Overview
Navigating alcohol consumption can be particularly challenging for individuals with type 1 diabetes. It’s important to recognize that while moderate drinking might be manageable, excessive intake can lead to serious complications, including hypoglycemia. This highlights the need for careful blood sugar management and personalized care.
Many patients find that proactive communication with healthcare providers is essential in ensuring safe drinking practices. By fostering a supportive dialogue, individuals can better understand their unique situations and make informed choices about their health.
Remember, your well-being is paramount, and taking these steps can help you enjoy life while managing diabetes effectively.
Introduction
In the complex landscape of diabetes management, it’s important to recognize the unique challenges that arise from the interplay between alcohol consumption and blood sugar regulation. For individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, social occasions often involve drinking, making it crucial to understand how alcohol affects glucose levels. Have you ever wondered how a night out might impact your health? From the risk of hypoglycemia to the potential for increased diabetes-related distress, the implications of alcohol use are significant and deserve our attention.
This article delves into the intricate relationships between alcohol and diabetes, offering insights into safe drinking strategies that can help you navigate these situations. It’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals who can provide personalized guidance tailored to your needs. Additionally, we’ll share practical tools designed to empower you on your health journey. By making informed choices, you can reclaim your well-being and enjoy social interactions without compromising your health.
The Interplay Between Alcohol and Type 1 Diabetes
Alcohol consumption can significantly influence the management of type 2 diabetes, affecting blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity in complex ways. It’s important to recognize that while moderate drinking may be manageable for some individuals, excessive alcohol intake can lead to serious health risks. These risks include disruptions in metabolic processes that may increase the likelihood of developing diabetes-related complications. Chronic heavy drinking has been shown to disrupt various metabolic processes, potentially heightening the risk for developing type 2 conditions.
Many patients find that chronic heavy drinking exacerbates management challenges related to blood sugar levels. For instance, a comprehensive analysis involving 934 adults with type 2 diabetes revealed that non-drinkers experienced lower levels of distress related to their condition and fewer severe hypoglycemic episodes compared to both former and current drinkers. This emphasizes the complex connection between beverage consumption and health outcomes, highlighting the potential for heightened health issues among those who drink regularly.
Additionally, beverages can affect glucose levels in several ways. Initially, alcohol may result in a decrease in glucose levels, but as the body processes the beverage, glucose levels can recover, leading to erratic variations. Heightened physical activity can further reduce blood sugar levels when alcoholic beverages are ingested, requiring careful oversight and management tactics.
Dr. Jason Shumard, with his advanced education in functional endocrinology and clinical nutrition, emphasizes the significance of comprehending these dynamics for efficient management of blood sugar. By offering patients at the Integrative Wellness Center actionable insights and practical tools, individuals can better navigate the complexities of beverage consumption and its effects on their health. This holistic approach empowers patients at the Integrative Wellness Center to reclaim their well-being while effectively managing their condition, aligning with the center’s commitment to personalized care and education.
The Integrative Wellness Center provides an extensive program aimed at assisting patients in reversing type 2 conditions, emphasizing customized nutrition and lifestyle approaches.
In conclusion, while moderate beverage intake may be manageable for certain individuals with type 2 conditions, it is essential to acknowledge the possible dangers linked to excessive drinking. By grasping how spirits affect glucose levels and insulin responsiveness, patients can make educated choices that enhance their overall well-being and condition management.
