Overview
This article offers a compassionate step-by-step guide on how to convert A1c levels to fructosamine, an alternative measure of blood sugar control over shorter periods. It’s important to recognize that this conversion plays a vital role in diabetes management. By understanding their recent glucose levels, patients can gain valuable insights, especially in situations where A1c may not fully reflect their glycemic status. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being, fostering a sense of control and confidence in their journey.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, it’s important to recognize that understanding the nuances of blood sugar markers can truly be a game-changer for patients striving for better health outcomes. A1c and fructosamine are two pivotal indicators that each provide unique insights into blood glucose levels, yet they serve distinct purposes in monitoring and managing diabetes.
While A1c offers a long-term overview of average glucose levels, many patients find that fructosamine delivers a snapshot of recent changes, making it invaluable for timely adjustments in treatment.
As healthcare providers and patients alike seek to navigate the complexities of diabetes care, integrating these markers into a comprehensive management strategy can empower individuals to take control of their health and achieve meaningful improvements in their well-being.
Understand A1c and Fructosamine: Key Blood Sugar Markers
Managing diabetes can be challenging, and understanding the various indicators of blood sugar levels is crucial for effective care. The comparison from A1c to fructosamine plays a vital role by reflecting average blood glucose readings over the past two to three months, serving as a cornerstone for evaluating long-term glycemic control. In contrast, another important marker provides an approximation of average blood glucose levels over the previous two to three weeks. This shorter timeframe is particularly beneficial for assessing recent changes in blood sugar control, especially in situations where the transition from A1c to fructosamine may not fully capture the picture, such as in patients with hemoglobinopathies or those experiencing rapid fluctuations in glucose levels.
It’s important to recognize that recent studies suggest this alternative marker can complement traditional glycemic measures, though further research is needed to fully understand its role. For instance, in a study involving 320 patients with type 2 diabetes, glycosylated albumin (GA) emerged as a significant predictor of coronary artery disease, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.62. This finding underscores the importance of combining different markers, including GA, to manage blood sugar conditions comprehensively, as it can provide valuable insights alongside A1c and other indicators.
