Overview
Another name for diabetes type 2 is “non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus” (NIDDM). This term reflects the characteristics of insulin resistance and a relative deficiency of insulin, highlighting that insulin therapy may not be immediately necessary. It’s important to recognize that evolving terminology plays a crucial role in understanding this condition. Misconceptions, such as labeling it as “adult-onset diabetes,” can mislead individuals about the demographics and management of diabetes type 2. This misunderstanding can significantly affect their approach to treatment and overall understanding of this chronic metabolic disorder.
Many patients find that gaining clarity on these terms can empower them in their journey. By addressing these misconceptions, we can foster a more accurate understanding that supports effective management strategies. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to help you navigate these challenges. Embracing knowledge is a vital step toward better health and well-being.
Introduction
In a world where type 2 diabetes is becoming increasingly common, it’s crucial to understand the complexities of this condition. Characterized by insulin resistance and fluctuating blood sugar levels, type 2 diabetes can pose significant health risks that may lead to serious complications if not managed effectively. It’s important to recognize that as the terminology surrounding diabetes evolves, both patients and healthcare providers must grasp the nuances of terms like “non-insulin-dependent” and “adult-onset.” These labels not only reflect the changing demographics of the disease but also influence how patients perceive their condition and the strategies used for management.
Many patients find that understanding these terms can be overwhelming, but it’s essential for fostering a clearer perspective on their health. By exploring the importance of accurate terminology, addressing common misconceptions, and sharing the latest insights into effective management, this article aims to illuminate the path toward better health outcomes for those affected by type 2 diabetes. Together, we can navigate this journey toward a healthier life, supporting one another along the way.
Define Type 2 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Overview
Another name for diabetes type 2 is a chronic metabolic disorder that can be overwhelming, characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance and a relative deficiency of insulin. Unlike type 1, where insulin production is absent, those with type 2 can produce insulin, yet their bodies struggle to use it effectively. This condition typically develops gradually and is often linked to several risk factors, including:
- Obesity
- A sedentary lifestyle
- Genetic predisposition
It’s important to recognize that recent statistics indicate around 3.4 million fatalities worldwide are associated with blood sugar issues, highlighting the urgent need to address this medical crisis, especially since another name for diabetes type 2 reflects the physiological processes crucial for effective treatment and management strategies. Many patients find that recognizing these intricate interactions between insulin resistance and various metabolic pathways can empower them to take control of their health.
For instance, a study examining emergency department visits for diabetic patients revealed that:
- 54.9% were treated and released
- 38.4% required hospitalization
This highlights the varying severity of diabetes-related emergencies and the necessity for timely intervention, and it is essential to address insulin resistance, which is another name for diabetes type 2, as a key element in its management. Recent studies have shown that lifestyle changes—such as increasing physical activity and making dietary adjustments—can significantly enhance insulin sensitivity and overall wellness outcomes. By acknowledging the complex characteristics of this condition and its risk factors, individuals can take meaningful steps in managing their health journeys. This proactive approach can lead to improved control and a reduction in reliance on traditional medical treatments, fostering a sense of empowerment and hope.
Explore Alternative Names and Terminology for Type 2 Diabetes
Condition 2, commonly known as another name for diabetes type 2, as well as adult-onset diabetes or non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), carries various names that reflect different aspects of the condition. The term ‘adult-onset diabetes’ emphasizes its traditional link to older age groups, while ‘non-insulin-dependent’ suggests that insulin therapy may not be required right away. Yet, with the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes among younger individuals, it’s essential to adapt our language to better represent those affected by the condition.
In the past, ‘adult-onset diabetes’ was the common term, primarily because it was diagnosed in adults. However, recent statistics show that around 18% of adolescents aged 12 to 18 had prediabetes between 2005 and 2016, pointing to a significant shift in the age distribution of this illness. This evolution in terminology is crucial for both healthcare professionals and individuals, as it fosters clearer communication regarding the condition and its management.
