Overview
The article titled “A1C Explained: A Comprehensive Tutorial on Understanding Your Diabetes Metrics” aims to provide you with a deeper understanding of the A1C test and its vital role in managing diabetes. It’s important to recognize that the A1C test is not just a number; it is crucial for tracking your long-term blood sugar control. This test measures your average glucose levels over the past two to three months, helping both you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions that can enhance your health outcomes.
Many patients find that understanding their A1C results empowers them to adjust their treatment plans effectively. By keeping a close eye on these metrics, you can take proactive steps toward better health. This knowledge can truly make a difference in your journey, fostering a sense of control and motivation.
As you navigate your diabetes management, remember that you are not alone. There are resources and support systems available to guide you. Engaging with programs like the 30-Day Diabetes Reset can provide you with the tools and community you need to thrive. Together, we can work towards healthier living and improved well-being.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, it’s important to recognize that the A1C test stands as a pivotal tool. This test offers valuable insights into long-term blood sugar levels and guides important treatment decisions. Not only does it aid in diagnosing diabetes, but it also plays a crucial role in monitoring ongoing health. Many patients find that understanding the implications of this test is critical, especially when nearly half of adults with diabetes struggle to maintain optimal A1C levels.
As healthcare continues to evolve, integrating innovative approaches alongside traditional A1C testing can enhance patient outcomes. This empowers individuals to take charge of their health and fosters a proactive stance against this chronic condition. By delving into the intricacies of the A1C test, its interpretation, and effective management strategies, patients can gain the knowledge necessary to navigate their diabetes journey with confidence.
What is the A1C Test and Why is it Important?
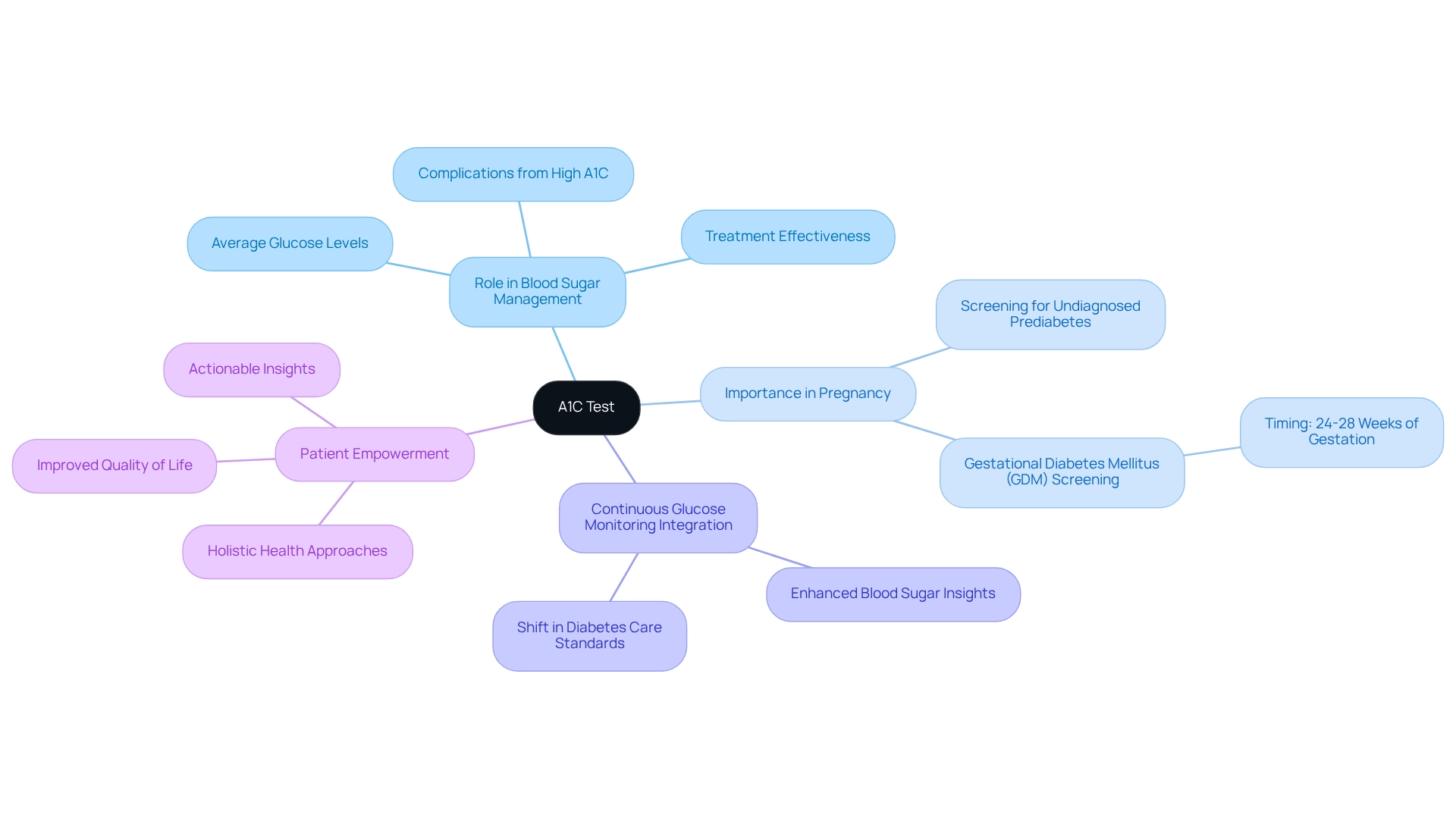
The A1C test, often referred to as the hemoglobin A1C test, serves as a vital tool in regulating blood sugar. It assesses average glucose levels over the past two to three months, playing an essential role not only in identifying blood sugar disorders but also in tracking how effective treatment strategies are. By evaluating the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that is glycated—essentially coated with sugar—the A1C test offers a clear view of long-term blood sugar control.