Moreover, many patients find it essential to be aware that elevated levels of ascorbic acid can interfere with the assay for certain glycation markers. This means it’s advisable to avoid ascorbic acid supplements for at least 24 hours before sample collection. Such considerations highlight the importance of precise monitoring in glucose management, as even minor factors can significantly impact outcomes.
By grasping the differences between A1c to fructosamine and other markers, patients and healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about diabetes management strategies, ultimately leading to better health outcomes. As Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.” Testimonials from patients further illustrate this impact, with many sharing transformative health journeys and significant improvements through the personalized programs at Integrative Wellness Center, especially in light of the concerning statistics surrounding hospital safety and medication errors.
Convert A1c to Fructosamine: Step-by-Step Process
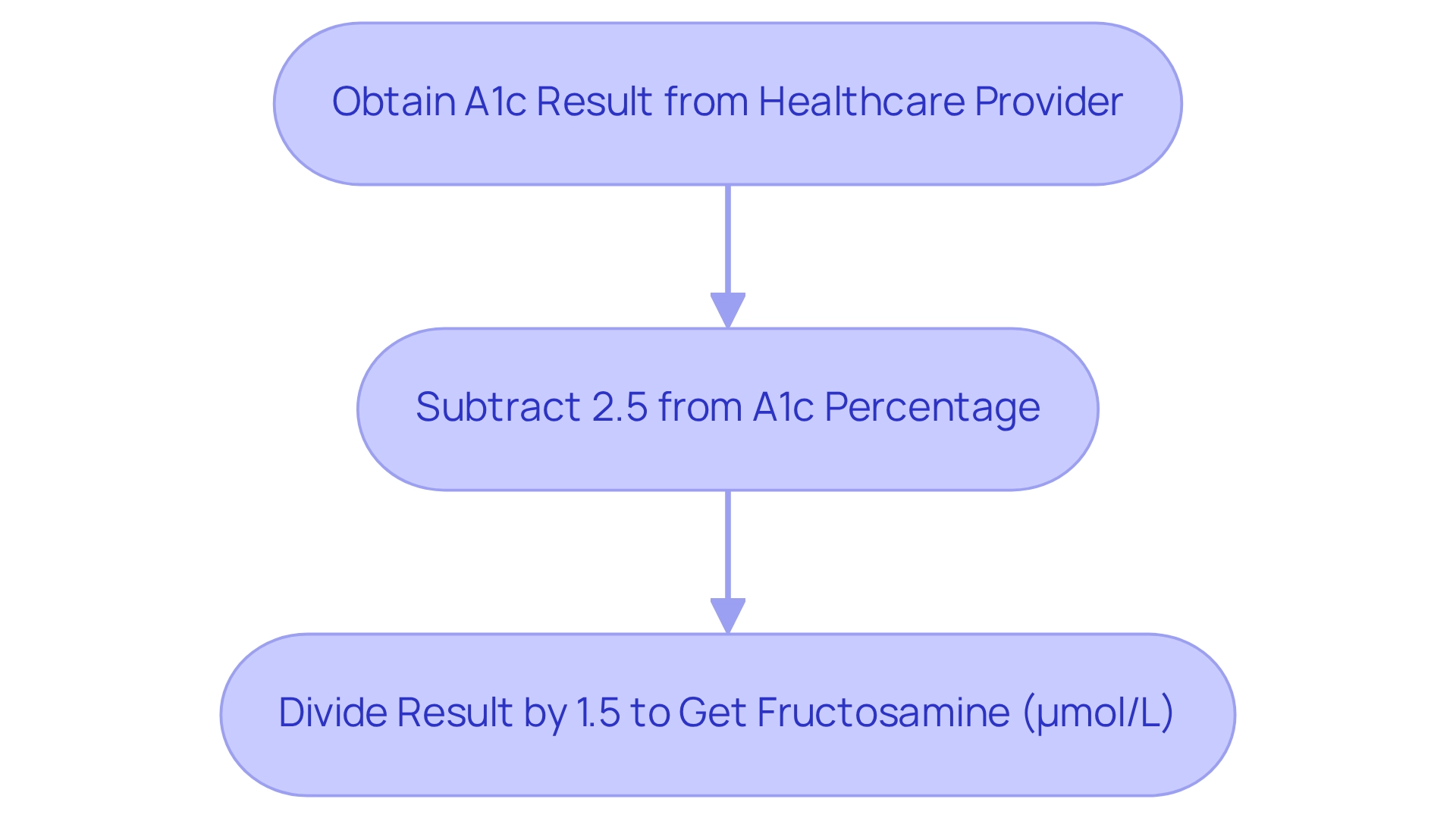
To convert A1c to fructosamine, you can apply this straightforward formula: Fructosamine (µmol/L) = (A1c (%) – 2.5) / 1.5.
- First, obtain your A1c result from your healthcare provider.
- Next, subtract 2.5 from your A1c percentage.
- Finally, divide the result by 1.5 to find your fructosamine level in µmol/L.
Example: If your A1c is 7.0%, the calculation goes like this: 7.0 – 2.5 = 4.5, then 4.5 / 1.5 = 3.0 µmol/L.
This conversion provides an alternative perspective on your recent blood sugar control, which can be particularly beneficial for tailoring your management plan. By incorporating this approach into your routine, you can deepen your understanding of your health metrics and empower yourself in managing type 2 diabetes effectively.
To keep track of your progress, consider using fitness applications or journals to regularly record your A1c and fructosamine measurements. Establishing SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—can further enhance your health monitoring. For example, you might aim to reduce your A1c by a certain percentage within a set timeframe.
Statistics indicate that the average A1c measurement among individuals with type 2 diabetes hovers around 7.5%, underscoring the importance of regular monitoring and adjustments in treatment approaches. Additionally, RPM services can track various health metrics, including blood glucose readings, highlighting the necessity of thorough health monitoring in managing blood sugar conditions.