Understanding these terms is vital for accurate diagnosis and effective education for those receiving care. For instance, the term ‘non-insulin-dependent’ might mislead some individuals into thinking insulin is never necessary, which can be quite misleading. As diabetes management evolves, so must the language we use to describe it, ensuring that everyone feels informed and empowered on their wellness journeys.
To manage their condition effectively, individuals are encouraged to set SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. This could mean aiming for a certain number of steps each day or gradually increasing exercise duration. Tracking methods like fitness apps, journals, and pedometers can significantly boost accountability and motivation. It’s also important to recognize that the difficulty of the goals set can influence achievement, highlighting the need for appropriately challenging targets. Regularly monitoring progress not only fosters responsibility but also allows for adjustments to objectives as wellness needs change.
Understand the Importance of Terminology in Diabetes Management
The terminology used in diabetes management extends beyond mere academic discussion; it significantly impacts care and outcomes. It’s important to recognize that the distinction between terms like ‘insulin resistance’ and ‘sugar intolerance’ can profoundly shape an individual’s understanding of their condition and their subsequent management strategies. By utilizing clear and precise language, we enhance communication between healthcare providers and patients, which is crucial for improving adherence to treatment plans and fostering proactive health behaviors.
Many patients find that effective communication strategies are essential, especially considering that research indicates 15.7% of adults diagnosed with diabetes also experience extreme obesity. This highlights the need for approaches that address the complexities of these issues. Furthermore, as the healthcare environment continues to evolve, adopting inclusive and individual-focused language can help reduce stigma and empower those living with diabetes. This empowerment is vital for motivating individuals to take an active role in their health management, ultimately resulting in improved outcomes.
Practical instances demonstrate that when individuals are informed using clear language, their comprehension of the condition improves, leading to better management of their health. The economic burden of managing diabetes, primarily attributed to services and complications rather than medications, further emphasizes the necessity for effective communication. By prioritizing clear terminology, healthcare providers can significantly influence outcomes for individuals and foster a more supportive environment for those facing the challenges of managing their condition.
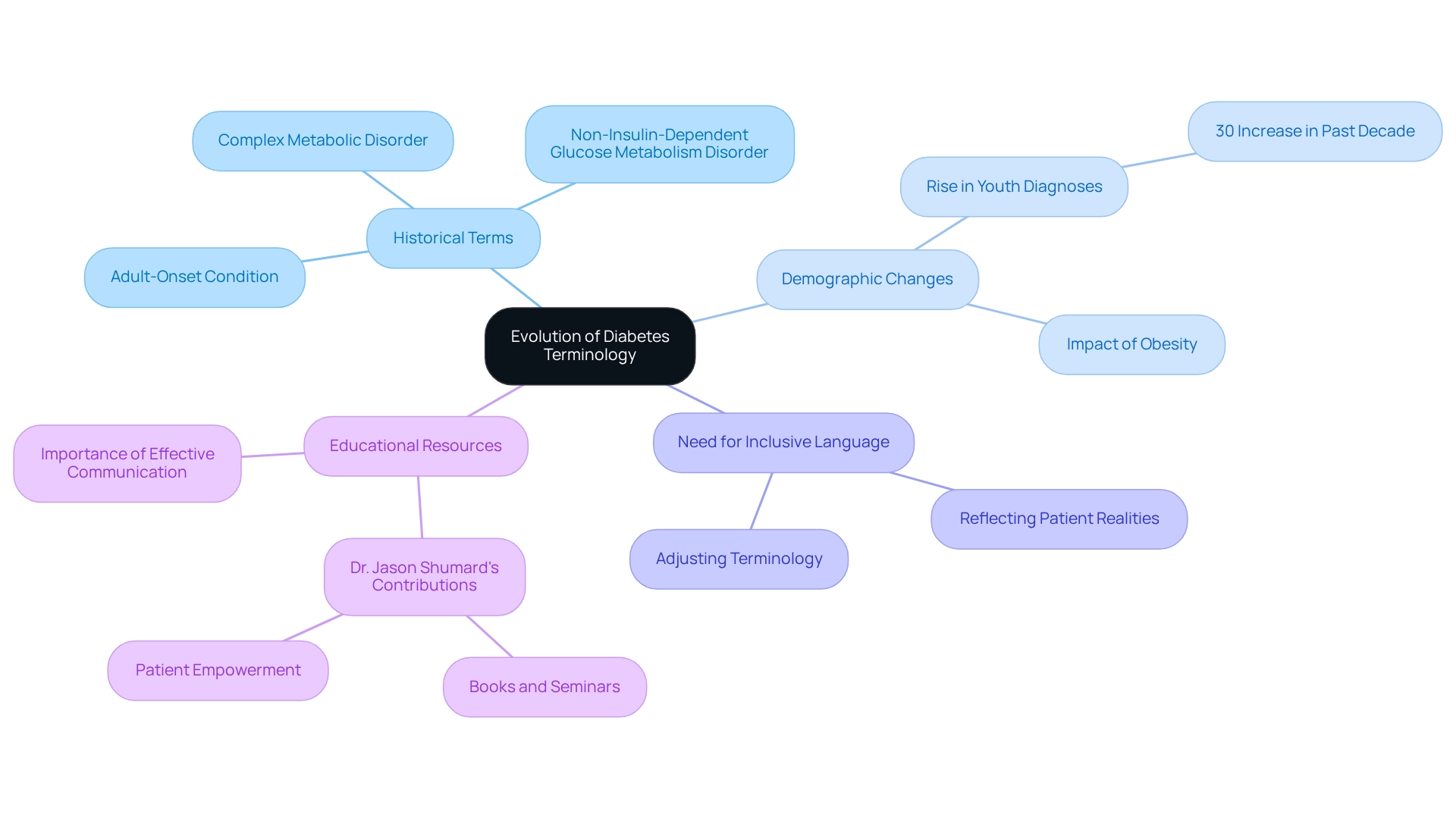
The Evolution of Diabetes Terminology