It’s important to recognize that a higher A1C percentage indicates inadequate blood sugar control, which can lead to serious complications if left unaddressed. Routine A1C assessments are crucial for individuals with high blood sugar, helping to ensure that glucose levels remain within target ranges. Many patients find that about 60% of individuals with the condition consistently monitor their A1C measurements, underscoring the test’s significance in effective care.
Recent studies have shown that combining continuous glucose monitoring data with A1C results can provide a more comprehensive perspective on a patient’s blood sugar levels. This emphasizes a shift in the medical community toward a more refined approach to managing the condition, as highlighted in the case study titled ‘Shifting Standards in Diabetes Care.’
Moreover, the importance of the A1C test extends beyond individual management. It is also critical in identifying abnormal glucose metabolism in individuals planning for pregnancy. Testing for undiagnosed prediabetes or blood sugar issues is advised, especially during pregnancy, to protect the well-being of both the mother and the child. Gestational glucose intolerance (GDM) screening should occur at 24-28 weeks of gestation for at-risk individuals, further highlighting the broader implications of A1C testing.
Considering these developments, the A1C test remains a cornerstone of blood sugar management, providing essential insights that empower patients to take control of their health. As Dr. Jason Shumard of Integrative Wellness Center states, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.” The center’s holistic approach, combined with tailored functional medicine strategies, supports patients in making empowering lifestyle changes that can effectively manage and even reverse type 2 conditions.
To learn more about how Dr. Shumard can assist you in managing your condition, please call 858-564-7081 or register for our upcoming events. Experience firsthand the transformative testimonials from individuals who have successfully navigated their health management journey with us. As the landscape of blood sugar management evolves, the integration of newer methodologies alongside traditional A1C testing will continue to enhance patient outcomes and foster a proactive approach to managing this chronic condition.
How the A1C Test Works: Process and Interpretation
The A1C test is a straightforward procedure that involves collecting a blood sample, which can be obtained either from a vein or through a finger prick. This sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where it measures the percentage of hemoglobin that has glucose attached to it. Results are usually conveyed as a percentage, with values below 5.7% regarded as normal.
Importantly, the A1C test does not require fasting, making it a convenient option for patients.
It’s important to recognize that understanding the A1C test procedure and analyzing the outcomes is essential for successful health control. For individuals with diabetes, maintaining an A1C value below 7% is often a goal to reduce the risk of complications. Recent advancements in testing technology have enhanced the precision and availability of A1C testing, enabling more frequent monitoring and improved strategies.
Many patients find that the interpretation of A1C results can vary based on individual health profiles. For example, a patient with an A1C level of 8% may need to modify their treatment plan, while another with a level of 6.5% might be on target with their objectives. Each patient’s experience with the A1C test can offer valuable insights into their overall health and the effectiveness of their health care plan.
To improve blood sugar control, individuals are encouraged to adopt effective methods for monitoring progress and establishing objectives. Utilizing methods such as fitness apps, journals, and regular check-ins can foster accountability and motivation. Setting SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—can significantly boost focus.
For instance, aiming to reduce A1C values by a certain percentage within a designated timeframe can offer a clear goal.
Statistics show that 70.8% of U.S. adults aged 18 years or older with diagnosed blood sugar issues had elevated blood pressure, highlighting the significance of thorough strategies that tackle both glycemic control and cardiovascular health. A study named “A1C Levels and Blood Pressure in Diabetic Adults” emphasized that numerous adults with high blood sugar also deal with increased A1C levels and blood pressure, reinforcing the need for coordinated treatment strategies. Moreover, the condition was the eighth primary cause of mortality in the United States in 2021, highlighting the necessity for effective strategies to handle it.
By understanding the A1C test and its implications, patients can take proactive steps in their health journey, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and a better quality of life. As Deborah Banerjee, a professional with more than 15 years of experience in public health, points out, tackling health disparities and chronic illnesses is essential in managing blood sugar conditions. This knowledge empowers patients to take control of their health and make informed decisions regarding their treatment plans.
Moreover, participating in community wellness initiatives, like those provided by Integrative Wellness Center, and concentrating on holistic lifestyle approaches—such as balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and stress control—can further enhance effective health oversight. For additional assistance, Dr. Jason Shumard’s book offers valuable insights and resources for patients managing their health journey.
Understanding A1C Levels: What Do the Numbers Mean?