Experts emphasize that understanding the connection between A1c to fructosamine and other markers can significantly improve diabetes management. Wendy O. Henderson, Associate Chief of Staff at Durham VA Health Care System, points out that “healthcare providers need to know that hemoglobin A1c does not correlate with capillary or venous blood glucose levels in some situations.” This insight reinforces the value of considering alternative measures for evaluating glycemic control.
Real-life examples show the practical benefits of this conversion. Patients who have utilized this method often report a better understanding of their blood sugar control, enabling them to make informed decisions in collaboration with their healthcare providers.
In clinical studies, the conversion rates from A1c to fructosamine have demonstrated consistent results, thereby reinforcing the reliability of this calculation in managing blood sugar levels. Furthermore, innovative strategies for handling chronic conditions, like those highlighted by CopilotIQ, illustrate the evolving landscape of glucose regulation. By prioritizing personalized functional medicine approaches and weaving this transformation into your routine, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of your health and enhance your strategies for controlling blood sugar.
Finally, remember to keep consulting with your primary care provider and other healthcare specialists as needed to ensure a holistic approach to your health.
Interpret Results and Apply to Diabetes Management
Understanding your measurement of glycated protein, such as the conversion from a1c to fructosamine, is essential for effectively managing blood sugar conditions.
-
Normal Range: A measurement below 285 µmol/L usually signifies good glycemic control, indicating stable blood sugar readings over the past two to three weeks. Research indicates that maintaining a1c to fructosamine concentrations within this range is linked to improved long-term health outcomes for individuals with blood sugar issues. It’s important to recognize that elevated values—measurements above this threshold—may suggest that blood sugar readings have been persistently high. This can indicate a need for modifications in your care strategy. For instance, many patients at Integrative Wellness Center have reported notable enhancements in their health after addressing elevated sugar levels through customized approaches that involve personalized nutrition and thorough testing.
-
Consult Your Healthcare Provider: It’s vital to review your a1c to fructosamine results with your healthcare provider to discuss potential adjustments to your diabetes management strategy. This collaborative approach is a key aspect of Dr. Shumard’s holistic philosophy, empowering you to take control of your health.
-
Monitor Your Diet: Emphasize a balanced diet consisting of whole foods, reducing processed sugars, and boosting fiber consumption to maintain stable blood sugar. Many individuals find that educational resources provided by Dr. Shumard can guide them in making informed dietary choices, including utilizing local produce from San Marcos to enhance their meals.
-
Increase Physical Activity: Participating in regular exercise can significantly reduce blood sugar levels and enhance insulin sensitivity. Numerous patients have discovered that incorporating physical activity into their routines, like enjoying walks in the beautiful parks of San Marcos, has resulted in improved glucose management and overall well-being.
- Set SMART Goals: It’s beneficial to implement SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—to track your progress effectively. For example, aim to gradually increase your daily steps or exercise duration.
- Regular Monitoring: Consistently observing your blood sugar readings allows you to comprehend their connection to your results, enabling informed modifications to your care plan. This proactive method empowers you to manage your health, a fundamental tenet of Dr. Shumard’s practice. By actively interpreting and responding to your a1c to fructosamine levels, you can make significant strides toward improved blood sugar management and overall wellness, aligning with the empowering strategies highlighted at Integrative Wellness Center.
Resources and Troubleshooting for Effective Diabetes Management
To enhance your diabetes management, it’s important to recognize that there are several valuable resources available to you:
- Diabetes Education Programs: Have you considered seeking out local or online programs that offer comprehensive education on diabetes management? These programs can significantly improve patient outcomes by equipping individuals with essential self-management strategies. Many patients with type 2 diabetes find it beneficial to evaluate their regimen every 6 weeks until their target is achieved and then every 3 to 6 months thereafter, highlighting the importance of regular assessment.
- Support Groups: Participating in a support group for managing blood sugar can provide invaluable emotional support and practical guidance from individuals facing similar challenges. Community support has been shown to effectively promote adherence to plans and enhance overall health outcomes. As a support group leader once shared, ‘The power of community backing cannot be overlooked; it plays an essential role in assisting individuals in remaining dedicated to their health objectives.’
