Overview
Type 2 diabetes often develops due to insulin resistance, a condition influenced by a mix of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Many individuals struggle with issues like obesity, sedentary behavior, and poor nutrition. It’s important to recognize that understanding these causes and risk factors is crucial for effective prevention and management strategies. By empowering ourselves with this knowledge, we can make healthier lifestyle choices that significantly reduce our risk of developing this condition.
Have you ever felt overwhelmed by the choices you face daily? You’re not alone. Many patients find that small, manageable changes can lead to significant improvements in their health. By focusing on understanding the underlying causes, we can take proactive steps toward a healthier future. Remember, every choice counts, and each step you take brings you closer to better health.
Introduction
Understanding the complex landscape of type 2 diabetes is crucial, especially as its prevalence continues to rise globally. With over 38 million Americans affected, this condition is not just a personal health issue but a significant public health challenge that intertwines genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
It’s important to recognize that as individuals navigate their health journeys, they may wonder: what truly drives the onset of type 2 diabetes, and how can one effectively mitigate these risks?
Exploring the interplay of these factors reveals not only the mechanisms behind this condition but also empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward prevention and management. Many patients find that gaining insight into these aspects can be a transformative experience, leading to better health outcomes and a renewed sense of control over their lives.
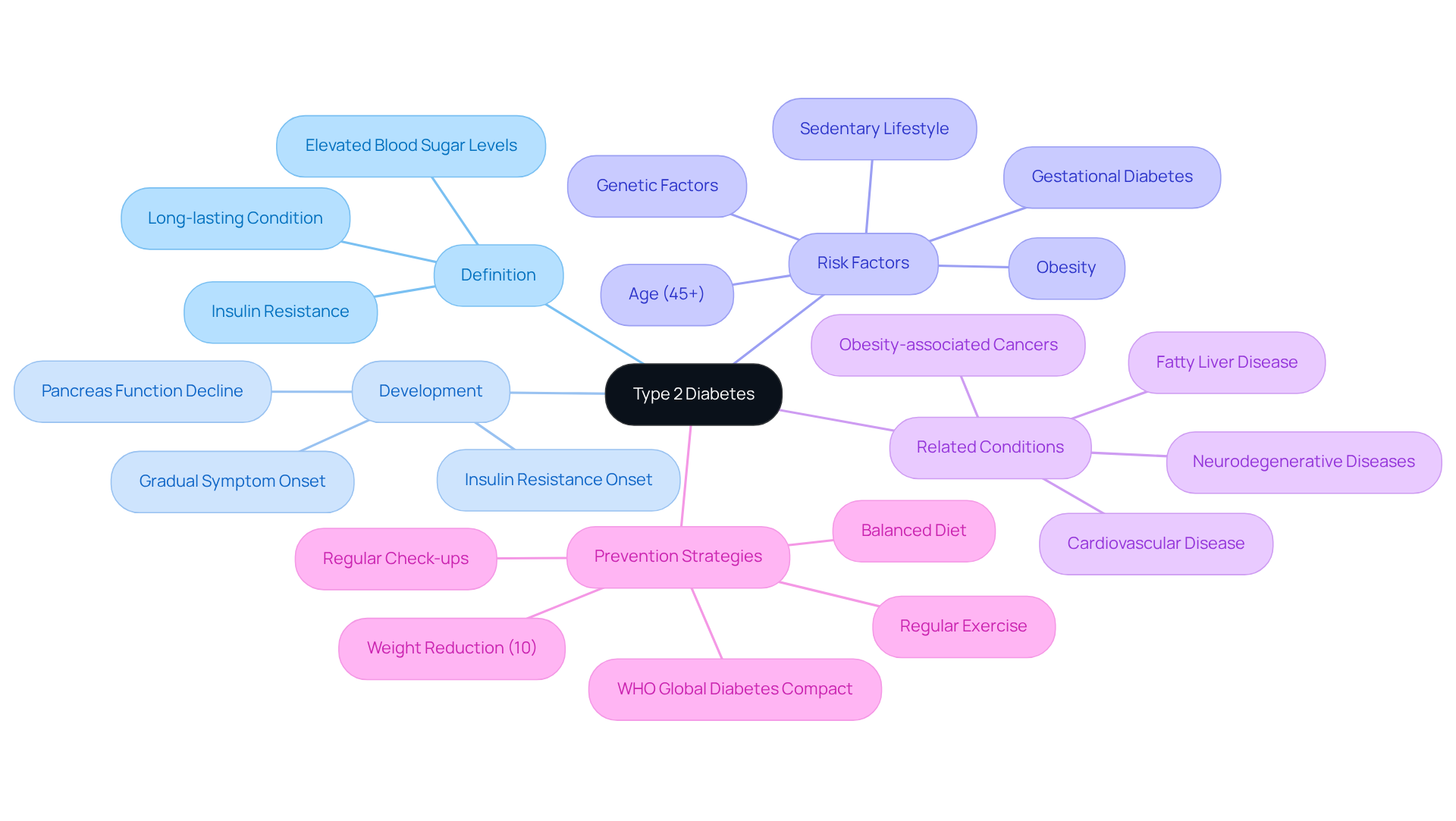
Understand Type 2 Diabetes: Definition and Development
Type 2 diabetes is a long-lasting condition that many individuals face, characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to either resistance to or inadequate production of insulin. It often progresses slowly, typically beginning with insulin resistance, where the body’s cells struggle to respond effectively. As time goes on, the pancreas may find it increasingly difficult to produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood glucose levels. This condition is frequently linked to obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetic factors, making it a significant public health concern. In fact, over 38 million Americans are impacted by this condition—about 1 in 10—highlighting its widespread presence in our communities.