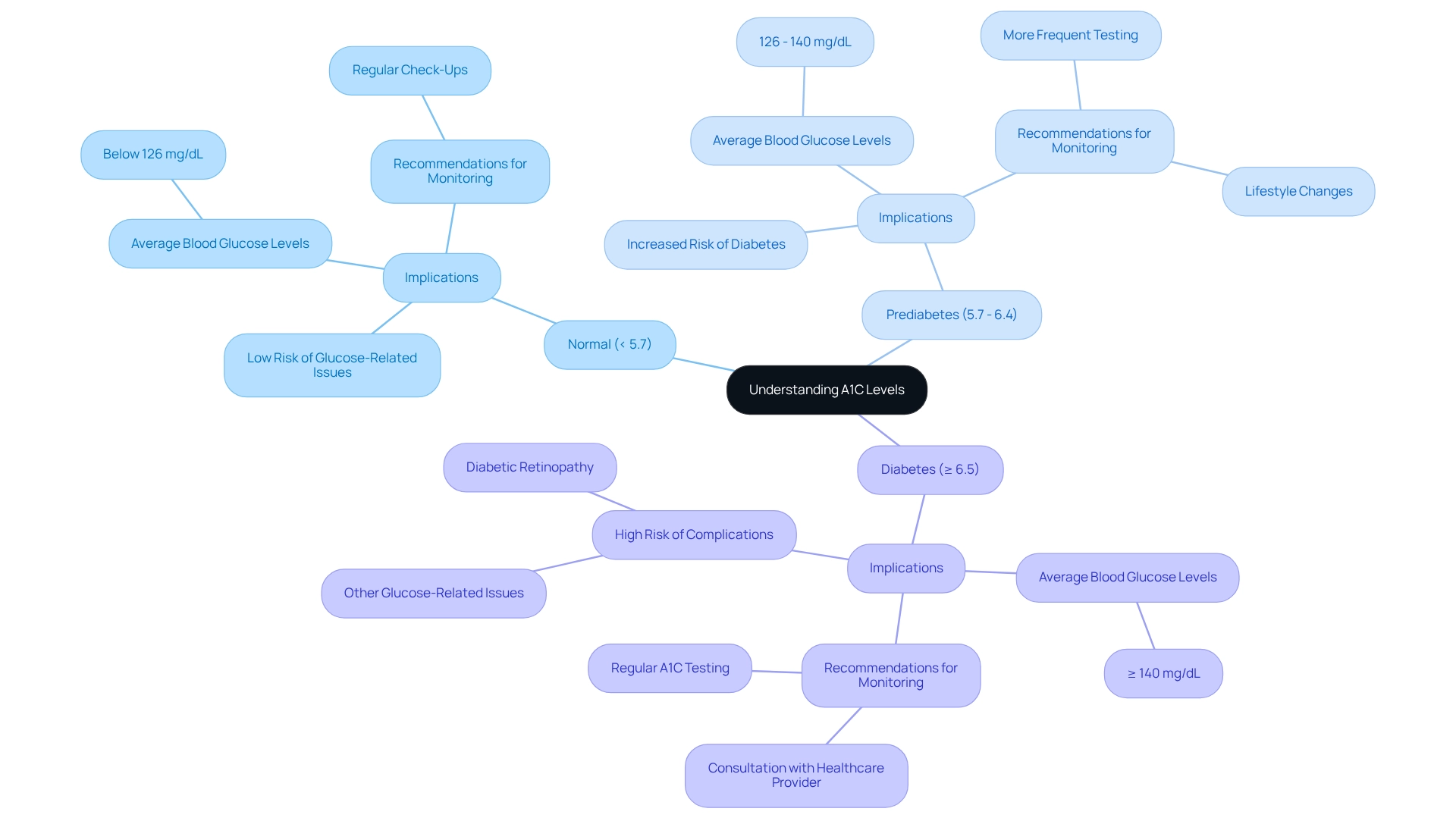
Understanding A1C readings can be a crucial step in managing your health. A1C explained categorizes these readings into groups that indicate your risk for glucose-related issues and associated complications. If your A1C measurement is below 5.7%, it’s considered normal. However, values ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% suggest prediabetes, and an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms a diabetes diagnosis. Each percentage point increase in A1C corresponds to a significant rise in average blood glucose levels; for example, an A1C of 7% correlates with an average blood glucose reading of approximately 154 mg/dL.
It’s important to recognize that comprehending these metrics is essential for patients. They highlight the potential for complications linked to increased A1C values. Findings from the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial suggest that elevated average A1C readings are a primary indicator of diabetic retinopathy progression. This underscores the necessity of consistent monitoring and proactive management.
In 2025, A1C will also be reported as estimated average glucose (eAG), providing a more relatable measure of average blood glucose values. However, many patients find that eAG may differ from readings obtained from home glucose meters due to the timing of checks, which can affect the accuracy of self-monitoring.
Expert opinions emphasize the necessity for clinicians to grasp the significance of A1C results and to refer patients for further evaluation when necessary. As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.” Real-world examples illustrate how patients have successfully implemented lifestyle changes based on their A1C levels, leading to improved health outcomes, as seen in the context of Dr. Shumard’s Functional Medicine Approach.
For instance, patients like Ed have experienced transformative results through Dr. Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, which emphasizes personalized functional medicine strategies tailored to individual health needs. To discover additional information on how you can take charge of your health, reach out to the Integrative Wellness Center at 858-564-7081 or sign up for our upcoming events. Furthermore, Dr. Shumard’s publication on reversing blood sugar issues is accessible as a complimentary resource for participants, offering additional insights into effective control strategies.
Ultimately, A1C explained empowers patients to comprehend their A1C values and their consequences. This understanding enables you to take charge of your condition and promotes a proactive strategy for health that aligns with the holistic care model endorsed by Dr. Jason Shumard at the Integrative Wellness Center.
Interpreting Your A1C Results: Normal vs. High Levels
Interpreting A1C results is not only straightforward but also essential for effectively managing your health. Understanding what these numbers mean can provide crucial insights into your blood sugar control. An A1C value below 5.7% is considered optimal, indicating good management. If your levels fall between 5.7% and 6.4%, it suggests a heightened risk of developing diabetes, while a result of 6.5% or above confirms a diagnosis of the condition.