Understanding the Risks of Alcohol for Type 1 Diabetics
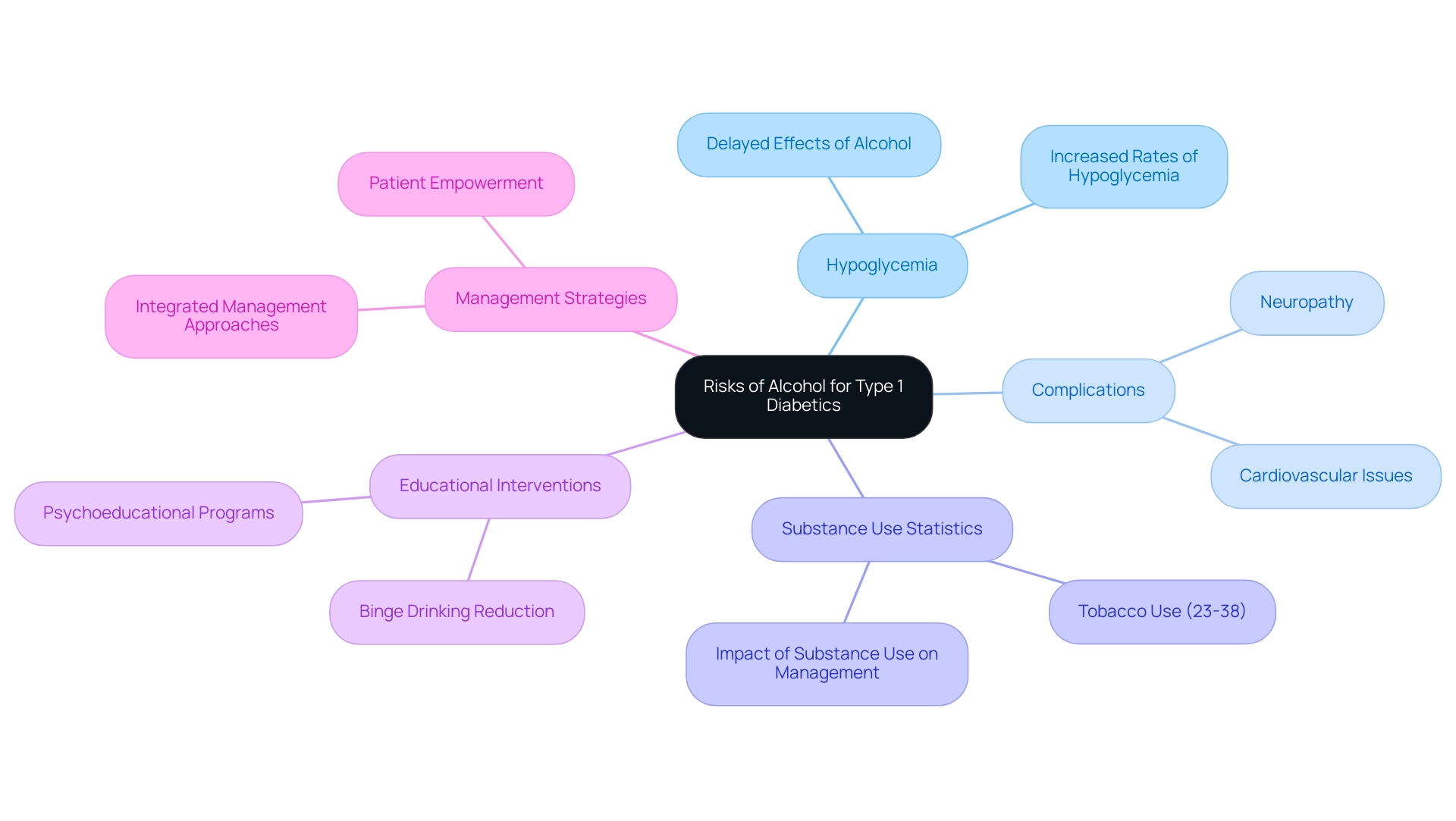
Individuals with type 1 diabetes face unique challenges when it comes to beverage choices, particularly concerning hypoglycemia. It’s important to recognize that this condition can emerge several hours after drinking, posing a significant risk. The effects of alcohol on those with type 1 diabetes can inhibit the liver’s ability to release glucose, leading to dangerously low blood sugar levels.
Studies show that hypoglycemia rates can significantly increase among individuals with type 1 diabetes when alcohol is involved. This highlights the need for careful monitoring and management of alcohol consumption in relation to diabetes.
Moreover, excessive alcohol intake can exacerbate complications associated with diabetes, such as neuropathy and cardiovascular issues, which are already prevalent in this population. A review of substance use among individuals with type 1 diabetes revealed that both alcohol and illicit drug use complicate management, increasing the risk of acute and chronic complications. This underscores the importance of integrated management strategies that address both blood sugar control and substance use disorders.
Statistics indicate that tobacco use among young adults with type 1 diabetes ranges from 23% to 38% in the past three months, illustrating a broader context of substance use in this group. Real-life experiences further illustrate the dangers of beverage consumption; many patients have reported episodes of hypoglycemia after drinking, often unaware of the delayed effects that alcohol can have on their blood sugar levels.