It’s important to recognize that insulin resistance is not just a precursor to type 2 diabetes; it also plays a crucial role in the progression of related chronic conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and fatty liver disease. Gerald I. Shulman, MD, PhD, emphasizes that insulin resistance presents a major health risk worldwide in the 21st century, connecting it with multiple chronic illnesses. Many patients find that the gradual onset of symptoms often goes unnoticed, leading to delayed diagnoses and an increased risk of complications. Regular check-ups and blood tests are vital for early detection, as many individuals may remain asymptomatic until serious health issues arise.
Understanding how does someone get type 2 diabetes from glucose intolerance is essential for creating effective management and prevention strategies. Participating in regular exercise, following a balanced diet, and achieving a modest weight loss of about 10% can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing this condition. This holistic approach not only addresses symptoms but also targets the underlying causes, empowering individuals to take control of their health and well-being. Additionally, the WHO launched the Global Diabetes Compact in April 2021 to improve prevention and care for diabetes, underscoring the urgency of addressing this public health challenge.
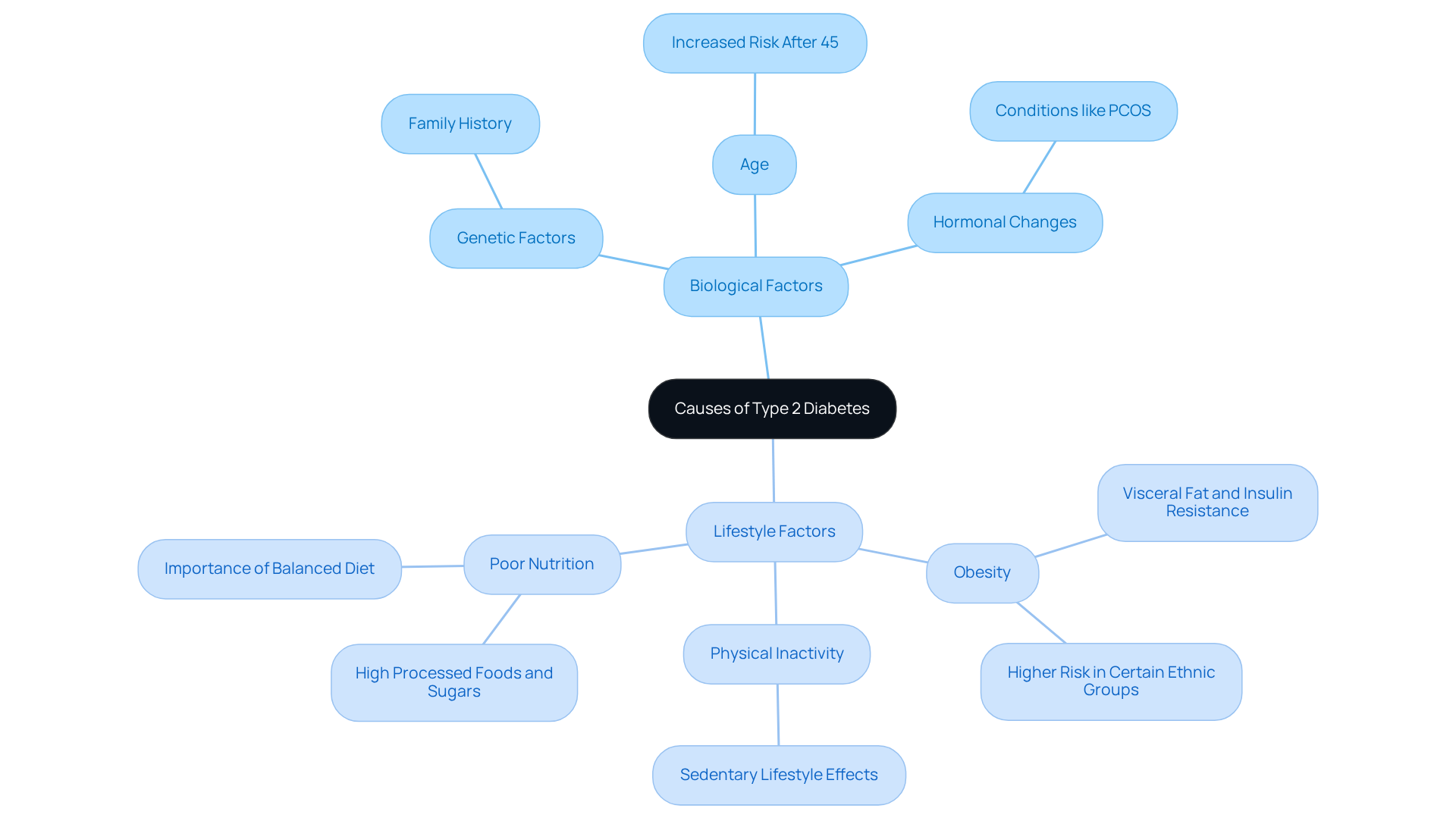
Explore the Causes of Type 2 Diabetes: Biological and Lifestyle Factors
The intricate and multifactorial causes of type 2 diabetes can be overwhelming, prompting many to wonder how does someone get type 2 diabetes, as they involve both biological and lifestyle factors. It’s important to recognize that understanding these elements can empower you on your journey toward better health.
-
Genetic Factors: If you have a family history of type 2 diabetes, you may feel concerned about your own risk. This condition often highlights a genetic predisposition, making awareness crucial in your prevention efforts.