It’s important to recognize that recent research shows roughly 50% of individuals with diabetes achieve A1C values under 7%, which is the target limit to reduce the likelihood of complications. Moreover, the average medical costs for those diagnosed with blood sugar-related conditions are 2.6 times greater than for those without, highlighting the financial impact of inadequate A1C management.
Consistent tracking of A1C values is crucial. By keeping an eye on your numbers, you can make informed adjustments to your treatment plan. Many patients find that utilizing effective tracking methods—like fitness apps, journals, and pedometers—can enhance this process. Setting SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—can significantly boost your focus and motivation in managing your health.
For instance, imagine setting a goal to reduce your A1C by a certain percentage within a specified timeframe. A major study involving over 600,000 participants revealed considerable regional differences in diabetes prevalence, emphasizing the need for personalized care in managing A1C values. Experts agree that maintaining A1C levels under 7% can greatly decrease the chances of complications, reinforcing the importance of proactive approaches.
Many individuals share their experiences with high A1C levels, often feeling overwhelmed by the implications of their results. However, with the right education and support, you can take control of your health. Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes empowering patients through education, helping them understand their A1C results and make necessary lifestyle changes.
Consider the story of one patient who lost 55 lbs and reduced their A1C from 9.1 to 5.7 after participating in a structured program. Another individual shared that they no longer needed medications after experiencing significant health improvements. These transformative stories highlight the importance of goal-setting and consistent progress tracking.
As Brian C. Moyer, Ph.D., noted, “All material appearing in this report is in the public domain and may be reproduced or copied without permission; citation as to source, however, is appreciated.” This emphasizes the significance of accessible information in managing health conditions.
In summary, understanding A1C thresholds—where below 5.7% is ideal, 5.7% to 6.4% indicates risk, and 6.5% or higher confirms the condition—is vital for effective oversight. By accurately interpreting these results and adjusting your treatment accordingly, you can significantly improve your health outcomes. Furthermore, recent developments concerning prediction equations for additional glucose level assessments provide timely context for the ongoing discussion about A1C interpretation and management strategies.
Setting A1C Goals: What Should Your Target Be?
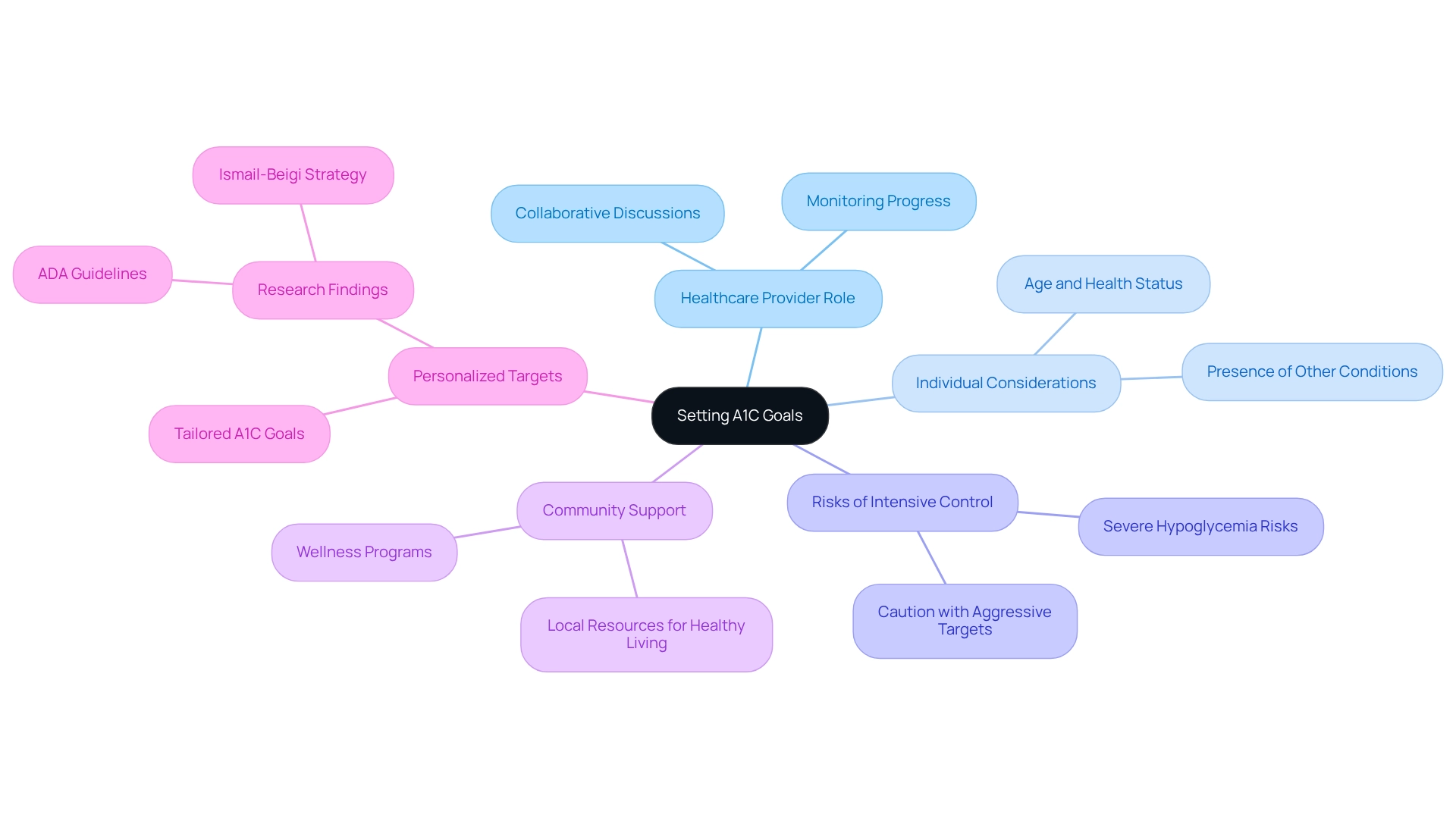
Setting A1C goals is a collaborative journey, one that truly thrives on the active participation of both patients and their healthcare providers. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) typically recommends an A1C goal of under 7% for most adults with diabetes. However, it’s important to recognize that individual goals can vary significantly based on factors like age, overall health, and the presence of other conditions.