The terminology surrounding this condition has undergone significant evolution, reflecting advancements in medical knowledge and shifts in patient demographics. Initially referred to as an ‘adult-onset condition,’ which is another name for diabetes type 2, this term implied exclusivity to adults. However, it’s crucial to recognize the alarming rise in obesity rates and lifestyle changes that have led to an increasing number of diagnoses in children and adolescents. This shift necessitates a reevaluation of our language.
Statistics reveal that the incidence of type 2 conditions in youth has increased dramatically, with recent studies indicating a rise of over 30% in diagnoses among this demographic in the past decade. Previously, terms like ‘non-insulin-dependent glucose metabolism disorder’ were used to suggest that insulin therapy was not always necessary. Today, many patients find that the discourse has shifted towards recognizing this condition, which is another name for diabetes type 2, as a complex metabolic disorder. This evolution prompts us to adopt terminology that reflects its multifaceted nature and the diverse management strategies required.
It’s important to emphasize the urgent need for a more inclusive and accurate vocabulary in diabetes care. Medical historians remind us that as demographics evolve, so too must the terminology we use to describe these conditions, ensuring it corresponds with the realities faced by individuals today. Moreover, educational resources offered by professionals such as Dr. Jason Shumard, who focuses on functional endocrinology and clinical nutrition, empower individuals to better understand their conditions. Dr. Shumard’s enthusiasm for helping individuals overcome their challenges through tailored guidance and comprehensive health solutions highlights the importance of effective communication in healthcare education and management.
As we continue to observe changes in the prevalence of diabetes-related conditions, it is essential to adjust our terminology to accurately reflect these alterations. This is particularly crucial given the ongoing safety concerns in hospitals that can impact patient care. Together, we can navigate this evolving landscape with compassion and understanding.
Common Misconceptions About Type 2 Diabetes Terminology
Misunderstandings regarding classification terminology can greatly hinder efficient management. Have you ever felt confused by terms like ‘adult-onset condition’? This common misconception suggests that only adults can develop the ailment, which can be misleading. In fact, the occurrence of condition 2 among younger groups is on the rise, indicating a wider demographic change. It’s important to recognize that the label ‘non-insulin-dependent’ can foster the false belief that insulin is never necessary for managing another name for diabetes type 2. In reality, many individuals may require insulin as their condition progresses.