-
Obesity: Many individuals struggle with excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen. This visceral fat significantly contributes to insulin resistance. Research indicates that individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater face a heightened risk of developing issues with sugar metabolism. This correlation is especially pronounced in certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans and Hispanics, who experience higher obesity rates and, consequently, a greater prevalence of diabetes.
-
Physical Inactivity: It’s common to lead a sedentary lifestyle, but this can reduce your body’s ability to use glucose effectively, leading to increased blood sugar levels. Many patients find that incorporating consistent physical exercise is essential for preserving glucose sensitivity and overall metabolic well-being.
-
Poor Nutrition: You might find that diets high in processed foods and sugars contribute to weight gain and worsen insulin resistance. Nutritionists emphasize the importance of a balanced diet, low in refined carbohydrates and rich in whole foods, as a crucial step in preventing blood sugar issues.
-
Age: As we age, particularly after 45, the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes increases. This is often due to the body’s declining ability to regulate blood sugar over time, which can be a source of concern for many.
-
Hormonal Changes: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can heighten the risk of developing high blood sugar in women. This connection between hormonal health and metabolic function is essential to consider.
Identifying these factors is vital for applying effective preventive strategies and lifestyle changes. By understanding these elements, you can take proactive steps to greatly diminish how does someone get type 2 diabetes. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are supportive resources available to guide you toward a healthier future.