Recent research highlights the value of personalized A1C targets, revealing that a one-size-fits-all approach may not be the most effective. For example, a study analyzing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that while 31% of U.S. adults with blood sugar challenges could aim for an A1C of less than 7.0% under ADA guidelines, a tailored strategy could allow up to 56% to set similar targets. This underscores the importance of healthcare providers engaging in meaningful discussions with patients to establish goals that are not only realistic but also supportive of their overall well-being.
Moreover, considering the risks associated with intensive glycemic control is crucial. Studies like ACCORD, ADVANCE, and VADT have shown that severe hypoglycemia is significantly more likely among participants in the intensive glycemic control group, reminding us to approach aggressive A1C targets with caution.
The combination of blood glucose monitoring (BGM) and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) plays a vital role in guiding medical nutrition therapy, physical activity, and medication oversight, further supporting the goal-setting process. Collaborative goal-setting fosters a sense of ownership among patients, empowering them to take charge of their health journey.
Integrating comprehensive lifestyle approaches, such as enjoying outdoor activities in San Marcos, CA, can greatly enhance blood sugar control. Embracing the local environment by utilizing parks and trails for exercise, alongside a balanced diet rich in fresh, local produce from farmers’ markets, can support effective blood sugar management. Community wellness programs also provide invaluable support, offering resources tailored to individual needs.
As we progress in managing blood sugar levels, staying informed about the latest guidelines and studies is essential. In 2025, ongoing conversations within the healthcare community will emphasize the need for tailored A1C targets, reflecting a shift towards more personalized care in blood sugar regulation. As Aviva G Nathan notes, personalized goals are key for effective blood sugar management.
By working closely with their healthcare teams, patients can set A1C goals that align with their unique health profiles, ultimately leading to improved adherence and better health outcomes.
Furthermore, the relationship between A1C levels and average glucose levels is strong enough to warrant reporting both measures when requesting the A1C test. This further emphasizes the significance of a holistic approach to managing diabetes. The case study titled “Individualized A1C Targets for U.S. Adults with Diabetes” suggests a need to revise research and performance measurement goals to promote individualized glycemic targets.
At Integrative Wellness Center, we understand that managing Type 2 diabetes requires a personalized approach. Our dedicated team is here to assist you in navigating your health journey with customized services, including individualized nutrition plans and community wellness initiatives. We also offer a breakthrough process designed specifically for Type 2 diabetes patients, empowering you to achieve a happy, healthy, and diabetes-free life.
How to Lower Your A1C: Practical Tips and Strategies
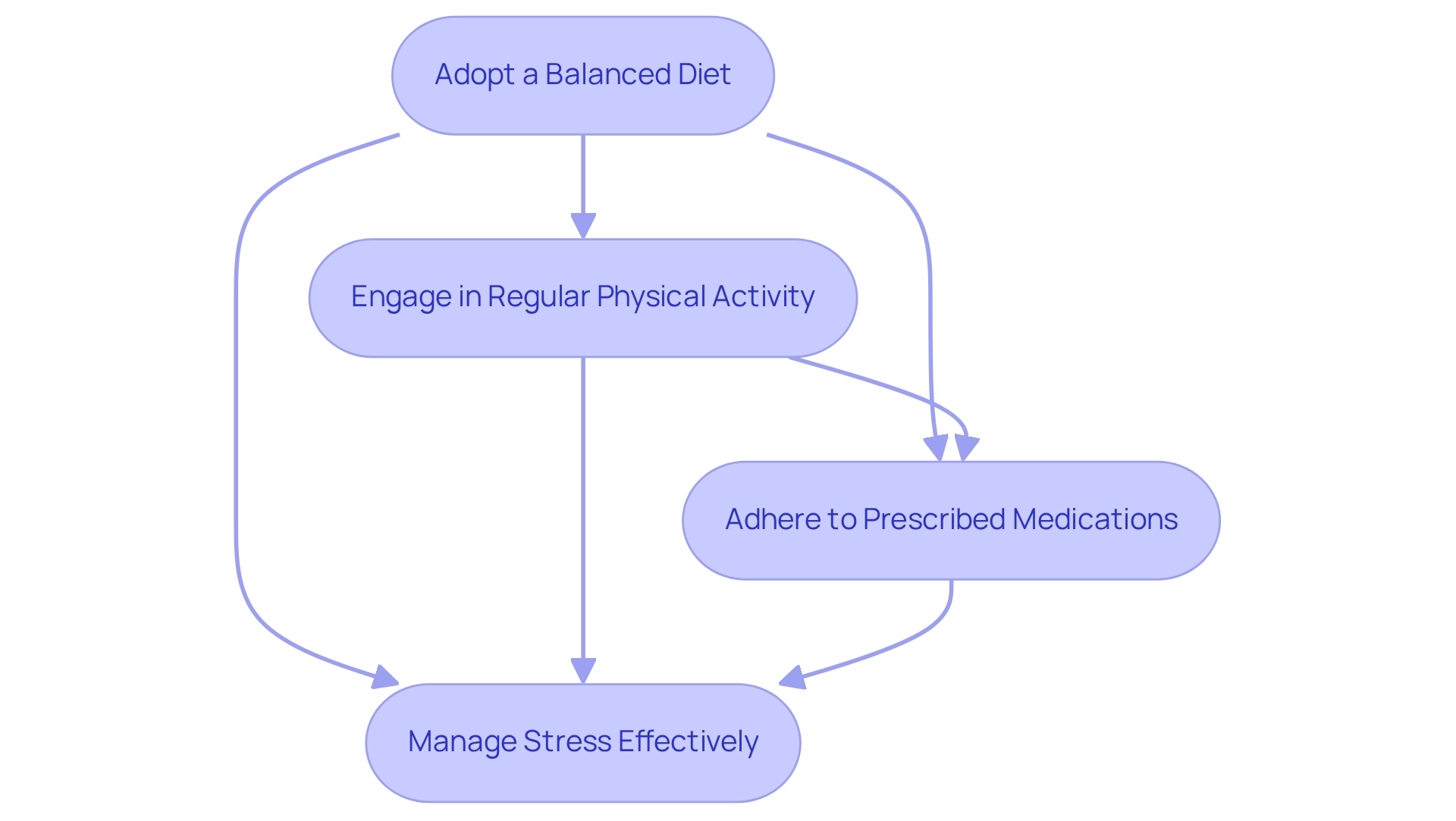
To understand how lowering your A1C can be effectively achieved, it’s important to recognize the significance of a strategic combination of lifestyle modifications and medical management. Here are several practical strategies to consider:
