Overview
Understanding the A1C diabetes cutoff is essential for effective diabetes management. Did you know that levels below 5.7% are considered normal? Conversely, a level of 6.5% or above confirms a diabetes diagnosis.
It’s important to recognize that these cutoff values are not just numbers; they empower you to take control of your health. By being informed, you can work with your healthcare provider to create personalized treatment plans that suit your needs. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the risk of serious complications associated with diabetes.
Remember, you are not alone on this journey, and understanding these values is a crucial step toward a healthier life.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, A1C testing is a cornerstone that offers vital insights into blood sugar control over time. This comprehensive blood test not only helps diagnose diabetes and prediabetes but also serves as an essential tool for monitoring how well treatments are working. It’s important to recognize that understanding A1C levels is crucial, as they guide personalized management strategies that can significantly lower the risk of serious complications.
Many patients find that as they navigate their health journeys, lifestyle factors—such as diet, exercise, and stress management—play a significant role in these important measurements. With the growing focus on holistic health solutions, the significance of effective A1C management cannot be overstated. It promises a better quality of life for those living with diabetes, and there is hope in knowing that small changes can lead to meaningful improvements.
Define A1C: Understanding the Diabetes Cutoff Test
A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, is an important blood test that assesses the average blood glucose concentrations over the past two to three months. Expressed as a percentage, it indicates the proportion of hemoglobin molecules that have glucose attached. This assessment is crucial for identifying blood sugar issues and prediabetes, as well as for tracking the effectiveness of diabetes control approaches.
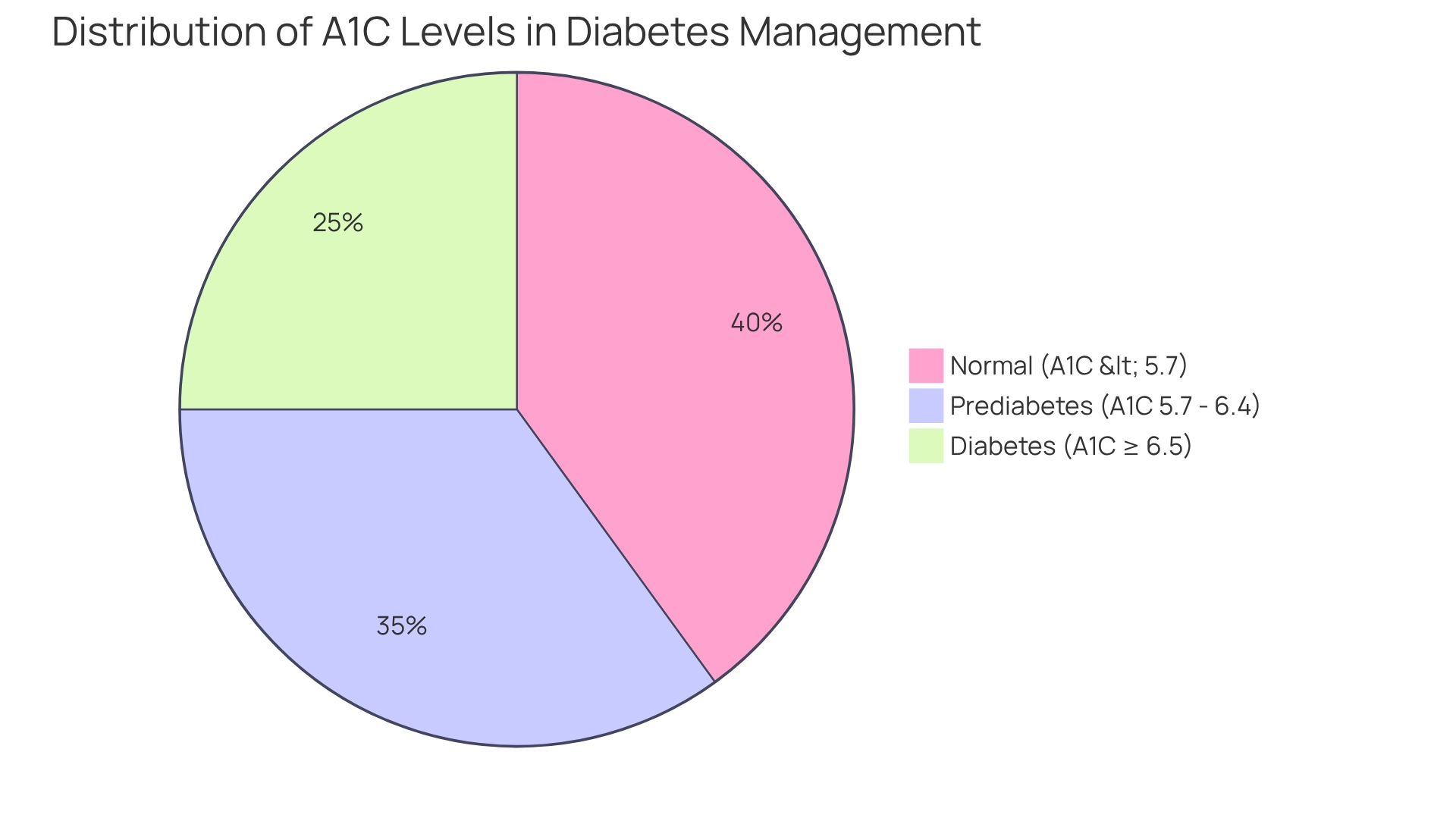
It’s important to recognize that the A1C diabetes cutoff under 5.7% is regarded as normal, while levels ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes, and levels of 6.5% or greater confirm a diagnosis of the condition. Many patients find that understanding these levels can be empowering.