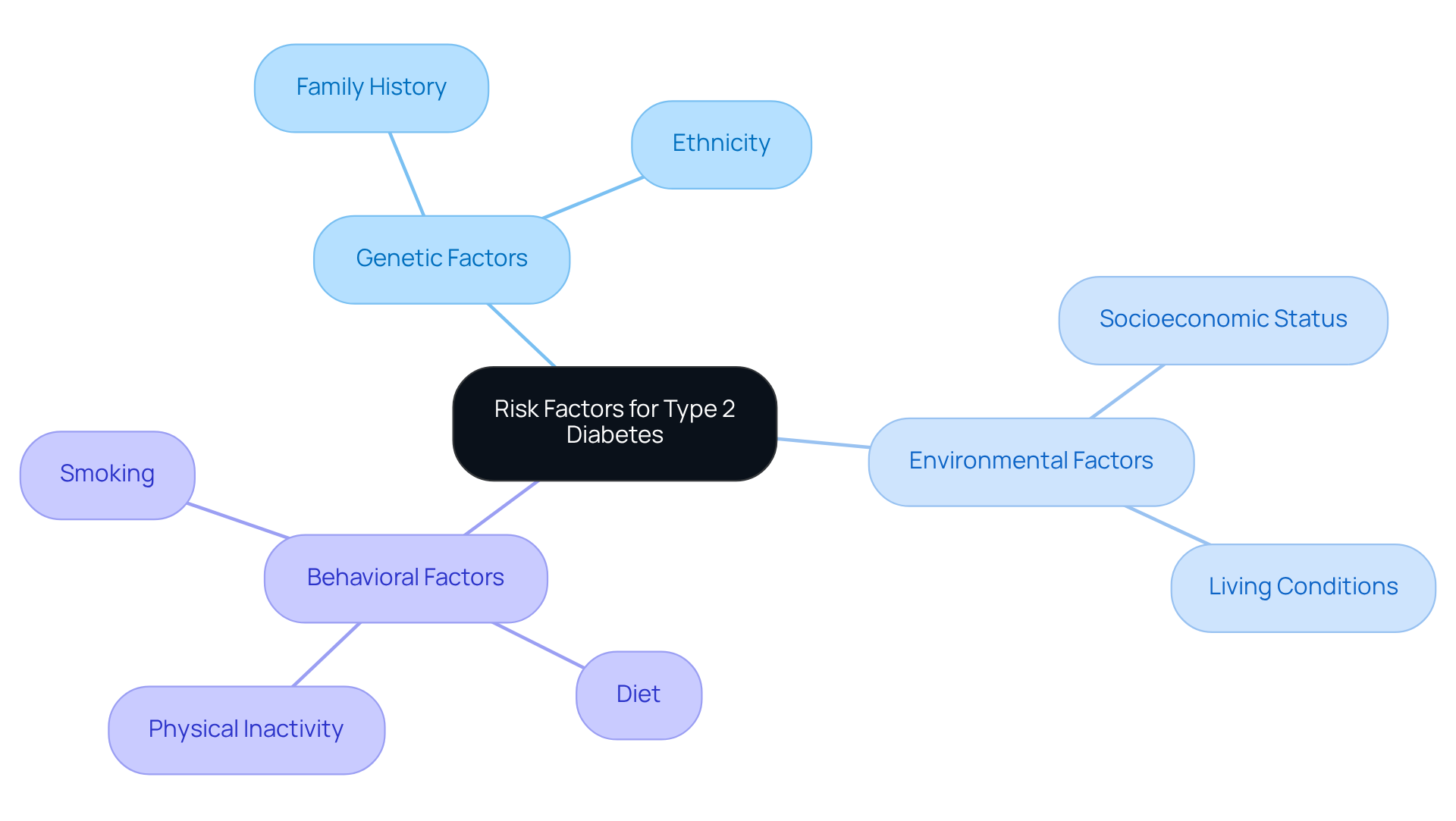
Identify Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes: Genetics, Environment, and Behavior
Several risk factors can influence how does someone get type 2 diabetes, and understanding them is important so you can take proactive steps toward your health.
Genetic Risk Factors:
- Family History: If you have a family history of diabetes, particularly with a parent or sibling affected, your risk may be significantly higher. It’s a tough reality, but knowing this can empower you to take action.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and some Asian Americans, face a greater likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. For instance, Asian Americans are considered overweight with a BMI of 23 or greater, while Pacific Islanders may experience challenges with a BMI of 26 or above. Recognizing these factors can help you stay vigilant.
Environmental Risk Factors:
- Socioeconomic Status: Many individuals in lower socioeconomic tiers encounter barriers to accessing healthy foods and healthcare services. This can lead to obesity and related health issues. It’s crucial to acknowledge these challenges and seek support where possible.
- Living Conditions: Urban areas that lack recreational spaces can contribute to sedentary lifestyles. Without parks or safe areas for physical activity, it’s easy to fall into a routine that discourages exercise. It’s important to recognize that even small changes in your environment can make a difference.
Behavioral Risk Factors:
- Diet: Diets rich in calories but poor in nutrients are often linked to obesity, a significant risk factor for diabetes. If you find yourself consuming processed foods and sugary beverages, consider how these choices may affect your weight and insulin sensitivity.