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables. Customized nutrition strategies, like those provided by Integrative Wellness Center, can assist in stabilizing blood sugar and enhancing metabolic function. These plans are tailored to individual needs, ensuring that dietary choices align with personal health goals. Many patients find that dietary modifications can lead to considerable enhancements in A1C values, and they often share their success stories of effectively reducing their A1C through nutritional changes.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Organized physical activity regimens, such as walking programs detailed in the walking program PDF, have been shown to significantly lower triglyceride amounts, with a notable decrease of 21.85 mg/dl after the intervention. This improvement can correlate with better A1C outcomes. Incorporating activities like walking, cycling, or swimming can enhance overall health and glycemic control. Consider starting with a daily walk of 10-15 minutes and gradually increasing the duration and frequency.
Monitoring blood sugar readings is crucial for understanding how your diet and physical activity impact what is A1C explained. This self-monitoring empowers patients to make informed decisions about their health and track their progress effectively.
- Adhere to Prescribed Medications: Always take medications as directed and maintain open communication with your healthcare provider regarding any concerns or side effects. This partnership is crucial for effective blood sugar control.
- Manage Stress Effectively: Implement mindfulness practices, yoga, or other relaxation techniques to help manage stress, which can adversely affect blood sugar levels. Participating in community wellness initiatives in San Marcos can offer extra assistance and resources designed for managing blood sugar levels. Stress management is a vital component of maintaining what is often A1C explained as a healthy level.
Recent findings emphasize that lifestyle interventions are not only safe and cost-effective but also essential in lowering the risk of progression to type 2 conditions in individuals with prediabetes. Moreover, educational initiatives focusing on lifestyle modifications have proven effective in motivating patients to adopt healthier habits, leading to improved glycemic control. As Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.”
By incorporating these strategies into everyday life, individuals can make substantial progress toward reducing their A1C values, as A1C explained, and enhancing their overall health.
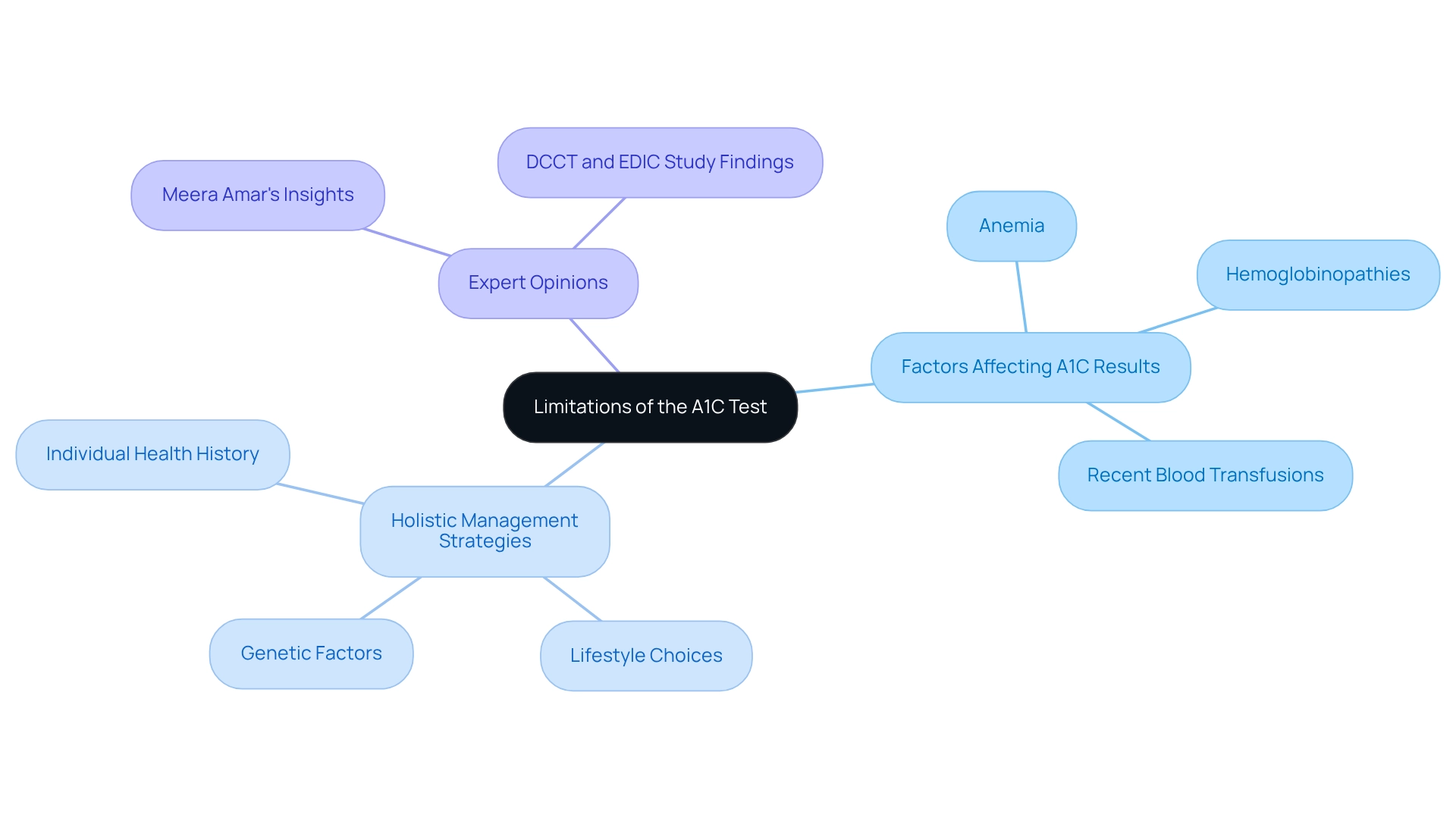
Limitations of the A1C Test: What You Need to Know
The A1C test serves as a crucial gauge in diabetes care, but it does come with its limitations. It’s important to recognize that various factors can skew A1C results, such as:
- Anemia
- Certain hemoglobinopathies
- Recent blood transfusions
For example, individuals with anemia may show artificially low A1C values, which can misrepresent their actual glycemic control.
Moreover, the A1C test does not reflect short-term variations in blood glucose, which are essential for daily decision-making. Many patients find that understanding these nuances is vital for effective management.
Integrating a customized functional medicine strategy, as promoted by Dr. Jason Shumard, highlights the significance of comprehending A1C readings within the framework of a comprehensive lifestyle management plan. This approach emphasizes personal health profiles, including:
- Individual health history
- Lifestyle choices
- Genetic factors
to develop tailored strategies for managing type 2 conditions. Recent studies suggest that a notable proportion of patients—91.3% in one study—did not follow specific dietary plans, potentially affecting their A1C values.
