrates that structured exercise programs can result in measurable enhancements in A1C values, which raises the question of whether 5.5 A1C is good, highlighting the significance of incorporating physical activity into daily routines.
-
Medication Oversight: Adherence to prescribed medications is vital for effective diabetes control. Patients should regularly consult with their healthcare providers to evaluate the effectiveness of their current regimen and consider switching to SGLT2 inhibitors or GLP-1 receptor agonists if they are on dual therapy without these agents.
This proactive approach can lead to improved glycemic control and reduced cardiovascular risks, as demonstrated in long-term studies, such as the VADT cohort study, which reported a decrease in cardiovascular events from 52.7 events per 1,000 person-years in the control group to 44.1 events per 1,000 person-years in the intervention group.
-
Regular Monitoring: Consistently observe blood glucose measurements and A1C readings to determine if the level is 5.5 A1C good, identify patterns, and make necessary modifications to your care plan.
The adoption of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology facilitates this process, allowing for remote access to data and insights critical for effective telemedicine.
-
Stress Management: Implement stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Managing stress is essential, as increased stress can negatively impact blood sugar control.
By integrating these practices into your daily routine, you can help reduce stress’s effect on your blood sugar control.
Additionally, a recent analysis from the ADAG study supports a more adaptable approach to blood sugar regulation, suggesting that pre-meal glucose goals could be eased without compromising overall glycemic balance, leading to a revision of the ADA-recommended pre-meal glucose target to 80-130 mg/dL.
Incorporating these strategies into your lifestyle not only fosters a healthier A1C measurement but also raises the question, is 5.5 A1C good, contributing to overall well-being and enhanced quality of life, which aligns with the Integrative Wellness Center’s commitment to empowering patients through holistic care.
When to Seek Professional Guidance
Seeking professional guidance is crucial when managing blood sugar levels, particularly under the following circumstances:
-
Notable Variations in A1C Measurements:
Fluctuations in your A1C readings can indicate that your existing strategy may need modifications, and it’s important to ask if 5.5 A1C is good. Early intervention is vital, especially if these changes persist over time.
-
Symptoms of Uncontrolled Diabetes:
Notable symptoms, including increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, or blurred vision, necessitate immediate consultation with your healthcare provider. These signs may indicate that your condition is not adequately controlled and require prompt action.
-
Difficulty Managing Blood Sugar:
If you find it hard to maintain stable blood sugar levels despite following your control plan, it is advisable to seek professional support to determine if 5.5 A1C is good for your health. A healthcare provider can help identify potential underlying issues affecting your control.
-
Changes in Health Status:
The emergence of new health conditions or modifications in medications warrants thorough discussion with your healthcare provider. Such changes can significantly influence your health care approach.
Interacting with a healthcare expert not only provides customized guidance but also improves your overall condition oversight, ensuring that you stay on course to reach your health objectives. To empower your health transformation, we invite you to schedule a complimentary consultation at the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego, where we prioritize patient-centered care. Recent studies indicate that adults who engage in self-management education and support (DSMES) are more likely to adhere to recommended preventive care practices, underscoring the value of professional guidance.
Additionally, it’s important to acknowledge that Hispanic individuals account for 5.0 million diagnosed cases of the condition and 1.9 million undiagnosed cases, highlighting the prevalence of the illness and the need for effective management. As M.S., a pleased patient, highlights, ‘The support I received changed my approach to managing my condition.’ Furthermore, case studies, such as the one on insulin regimens for noncritically ill patients, illustrate the practical applications of professional guidance in managing diabetes effectively, showcasing how personalized care can lead to improved health outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively managing A1C levels is paramount for individuals living with diabetes. The A1C test serves as a critical indicator of long-term blood glucose control, and its implications extend far beyond mere numbers. Elevated A1C levels can signify a heightened risk for serious complications, from cardiovascular disease to kidney failure. Therefore, regular monitoring and comprehension of A1C results are essential in informing dietary, exercise, and medication choices.
A multifaceted approach is necessary to maintain healthy A1C levels. This includes:
- A balanced diet rich in whole foods
- Regular physical activity
- Strict medication adherence
- Stress management techniques
Each of these components plays a vital role in not only achieving but also sustaining optimal A1C levels. Personalization of management strategies, tailored to individual health conditions and lifestyle, is crucial for effective diabetes care.
Seeking professional guidance is equally important, particularly when faced with significant changes in A1C levels or symptoms of uncontrolled diabetes. Engaging with healthcare providers fosters a supportive environment where tailored advice can lead to meaningful improvements in health outcomes. As diabetes management continues to evolve, prioritizing comprehensive care and continuous education will empower individuals to navigate their health with confidence. By taking proactive steps and embracing a holistic approach, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of complications and enhance their overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, measures average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months and is expressed as a percentage. It is essential for assessing blood sugar control and identifying the risk of diabetes-related complications.
What complications are associated with elevated A1C levels?
Elevated A1C levels indicate poor blood sugar control, which significantly increases the risk of complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and neuropathy.
What strategies are recommended for managing A1C levels?
The Integrative Wellness Center recommends a holistic approach that includes dietary adjustments, stress management techniques, and regular physical activity to address the root causes of blood sugar issues.
How often should individuals monitor their A1C levels?
Regular A1C monitoring is essential for individuals with diabetes, as it helps inform important lifestyle choices related to diet, physical activity, and medication adherence.
What is the recommended A1C level according to the American Diabetes Association?
The American Diabetes Association advises aiming for an A1C level below 7%. However, whether an A1C of 5.5% is considered good can vary based on individual health conditions and treatment goals.
What are the statistics regarding prediabetes and hypoglycemia in the U.S.?
In 2021, approximately 97.6 million U.S. adults aged 18 years or older were estimated to have prediabetes. Additionally, there were about 202,000 emergency department visits in 2020 linked to hypoglycemia, highlighting the need for effective A1C oversight.
How can personalized care impact A1C levels?
Personalized care can lead to significant improvements in A1C levels. For instance, one patient at the Integrative Wellness Center reduced their A1C from 7.5% to 5.4% in six months through tailored strategies.
Why is it important to consider individual factors when evaluating A1C levels?
Individual factors such as age, overall health, and comorbidities play a crucial role in determining the appropriateness of A1C targets. For example, older individuals or those with specific health issues may require different thresholds for effective blood sugar control.
What treatment options does the Integrative Wellness Center offer for managing A1C levels?
The Integrative Wellness Center provides various treatment options, including nutritional counseling and exercise programs, aimed at improving overall health outcomes for patients.