- Physical Inactivity: Regular exercise is vital for maintaining a healthy weight and reducing blood sugar risks. A sedentary lifestyle, where physical activity occurs less than three times a week, can significantly increase your risk of chronic conditions. Remember, even small steps can lead to big changes.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is associated with insulin resistance, which means smokers may be more susceptible to developing diabetes. If you smoke, seeking help to quit can be a powerful step toward better health.
By recognizing these risk factors, you can take proactive measures to understand how does someone get type 2 diabetes and reduce your likelihood of developing it. Minor, gradual lifestyle changes, such as improving your diet and increasing physical activity, can significantly lower your risk of prediabetes and diabetes. You are not alone in this journey; many have found success through small, consistent steps. Together, we can work towards a healthier future.
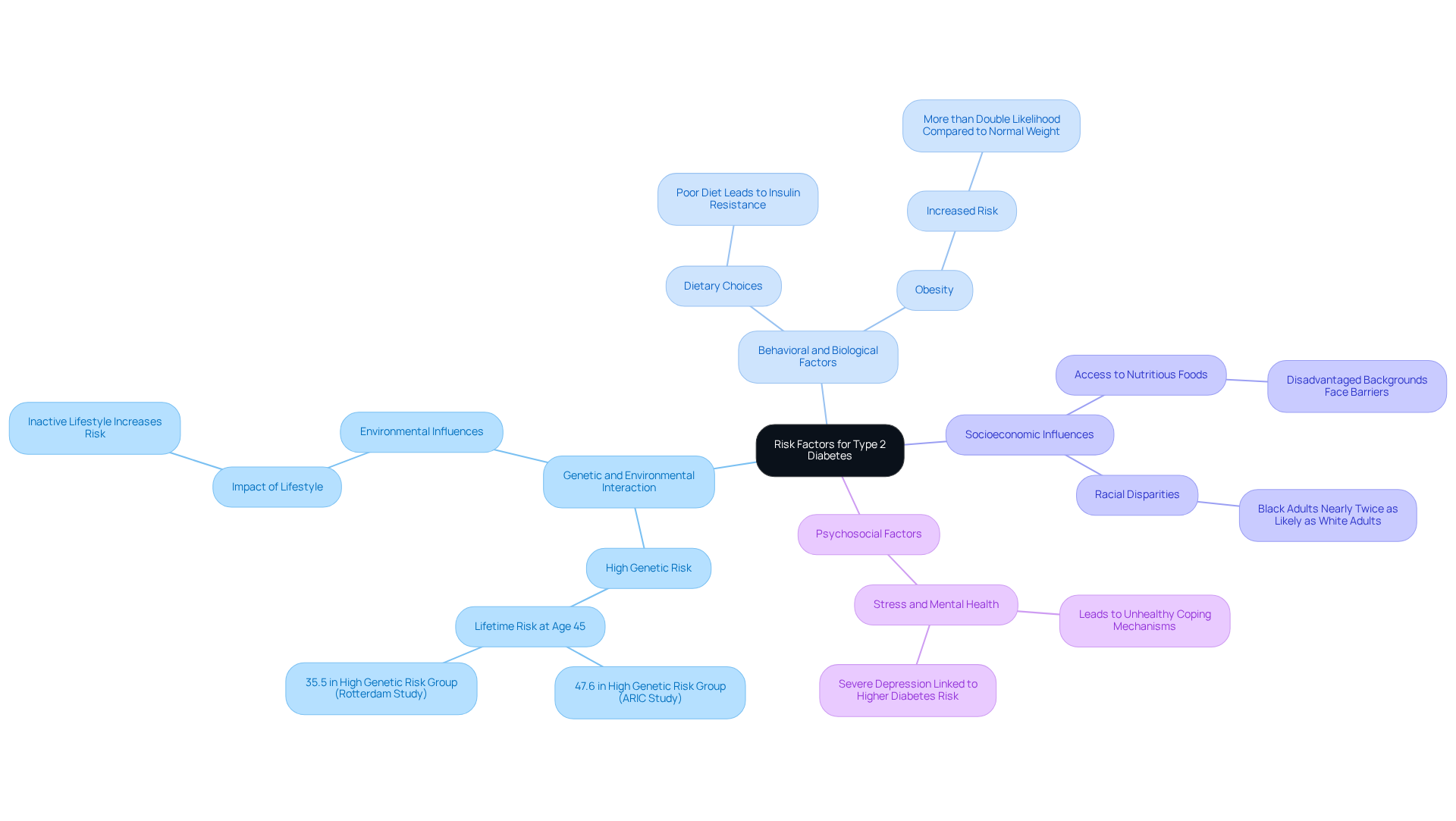
Assess the Interplay of Risk Factors: How They Contribute to Type 2 Diabetes
Understanding how does someone get type 2 diabetes can feel overwhelming, but it’s essential to recognize that various risk factors interact in complex ways. Let’s explore these together, as knowing them can empower you on your health journey.