This underscores the need for holistic strategies that encompass tailored nutrition, regular exercise, and community support alongside A1C monitoring. Have you considered how these elements might fit into your daily routine?
Real-world examples illustrate the complexity of A1C accuracy. A study involving 2,791 individuals with type 2 blood sugar issues in Iran utilized Linear Mixed Quantile Regression Models (LMMs) to analyze the relationship between HbA1c values and various factors such as:
- Age
- Sex
- BMI
- Treatment regimens
The results revealed notable connections between HbA1c values and elements like cholesterol and triglycerides, emphasizing the intricate aspects of managing blood sugar conditions.
Experts in the field, including endocrinologists like Meera Amar, have voiced concerns regarding the accuracy of the A1C test. Amar states, “While the A1C test is a valuable tool, it should not be the sole measure of glycemic control.” This sentiment reinforces the importance of engaging in discussions with healthcare providers about A1C results.
Furthermore, the DCCT extension into the EDIC study suggested long-term cardiovascular risk and mortality advantages for patients with lower HbA1c levels, further emphasizing the importance of effective A1C control. Individuals are encouraged to explore additional monitoring techniques, such as daily blood glucose testing, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of their condition. By integrating these insights with lifestyle modifications—such as embracing outdoor activities available in San Marcos, focusing on a balanced diet rich in local produce, and participating in community wellness programs—individuals can empower themselves to achieve better health outcomes and improve their quality of life.
The Role of Regular A1C Monitoring in Diabetes Care
Regular A1C monitoring is essential for effectively managing your condition, serving as a key indicator of long-term blood sugar control. It’s important to recognize that current guidelines recommend individuals with high blood sugar have their A1C measurements assessed at least twice a year if they are consistently achieving their treatment objectives. However, for those whose treatment plans have recently changed or who are struggling to meet their targets, more frequent testing—potentially every three months—may be necessary.
This proactive approach allows healthcare providers to make timely adjustments to treatment strategies, optimizing blood sugar control and minimizing the risk of complications. Have you ever wondered how often you should be checking your A1C? Statistics show that around 47.4% of adults with high blood sugar have A1C readings of 7.0% or above, indicating inadequate glycemic management. This highlights the pressing need for enhanced strategies to control blood sugar levels, as discussed in the case study titled ‘A1C Levels and Diabetes Complications.’ Furthermore, expert recommendations emphasize that regular A1C testing not only aids in tracking progress but also empowers you to take an active role in your health journey.
Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the Integrative Wellness Center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.”
To effectively monitor and enhance your progress, consider utilizing various tracking methods, such as fitness apps, journals, and pedometers, alongside regular A1C testing. Implementing SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—can significantly boost your focus and motivation. For example, you might set a goal to reduce your A1C values by a certain percentage within a designated timeframe.