These experiences emphasize the critical need for education and awareness about safe drinking practices for those managing type 1 diabetes. Many patients find that understanding these risks can empower them to make informed decisions regarding their health.
Furthermore, an intervention study highlighted that college students with type 1 diabetes reported significant decreases in binge drinking after participating in a psychoeducational program. Such interventions are essential in fostering a better understanding of the relationship between beverage consumption, especially alcohol, and blood sugar management.
As Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.”
This comprehensive strategy is vital for effectively managing blood sugar challenges, particularly those related to drinking. It’s crucial to approach these issues with compassion and support, ensuring that individuals feel understood and empowered in their journey toward better health.
How Alcohol Affects Blood Sugar Levels in Type 1 Diabetes
Alcohol intake can significantly affect glucose levels in individuals with type 1 diabetes, leading to both immediate and delayed consequences that require careful monitoring. Initially, spirits may cause a surge in glucose levels, especially when mixed with sweet beverages, which can lead to inaccurate readings. However, as the liver processes ethanol, it inhibits glucose production, potentially resulting in a decrease in sugar levels several hours later.
It’s important to recognize that this dual effect underscores the significance of careful glucose monitoring before, during, and after consuming beverages to prevent hypoglycemia.
Research indicates that the risk of complications related to high sugar levels can increase dramatically with beverage consumption. Studies show a 77% rise in risk among certain populations, highlighting the essential need for individuals with type 2 diabetes to understand how beverages impact their condition. This aligns with Dr. Jason Shumard’s approach to personalized care and education.
To effectively manage these risks, individuals are encouraged to implement SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—related to their beverage intake and overall health. For instance, a patient might set a target to reduce beverage consumption to a specific number of drinks weekly or to track glucose levels more frequently on days when beverages are consumed. Many patients find that utilizing tracking methods such as fitness apps, journals, and pedometers enhances accountability and motivation.
Consistently assessing one’s progress not only promotes responsibility but also allows for adjustments in response to evolving health circumstances.
Practical examples demonstrate the variability in glucose responses to beverages. Some individuals may experience significant fluctuations, with glucose levels rising shortly after consuming a beverage and then dropping hours later. Expert insights suggest that these fluctuations can be influenced by factors such as the type of drink consumed, the presence of food, and personal metabolic responses.
While completely reversing alcohol-related health issues can be challenging, case studies show that removing such beverages can lead to significant improvements in managing the condition. For example, individuals who refrain from beverages containing ethanol often report better glucose control and overall metabolic wellness. This strengthens the possibility that lifestyle modifications can positively affect health outcomes. The case study titled ‘Reversibility of Alcohol-Induced Diabetes’ illustrates this point, showing that lifestyle changes can greatly enhance management of the condition.
In summary, understanding the immediate and delayed effects of alcohol on glucose levels in type 1 diabetes is crucial for effective management. By providing actionable insights and practical tools, as Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, individuals can navigate their health journeys more effectively, reclaiming control over their well-being and reducing reliance on conventional medical interventions. By prioritizing goal-setting and consistent progress tracking, including various tracking methods, patients can cultivate a sense of achievement and maintain engagement in their health management.
Safe Drinking Strategies for Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes
To ensure safe drinking practices for individuals with type 2 diabetes, it’s important to recognize the challenges you may face. Adopting the following strategies can help you maintain control over your health while enjoying social occasions:
- Always consume a meal or snack that includes carbohydrates before drinking. This simple step assists in stabilizing your glucose levels and reduces the risk of hypoglycemia, allowing you to enjoy your time without worry.
- Regularly monitoring your glucose levels, particularly before and after consuming alcohol, is essential. Many patients find that staying aware of fluctuations helps them feel more secure in their choices, especially in the context of alcohol and type 1 diabetes.
- Opt for drinks with reduced sweetness, such as dry wines or spirits mixed with calorie-free mixers. This choice can lessen the impact on your glucose levels, making it easier to manage your health.
- Adhering to moderate drinking guidelines—typically one drink per day for women and two for men—can significantly reduce potential health risks, enabling you to enjoy social interactions more safely.
- Always keep a source of fast-acting carbohydrates, like glucose tablets or juice, on hand. This preparation allows you to quickly address any episodes of hypoglycemia that may arise, providing peace of mind.