-
Genetic and Environmental Interaction: Many people find that their genetic predisposition can be significantly influenced by their environment, including diet and activity levels. For instance, those with a family history of diabetes who lead inactive lifestyles often question how does someone get type 2 diabetes, as they face a much higher risk of developing the condition. In fact, if you are in a high genetic susceptibility group, your chance of developing type 2 diabetes by age 45 is around 47.6%. This statistic might sound alarming, but understanding it is the first step toward taking control of your health.
-
Behavioral and Biological Factors: Poor dietary choices can lead to obesity, a significant contributor to insulin resistance. This creates a challenging cycle where obesity worsens insulin resistance, further increasing the risk of developing diabetes. Did you know that individuals with obesity often wonder how does someone get type 2 diabetes, as they have more than double the likelihood of developing it compared to those with a normal weight? Recognizing this link can inspire you to make healthier choices.
-
Socioeconomic Influences: It’s important to acknowledge that individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds often face barriers to accessing nutritious foods and healthcare. This lack of resources can increase the risk of health issues, including diabetes. For example, black adults in the U.S. are nearly twice as likely as white adults to develop type 2 diabetes, raising the question of how does someone get type 2 diabetes, which highlights the critical role of socioeconomic factors. Addressing these disparities is vital for effective health interventions.
-
Psychosocial Factors: Stress and mental health challenges can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as overeating or reduced physical activity, which can further elevate diabetes risk. Studies show that severe depression is linked to a higher likelihood of developing adult-onset glucose intolerance, particularly in those who are not obese. Understanding this connection can help you seek the support you need.
By grasping these interactions, you can take proactive steps toward improving your health. With 11.1% of the adult population aged 20-79 currently living with diabetes, recognizing these risk factors is more urgent than ever. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and there are resources available, like the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, to help you take charge of your health.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a complex condition influenced by various factors, including genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, and environmental conditions. It’s important to recognize how someone develops type 2 diabetes, as this understanding is crucial for effective prevention and management strategies. By acknowledging the interplay of insulin resistance, obesity, and sedentary behavior, individuals can take proactive steps to mitigate their risk and promote better health outcomes.
The article delves into the multifaceted causes of type 2 diabetes, highlighting the significant roles of:
- Genetics
- Physical inactivity
- Poor nutrition
- Hormonal changes
Many patients find that these factors interact, creating a web of risks that can lead to the development of this chronic condition. Moreover, the emphasis on early detection through regular check-ups and lifestyle modifications underscores the importance of being proactive in one’s health journey.
In light of the rising prevalence of type 2 diabetes, it is essential for individuals to equip themselves with knowledge and resources to combat this public health challenge. Adopting healthier eating habits, increasing physical activity, and understanding personal risk factors can empower individuals to take control of their health. By fostering awareness and encouraging lifestyle changes, communities can work together to reduce the impact of type 2 diabetes and promote a healthier future for all. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; together, we can make a difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a long-lasting condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to either insulin resistance or inadequate production of insulin.
How does Type 2 diabetes develop?
It typically begins with insulin resistance, where the body’s cells struggle to respond to insulin. Over time, the pancreas may have difficulty producing enough insulin to maintain normal blood glucose levels.
What factors contribute to the development of Type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is often linked to obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetic factors.
How prevalent is Type 2 diabetes in the United States?
Over 38 million Americans are impacted by Type 2 diabetes, which is about 1 in 10 individuals.
What are the health risks associated with insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance is not only a precursor to Type 2 diabetes but also contributes to the progression of related chronic conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and fatty liver disease.
Why is early detection of Type 2 diabetes important?
Many individuals may remain asymptomatic until serious health issues arise, making regular check-ups and blood tests vital for early detection.
How can individuals reduce their risk of developing Type 2 diabetes?
Regular exercise, following a balanced diet, and achieving a modest weight loss of about 10% can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk.
What initiatives are in place to address diabetes as a public health challenge?
The World Health Organization launched the Global Diabetes Compact in April 2021 to improve prevention and care for diabetes, highlighting the urgency of addressing this issue.