Research suggests that goal-setting persistence scores can positively influence performance, showcasing the effectiveness of structured goal-setting in diabetes care. Many patients find that consistently monitoring their A1C levels leads to tailored interventions that improve outcomes. By understanding your A1C metrics, you can work collaboratively with your healthcare provider to refine your management plan, enhancing your quality of life and reducing reliance on conventional medical interventions.
Moreover, recent conversations in the healthcare community highlight the necessity for enhanced surveillance and resource distribution for assessing HbA1c, further emphasizing the importance of regular A1C monitoring in today’s healthcare environment.
A Holistic Approach to Managing Your A1C and Diabetes
Effectively managing this condition requires a holistic approach that embraces various lifestyle factors, including diet, exercise, mental health, and consistent medical care. At Integrative Wellness Center, we understand that a balanced lifestyle is essential. This means consuming nutritious foods, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and ensuring adequate sleep. It’s important to recognize that in the U.S., 37% of adults were affected by prediabetes in 2012, with many undiagnosed. This highlights the prevalence of diabetes-related issues and the urgent need for lifestyle changes.
Many patients find that lifestyle changes can significantly influence A1C levels. Research indicates that those who adopt healthier habits experience better management of their condition and an enhanced quality of life.
Regular consultations with healthcare providers are vital. They offer valuable insights and resources that empower patients to take charge of their health. Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.” Our process includes detailed testing that goes beyond typical lab work, allowing us to create a customized plan specifically targeting the contributing factors of your condition.
For example, the HiPAPD model for managing blood sugar has proven effective in providing health training and support to underserved communities. This model exemplifies how holistic care can lead to better treatment outcomes for individuals with blood sugar issues, improving access to essential health services and promoting self-care.
Moreover, expert views underscore the importance of a comprehensive strategy for managing the condition. Recent studies suggest that holistic care services significantly enhance treatment outcomes for individuals facing blood sugar challenges. By concentrating on the interconnectedness of lifestyle factors, patients can achieve improved management of their A1C readings and enhance their overall well-being.
Engaging in community seminars and utilizing educational materials can further enhance understanding and foster a supportive environment for those navigating their diabetes journey. Ultimately, this multifaceted strategy not only aids in managing A1C levels but also promotes a higher quality of life, reducing reliance on conventional medical interventions. As one patient shared, “Joining Integrative Wellness Center was the best decision I ever made; I feel healthier and more empowered than ever before!
Conclusion
Regular A1C monitoring is truly a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. It provides essential insights into long-term blood sugar control and guides treatment decisions. In this article, we’ve explored the significance of the A1C test, emphasizing its vital role in:
- Diagnosing diabetes
- Monitoring treatment efficacy
- Informing patient health strategies
Understanding A1C levels, interpreting results accurately, and setting personalized goals are crucial steps that empower you to take charge of your health journey.
It’s important to recognize that a holistic approach to diabetes management is essential. This means integrating lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and personalized healthcare strategies. Such an approach not only enhances A1C management but also supports your overall well-being, addressing the multifaceted nature of diabetes. Many patients find that by adopting practical tips—like enjoying a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress—they can significantly lower their A1C levels and improve their quality of life.
As diabetes care continues to evolve, the integration of innovative methodologies alongside traditional A1C monitoring will further enhance patient outcomes. By fostering an environment of education and support, you can navigate your diabetes journey with confidence. This ultimately leads to better health and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions. Remember, taking proactive steps today can pave the way for a healthier tomorrow, reinforcing the importance of staying informed and engaged in your personal health management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and what does it measure?
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C test, measures the average glucose levels in the blood over the past two to three months. It evaluates the percentage of hemoglobin that is glycated, providing insights into long-term blood sugar control.
Why is the A1C test important for individuals with high blood sugar?
The A1C test is crucial for individuals with high blood sugar as it helps identify blood sugar disorders and tracks the effectiveness of treatment strategies. A higher A1C percentage indicates inadequate blood sugar control, which can lead to serious health complications.
How is the A1C test conducted?
The A1C test is a simple procedure that involves collecting a blood sample, either from a vein or through a finger prick. The sample is analyzed in a laboratory to measure the percentage of glycated hemoglobin.
Do patients need to fast before taking the A1C test?
No, the A1C test does not require fasting, making it a convenient option for patients.
What do the A1C test results indicate?
A normal A1C result is below 5.7%. A result between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms a diabetes diagnosis. Each percentage point increase in A1C correlates with a rise in average blood glucose levels.
How can patients use A1C results to manage their health?
Patients can use A1C results to assess their blood sugar control and make necessary adjustments to their treatment plans. Setting specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals can help improve blood sugar control.
What advancements have been made in A1C testing technology?
Recent advancements in testing technology have improved the precision and availability of A1C testing, allowing for more frequent monitoring and better management strategies.
How does the A1C test relate to pregnancy?
The A1C test is important for identifying abnormal glucose metabolism in individuals planning for pregnancy. It is recommended to test for undiagnosed prediabetes or blood sugar issues during pregnancy, especially at 24-28 weeks of gestation for at-risk individuals.
What are some lifestyle changes that can help manage A1C levels?
Effective lifestyle changes include balanced nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, and utilizing tools like fitness apps or journals to monitor progress and set goals.
How do A1C levels relate to other health conditions?
Studies have shown that many adults with high blood sugar also have elevated blood pressure, indicating the need for coordinated treatment strategies that address both glycemic control and cardiovascular health.