Addressing these misconceptions is crucial. By enhancing individual understanding and engagement in care strategies, healthcare providers can make a significant difference. Did you know that the yearly rise in type 2 conditions in the U.S. is currently at 4.8%? This statistic emphasizes the necessity of clearly defining these terms to improve health outcomes. Furthermore, case studies indicate that the age-adjusted occurrence of diagnosed metabolic disorder among U.S. adults has remained stable from 2000 to 2021, with a notable reduction in incidence rates following 2008. However, many patients find that caution is advised in interpreting these trends due to changes in survey methodologies, suggesting a potential shift in management strategies. By promoting a more precise comprehension of diabetes-related terms, including that another name for diabetes type 2 is essential, individuals can be better prepared to take charge of their well-being and manage their treatment choices effectively. As Dr. Jason Shumard highlights, ‘By offering individuals actionable insights and practical tools, the center cultivates an atmosphere where people can regain their wellness and well-being, ultimately resulting in enhanced quality of life and decreased dependence on traditional medical interventions.’
At Integrative Wellness Center, we prioritize a holistic approach to managing blood sugar levels. We empower our patients to make informed lifestyle changes that can significantly impact their health outcomes. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you manage your diabetes effectively.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a complex condition that requires a nuanced understanding of its terminology, risk factors, and management strategies. It’s important to recognize that this multifaceted nature can often lead to confusion. Terms like “adult-onset” and “non-insulin-dependent” may mislead patients and hinder effective management. With the rising prevalence of the disease among younger populations, both patients and healthcare providers must adapt their understanding and communication regarding this condition.
Many patients find that effective management hinges on recognizing and addressing misconceptions surrounding the terminology. The distinction between terms can significantly impact patient education and adherence to treatment plans, ultimately influencing health outcomes. By fostering clear communication and utilizing inclusive language, healthcare providers can empower individuals to take an active role in their health. This empowerment can lead to better management and an improved quality of life.
As the landscape of diabetes care continues to evolve, so too must the terminology used to describe it. Embracing a more accurate and inclusive vocabulary not only reflects the realities faced by patients today but also reinforces the importance of personalized care and education. By equipping individuals with the knowledge and tools needed to understand their condition, a path toward better health outcomes can be forged. This enables patients to reclaim their well-being and thrive in their management of type 2 diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is diabetes type 2?
Diabetes type 2 is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance and a relative deficiency of insulin. Unlike type 1 diabetes, individuals with type 2 can produce insulin but struggle to use it effectively.
What are the main risk factors associated with diabetes type 2?
The main risk factors for diabetes type 2 include obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetic predisposition.
How serious is the global impact of diabetes type 2?
Recent statistics indicate that around 3.4 million fatalities worldwide are associated with blood sugar issues, underscoring the urgent need to address diabetes type 2 as a significant medical crisis.
What percentage of diabetic patients require hospitalization?
A study showed that 38.4% of diabetic patients who visited emergency departments required hospitalization, while 54.9% were treated and released.
How can lifestyle changes affect diabetes type 2 management?
Lifestyle changes, such as increasing physical activity and making dietary adjustments, can significantly enhance insulin sensitivity and improve overall wellness outcomes for individuals with diabetes type 2.
What are some alternative names for diabetes type 2?
Diabetes type 2 is also known as adult-onset diabetes and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM).
Why is the terminology around diabetes type 2 important?
The terminology is important as it reflects the condition’s characteristics and helps in accurate diagnosis and effective education for those receiving care. For example, the term ‘non-insulin-dependent’ could mislead individuals into thinking insulin is never necessary.
What are SMART goals in the context of managing diabetes type 2?
SMART goals are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound objectives that individuals can set to manage their diabetes effectively, such as aiming for a certain number of steps each day.
How can individuals track their progress in managing diabetes type 2?
Individuals can track their progress using fitness apps, journals, and pedometers, which can enhance accountability and motivation in achieving their health goals.