Diabetes is among the primary contributors to cardiovascular disease, blindness, kidney failure, and lower limb amputation, which emphasizes the significance of effective control through tools such as the A1C test and the A1C diabetes cutoff. Unlike daily glucose monitoring, the A1C test provides a broader perspective on blood sugar regulation, rendering it essential for long-term health oversight.
Current statistics indicate that a significant percentage of patients with the condition utilize A1C testing to guide their treatment plans, underscoring its importance in effective care. Furthermore, suggestions for testing frequency according to age and risk factors can assist patients in staying on course with their strategies.
Amidst concerns about hospital safety, such as the alarming rates of incorrect medications and infections, Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes the need for holistic health solutions. He states, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.”
This tailored method for controlling blood sugar not only tackles the clinical elements but also enables patients to implement informed lifestyle adjustments that are essential for reversing Type 2 diabetes. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to support you every step of the way.
Explain the Importance of A1C Levels in Diabetes Management
A1C readings play an essential role in blood sugar care, serving as a vital sign of a patient’s average glucose regulation over time. For most adults with diabetes, maintaining an A1C measurement below the A1C diabetes cutoff of 7% is advised. It’s important to recognize that higher figures, exceeding the A1C diabetes cutoff, correlate with an increased risk of serious complications, including cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and retinopathy. Regular A1C testing is crucial, enabling healthcare providers to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment plans and make necessary adjustments to optimize patient outcomes.
Comprehending A1C values empowers patients to engage actively in their health oversight. This knowledge fosters a sense of control, encouraging adherence to lifestyle changes and medication regimens. Many patients find that maintaining A1C measurements below the A1C diabetes cutoff of 7% can significantly decrease the likelihood of complications, emphasizing the necessity of regular monitoring.
Real-life examples illustrate the impact of effective A1C management. Patients who use continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) often report greater freedom in managing their diets and schedules, as these devices provide timely insights into their blood sugar readings. A recent study promoting increased Medicaid coverage of CGMs emphasizes the positive reception and advantages noted in a Medicaid group. This indicates that wider access to these devices could greatly enhance health outcomes and lessen health disparities among marginalized communities.
As we look toward 2025, the focus on tracking the A1C diabetes cutoff measurements remains vital. Expert views continue to emphasize the significance of the A1C diabetes cutoff in diabetes care. By prioritizing A1C monitoring, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce reliance on conventional medical interventions. Transformative patient experiences from Dr. Jason Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program further illustrate this point. One participant shared, “I lost 55 lbs. My A1C began at 9.1 and after 8 months it is now 5.7,” highlighting the significant effect of effective A1C control. Another noted, “I feel so much better… I lost a lot of weight, have more energy and feel great,” emphasizing the holistic benefits of addressing A1C levels. As one participant succinctly put it, “It’s given me freedom to not have to worry about food. I can eat at certain times and I know when to eat and what to eat,” illustrating the transformative impact of effective A1C management.
Discuss A1C Cutoff Values: Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment
A1C test results are classified into particular ranges that play a vital role in diagnosing and managing blood sugar conditions, particularly with respect to the A1C diabetes cutoff. If your A1C level is below 5.7%, it is considered normal. However, levels between 5.7% and 6.4% suggest prediabetes, which indicates an elevated risk for developing type 2 diabetes. A diagnosis of diabetes is confirmed with an A1C level at or above the A1C diabetes cutoff of 6.5%. For those diagnosed, treatment goals typically target an A1C of less than 7%.
It’s important to recognize that these targets can vary significantly based on factors such as age, overall health, and individual circumstances, particularly the A1C diabetes cutoff. Understanding these cutoff values is essential for healthcare providers in crafting personalized treatment plans that effectively manage blood sugar levels and mitigate the risk of complications. Many patients find that early intervention is crucial; recent statistics indicate that approximately 70% of prediabetes patients fall within the A1C range of 5.7% to 6.4%.
The implications of A1C test results extend beyond mere numbers; they guide treatment strategies and inform lifestyle changes. For instance, moderate exercise for at least 30 minutes daily, five days a week, is essential for preventing diabetes and can greatly influence A1C levels, particularly as the understanding of the A1C diabetes cutoff values continues to evolve into 2025, influencing care for diabetes.