As we look ahead to 2025, these guidelines remain crucial. Recent studies highlight the importance of effectively managing blood sugar levels, particularly when it comes to alcohol and type 1 diabetes. Notably, a clinical investigation in Da Qing, China, revealed that diet, exercise, or a combination of both was linked to reductions in the probability of acquiring the condition by 31%, 46%, and 42%. This underscores the significance of lifestyle choices in your management journey. Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the Integrative Wellness Center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.”
Additionally, it’s essential to understand that type 2 blood sugar issues can develop at any age. With 58% of cases diagnosed in individuals aged 30 or younger, and 42% in those aged 31 to 60, the need for effective management strategies across all age groups is clear. Enhanced A1C levels can also lower the risk of cognitive decline in individuals with glucose regulation issues, further highlighting the importance of blood sugar control in relation to beverage intake.
By applying these strategies, you can enjoy social occasions while confidently maintaining control over your health management.
The Importance of Consulting Healthcare Providers About Alcohol Use
Before consuming alcohol, it’s essential for individuals with type 1 diabetes to have a thorough discussion with their healthcare providers, especially at Integrative Wellness Center. This proactive step is vital for identifying potential interactions with blood sugar medications and assessing individual health risks, particularly regarding alcohol and type 1 diabetes. Establishing safe drinking limits tailored to each patient’s unique circumstances is crucial. At our clinic, we prioritize personalized functional medicine approaches, including advanced testing that pinpoints individual dietary needs. This ensures that healthcare providers can offer tailored strategies for managing blood sugar levels in relation to alcohol, fostering a safer and more enjoyable experience.
Statistics reveal that many healthcare providers advocate for discussions about alcohol and type 1 diabetes with patients experiencing high blood sugar. In fact, studies from 2025 indicate that nearly 70% of healthcare professionals support these crucial conversations, highlighting the importance of personalized medical guidance in preventing complications related to substance use. Moreover, stopping alcohol consumption can significantly enhance blood sugar management for those with type 1 diabetes, reducing the risk of complications and underscoring the necessity for these discussions.
Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.” This quote beautifully reinforces the message of patient empowerment and education, which is central to effective management at Integrative Wellness Center, especially when compared to the one-size-fits-all approach of fad diets.
Real-world examples further illustrate the positive outcomes of these discussions. Patients who engaged with their healthcare providers about beverage consumption, particularly alcohol and type 1 diabetes, reported better control over their blood sugar levels and a deeper understanding of how such substances impact their condition. This aligns perfectly with the center’s holistic approach, which prioritizes patient education and empowerment.
Additionally, case studies demonstrate that structured programs promoting open communication between patients and healthcare providers lead to improved health outcomes. For instance, the case study titled “Youth Physical Activity and Diabetes Prevention” underscores how structured support can enhance health management. By fostering an environment where individuals feel comfortable discussing their beverage intake, including alcohol and type 1 diabetes, healthcare providers at Integrative Wellness Center can greatly improve blood sugar management and overall health.
This collaborative approach not only aids in symptom management but also empowers patients to take charge of their health journey.