- Mobile Apps: Have you tried utilizing apps for blood sugar control? They can help you track your glucose levels, food consumption, and workout habits, keeping you organized and informed about your health.
- Consultation with a Health Educator: If you find yourself struggling with your care plan, seeking advice from a health educator can provide personalized support tailored to your individual needs. For those facing ongoing challenges with adherence, a referral to educators in chronic illness management or mental health professionals may be necessary to address underlying issues.
Incorporating holistic lifestyle strategies can profoundly influence your blood sugar management. Many patients find that embracing the outdoor lifestyle in San Marcos by utilizing local parks and trails for regular exercise can enhance insulin sensitivity and help control weight. Focusing on a balanced diet rich in local produce, such as avocados and berries available at vibrant farmers’ markets, can also make a difference. Engaging with community wellness programs can provide additional support and resources tailored to managing diabetes effectively, especially when considering the relationship of a1c to fructosamine levels. Adjustments in these areas can lead to improved results.
- For frequent fluctuations in blood sugar, consider discussing your medication or insulin regimen with your healthcare provider to ensure it aligns with your current lifestyle.
- Maintaining a journal documenting your food intake and blood sugar readings can help identify patterns and triggers affecting your levels. This practice can offer insights that enhance better decision-making.
- Furthermore, employing the ADCES7 Self-Care Behaviors framework can assist in providing thorough education on your condition, addressing individual patient requirements, and encouraging ongoing self-management initiatives.
For personalized guidance and support tailored to your unique needs, consider reaching out to the Integrative Wellness Center. Our expert team is dedicated to helping you navigate your diabetes management journey with care and expertise.
Conclusion
Understanding the critical roles of A1c and fructosamine in diabetes management is essential for your health journey. These blood sugar markers can significantly improve your health outcomes. A1c offers a long-term view of average glucose levels, while fructosamine reveals recent fluctuations, allowing for timely adjustments in your treatment plan. Together, they empower you and your healthcare provider to create a personalized diabetes management strategy that truly fits your needs.
It’s important to recognize that converting A1c to fructosamine enhances your ability to track progress and make informed decisions. By actively monitoring these levels and interpreting their significance, you can engage in proactive health management. Many patients find that incorporating lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular physical activity, further optimizes blood sugar control. This can lead to better overall well-being and a more fulfilling life.
Ultimately, comprehensive diabetes care is not just about monitoring numbers; it’s about fostering an environment where you feel empowered to take charge of your health. Utilizing available resources, support systems, and expert guidance can significantly enhance your management journey. As you embrace these insights and strategies, you can achieve meaningful improvements in your diabetes management and overall quality of life. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; support is always available to help you thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is understanding blood sugar indicators important for managing diabetes?
Understanding blood sugar indicators is crucial for effective diabetes management as they reflect average blood glucose readings over time, helping evaluate long-term glycemic control and recent changes in blood sugar levels.
What is the difference between A1c and fructosamine?
A1c reflects average blood glucose readings over the past two to three months, while fructosamine provides an approximation of average blood glucose levels over the previous two to three weeks, making it useful for assessing recent changes in blood sugar control.
How can glycosylated albumin (GA) be beneficial in diabetes management?
Glycosylated albumin (GA) can complement traditional glycemic measures and has been identified as a significant predictor of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes, highlighting the importance of combining different markers for comprehensive blood sugar management.
What should patients know about ascorbic acid and glycation markers?
Patients should be aware that elevated levels of ascorbic acid can interfere with the assay for certain glycation markers, so it is advisable to avoid ascorbic acid supplements for at least 24 hours before sample collection.
How can combining different blood sugar markers improve diabetes management?
Combining different blood sugar markers, such as A1c, fructosamine, and GA, provides valuable insights into a patient’s glycemic control, enabling healthcare professionals and patients to make informed decisions regarding diabetes management strategies.
What impact do personalized programs at Integrative Wellness Center have on patients?
Testimonials from patients indicate that personalized programs at Integrative Wellness Center have led to transformative health journeys and significant improvements in managing diabetes, showcasing the effectiveness of tailored care.