Specialists emphasize the necessity for customized approaches that take into account individual patient profiles. This personalized focus not only enhances the effectiveness of treatment plans but also empowers patients to take an active role in managing their health. Dr. Shumard arranges seminars and events to engage the community, offering free educational materials, including his publications on blood sugar management and thyroid wellness. This effort significantly improves community awareness and understanding of chronic health matters.
Patients are also encouraged to consult their healthcare providers about Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) to determine their suitability for managing blood sugar.
Highlighting a comprehensive lifestyle strategy—encompassing a balanced diet rich in local produce, consistent outdoor activity, and community support—can significantly influence the management of type 2 diabetes. By doing so, individuals can experience enhanced health outcomes and a better quality of life. Remember, you are not alone on this journey, and with the right support and resources, positive change is within reach.
Explore Lifestyle Factors Affecting A1C Levels and Health Outcomes
A range of lifestyle factors greatly influence A1C measurements and the A1C diabetes cutoff, impacting overall health results for individuals with diabetes. It’s important to recognize that diet plays a crucial role; a balanced consumption of whole foods and fiber, while reducing refined sugars, is vital for stabilizing blood sugar. Many patients find that consistent physical activity serves an essential function, as exercise enhances insulin sensitivity and aids in weight management, both of which are important for reducing A1C values.
To effectively start a walking routine, individuals should refer to the walking program pdf. Evaluating your current fitness level and establishing realistic goals, such as committing to a daily walk of 10-15 minutes, can make a significant difference. Selecting an appropriate environment is crucial; ensure it aligns with your safety and comfort preferences, whether that be indoors or outdoors. Developing a consistent schedule is imperative, with an emphasis on gradually increasing both the duration and frequency of walks over time.
Tracking progress is also highly beneficial; utilizing a journal or an app can help maintain motivation and allow you to celebrate achievements along the way. Current statistics indicate that only about 23% of diabetes patients engage in regular physical activity, highlighting a significant area for improvement. Additionally, incorporating stress reduction methods, including mindfulness practices and ensuring sufficient sleep, can positively impact blood sugar regulation.
For example, a case study on prediabetes control showed that patients who tracked their A1C, blood pressure, and cholesterol readings were enabled to take control of their health, resulting in better outcomes. As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.”
Moreover, average medical expenditures for people with diagnosed diabetes are 2.6 times higher than expenditures would be in the absence of diabetes, underscoring the financial implications of poor A1C management. By adopting healthier lifestyle habits, including a structured walking program as outlined in the walking program pdf, individuals can enhance their A1C levels and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, ensuring they remain below the A1C diabetes cutoff. Ultimately, this approach fosters better health and well-being.
Conclusion
Effective management of A1C levels is crucial for those facing the challenges of diabetes. It’s important to recognize that A1C testing is not just a medical procedure; it is a vital tool for diagnosing diabetes, monitoring treatment effectiveness, and guiding personalized management strategies. Understanding A1C cutoff values empowers both patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions that can significantly lower the risk of serious complications associated with diabetes.
Many patients find that maintaining A1C levels below 7% can lead to improved health outcomes. This highlights the importance of regular testing and lifestyle modifications. Integrating a balanced diet, consistent physical activity, and stress management techniques can profoundly impact A1C levels and overall well-being. Real-life success stories illustrate how effective A1C management not only improves health metrics but also enhances quality of life, allowing individuals to regain control over their health.
Ultimately, the journey towards optimal A1C management is a collaborative effort that requires active participation from patients, healthcare providers, and the community. By prioritizing education, personalized care, and lifestyle changes, individuals can achieve better health outcomes and reduce the burden of diabetes. Embracing these strategies fosters a healthier future and instills hope for those living with diabetes, proving that meaningful improvements are within reach through informed and proactive management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and what does it measure?
The A1C test, or glycated hemoglobin test, assesses the average blood glucose concentrations over the past two to three months. It indicates the proportion of hemoglobin molecules that have glucose attached, expressed as a percentage.
What do the A1C levels indicate regarding diabetes?
A1C levels under 5.7% are considered normal, levels from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes, and levels of 6.5% or greater confirm a diagnosis of diabetes.
Why is the A1C test important for diabetes management?
The A1C test is crucial for identifying blood sugar issues, tracking the effectiveness of diabetes control approaches, and providing a broader perspective on blood sugar regulation compared to daily glucose monitoring.
How does diabetes impact health, and why is A1C testing significant?
Diabetes is a major contributor to cardiovascular disease, blindness, kidney failure, and lower limb amputation. A1C testing is significant as it helps in effective control of blood sugar, which is essential for long-term health oversight.
How often should A1C testing be done?
The frequency of A1C testing can vary based on age and risk factors, and it is suggested that patients consult their healthcare providers to determine the appropriate testing schedule.
What is Dr. Jason Shumard’s perspective on health solutions for diabetes patients?
Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes the need for holistic health solutions, providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools to reclaim their health and well-being.
How can patients manage their diabetes beyond clinical measures?
Patients can implement informed lifestyle adjustments that are essential for reversing Type 2 diabetes, supported by resources available to assist them in their journey.