Navigating Social Situations: Drinking with Type 1 Diabetes
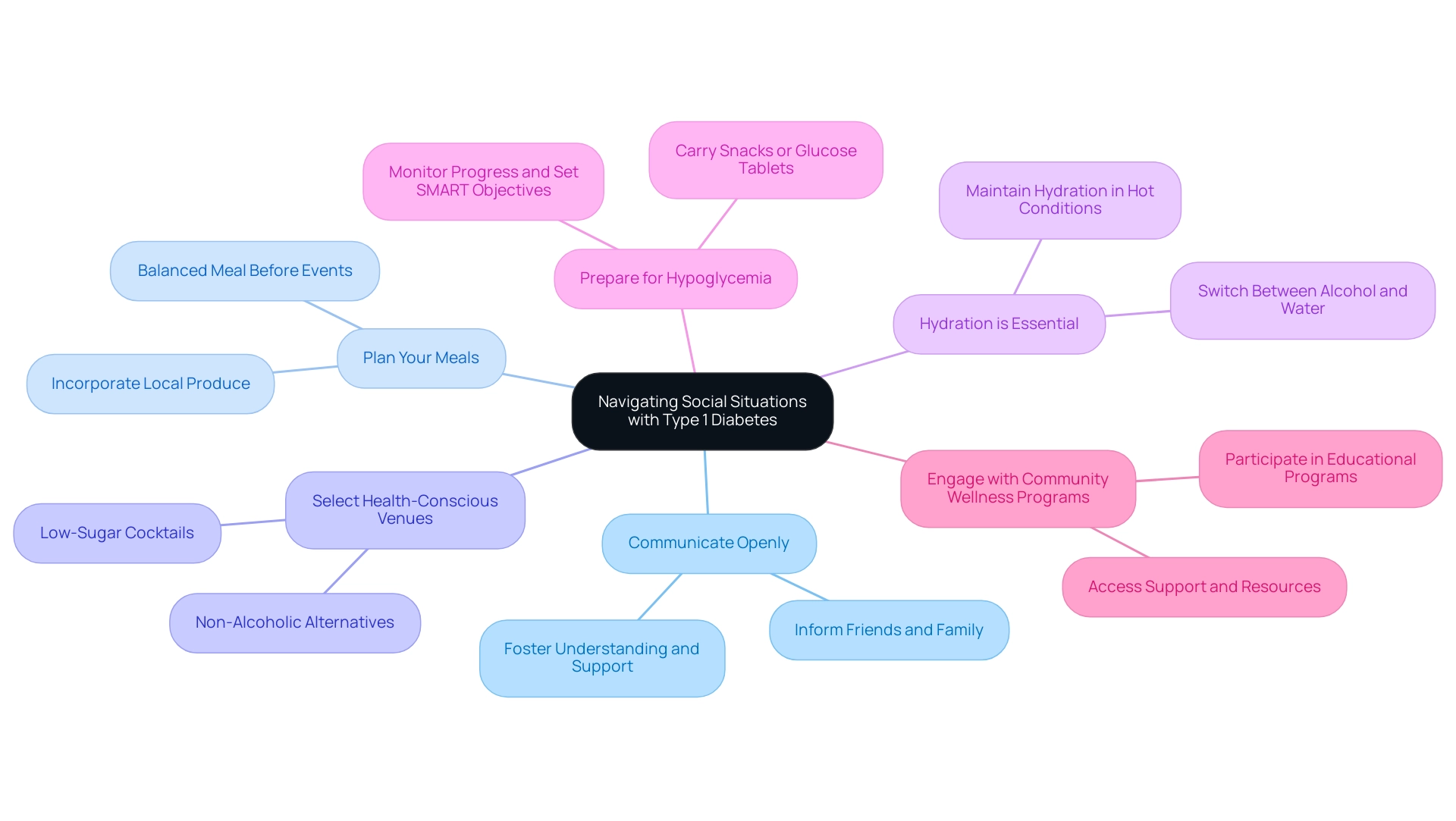
Navigating social situations where alcohol is present can be particularly challenging for individuals with type 1 diabetes. It’s important to recognize that these moments can stir up concerns about health and safety. To ensure a safe and enjoyable experience, consider these supportive strategies:
- Communicate Openly: Inform friends and family about your diabetes and the significance of monitoring your blood sugar levels. This fosters understanding and support in social settings, creating a nurturing environment for you.
- Plan Your Meals: Consuming a balanced meal before going to events can assist in stabilizing glucose levels. Aim for a meal rich in complex carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats to provide sustained energy. Incorporating local produce, such as avocados and leafy greens, can enhance your meal’s nutritional value.
- Select Health-Conscious Venues: Choose locations that offer healthier drink options, such as low-sugar cocktails or non-alcoholic alternatives. This can help you maintain better control over your glucose levels and ensure you enjoy your time out. Look for venues that prioritize fresh, whole ingredients in their food and drink offerings.
- Hydration is Essential: Switch between alcoholic drinks and water to remain hydrated and lessen the chance of dehydration, which can impact glucose regulation. Maintaining hydration is essential, particularly in hotter conditions, to promote overall health and glucose regulation.
- Prepare for Hypoglycemia: Always have a plan in place for managing potential hypoglycemia. Carry snacks or glucose tablets to quickly address any drops in blood sugar. Consistently monitoring your progress and establishing SMART objectives can assist you in remaining focused and motivated in managing your condition.
According to the American Diabetes Association, it is recommended that women limit their beverage intake to one standard drink (14 g of ethanol) per day, while men should limit it to two, particularly when considering the effects of alcohol and type 1 diabetes. Incorporating health technology can also enhance safety during social drinking. For example, contemporary glucose monitoring systems can assist in tracking sugar levels and provide notifications, enabling improved management of the substance’s effects.
Many patients find that being proactive and informed can make a significant difference. As noted by a participant in recent studies, “With alcohol and type 1 diabetes, I guess it did help prevent those rapid crashes that sometimes I would experience. I would gradually stable out, rather than dropping really quick.” By taking these steps, individuals can navigate social situations with confidence and enjoy their time without compromising their health.
Additionally, engaging with community wellness programs can provide further support and resources tailored to managing diabetes effectively. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are many resources available to help you thrive.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between alcohol consumption and diabetes management is essential for individuals living with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The potential risks associated with alcohol intake can lead to significant health complications, including hypoglycemia and increased diabetes-related distress. It’s important to recognize how alcohol can affect blood sugar levels, as its unpredictable impacts necessitate vigilant monitoring and tailored management strategies.
For individuals with type 1 diabetes, the danger of hypoglycemia is heightened. Alcohol can inhibit the liver’s ability to release glucose, leading to dangerously low blood sugar levels. Similarly, those with type 2 diabetes must be aware of how excessive drinking can exacerbate existing health challenges, disrupt metabolic processes, and increase the likelihood of complications. Many patients find that by integrating safe drinking strategies—such as consuming meals prior to drinking and opting for lower-sugar beverages—they can mitigate these risks and maintain better control over their diabetes.
Consulting healthcare providers about alcohol use is a vital component of effective diabetes management. Personalized guidance can help individuals navigate the complexities of alcohol consumption, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their health goals. By fostering open communication with healthcare professionals, individuals can reclaim their health and well-being, empowering themselves to enjoy social interactions without compromising their diabetes management.
In summary, making educated choices about alcohol consumption is paramount for those managing diabetes. By prioritizing safety, engaging in proactive health discussions, and implementing practical strategies, individuals can navigate social situations confidently while safeguarding their health. Embracing these principles can lead to improved diabetes management and a richer, more fulfilling social life.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does alcohol consumption affect individuals with type 2 diabetes?
Alcohol consumption can significantly influence blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity in individuals with type 2 diabetes. While moderate drinking may be manageable for some, excessive intake can lead to serious health risks, including disruptions in metabolic processes and increased likelihood of diabetes-related complications.
What are the risks associated with chronic heavy drinking for those with type 2 diabetes?
Chronic heavy drinking can exacerbate management challenges related to blood sugar levels and has been associated with higher distress levels and more severe hypoglycemic episodes compared to non-drinkers.
How do alcoholic beverages affect glucose levels?
Alcohol initially decreases glucose levels, but as the body processes it, glucose levels can recover, leading to erratic variations. Increased physical activity after drinking can further lower blood sugar levels, requiring careful management.
What approach does the Integrative Wellness Center take to support patients with type 2 diabetes?
The Integrative Wellness Center offers a comprehensive program that emphasizes customized nutrition and lifestyle approaches to assist patients in reversing type 2 diabetes, providing actionable insights and practical tools for effective blood sugar management.
What challenges do individuals with type 1 diabetes face regarding alcohol consumption?
Individuals with type 1 diabetes face unique challenges, as alcohol can inhibit the liver’s ability to release glucose, increasing the risk of hypoglycemia. This condition can occur several hours after drinking, necessitating careful monitoring.
How does alcohol consumption impact complications associated with type 1 diabetes?
Excessive alcohol intake can exacerbate complications such as neuropathy and cardiovascular issues, which are already common in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Substance use can complicate management and increase the risk of both acute and chronic complications.
What educational strategies are effective for individuals with type 1 diabetes regarding alcohol?
Psychoeducational programs have shown to significantly decrease binge drinking among college students with type 1 diabetes, highlighting the importance of education and awareness about safe drinking practices and their effects on blood sugar management.
What is the significance of understanding the relationship between alcohol and diabetes management?
Understanding the risks associated with alcohol consumption empowers individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions about their health, which is crucial for effective management and improving overall well-being.