Overview
The article provides a comprehensive step-by-step guide on how to follow the American Diabetes Association recommended diet, emphasizing the importance of whole foods, moderation, and personalized meal planning. It supports this by outlining key dietary principles, practical meal planning strategies, and the significance of physical activity, all aimed at improving blood sugar management and overall health outcomes for individuals with diabetes.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of diabetes management requires a multifaceted approach, particularly when it comes to nutrition. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) diet serves as a foundational framework for individuals seeking to balance their dietary choices with effective blood sugar control. By emphasizing whole foods, fiber intake, and personalized meal planning, this diet empowers individuals to take charge of their health.
Moreover, understanding the role of carbohydrates, practicing portion control, and incorporating regular physical activity are essential components that can significantly enhance diabetes management.
This article delves into the key principles of the ADA diet, practical strategies for meal planning, and actionable tips for integrating physical activity, all aimed at fostering better health outcomes for those living with diabetes.
Understanding the American Diabetes Association Diet Principles
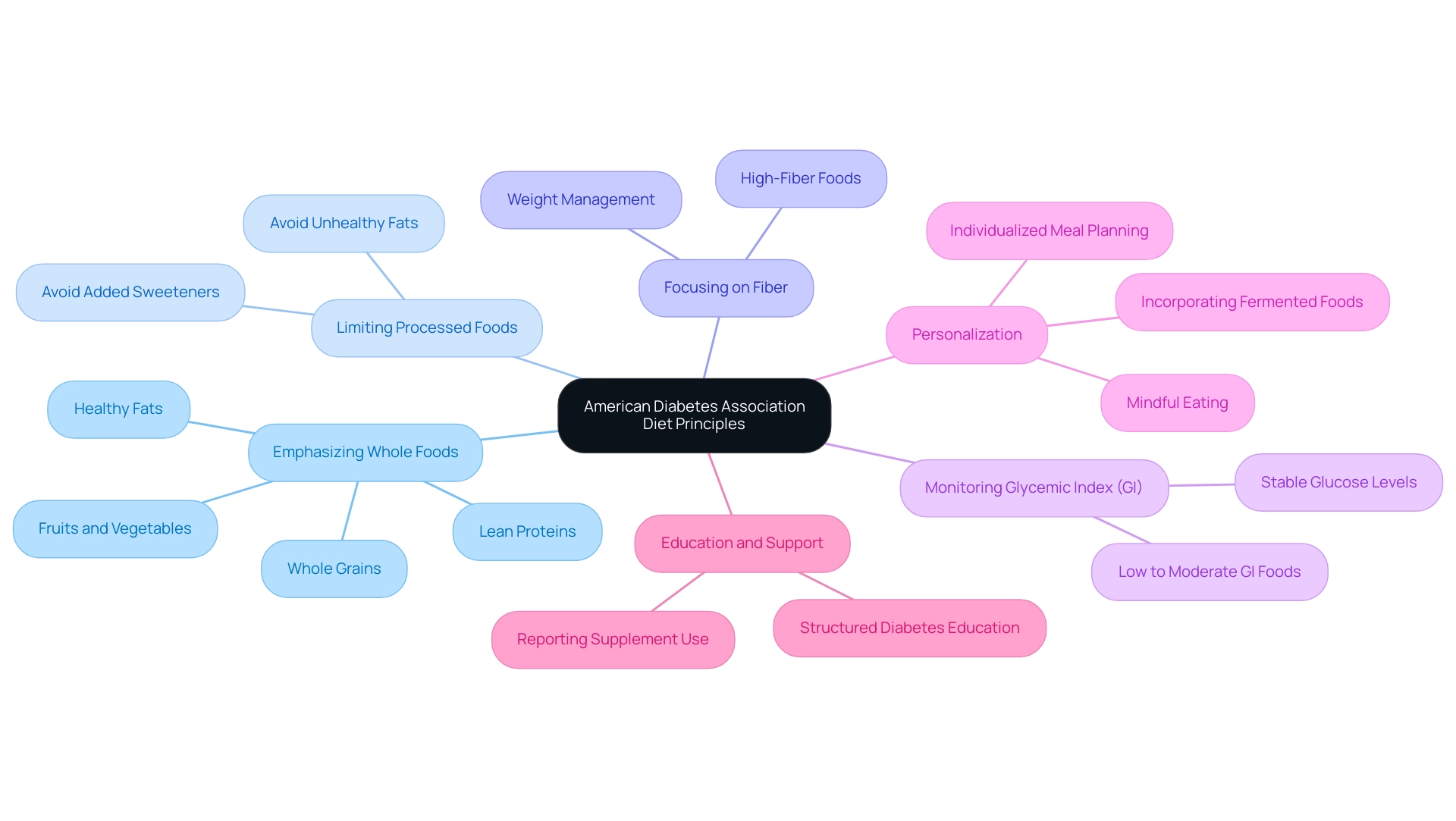
The American Diabetes Association recommended diet advocates for a comprehensive and balanced nutritional framework, fundamentally centered on whole foods, nutrient density, and moderation. The key principles of this diet include:
- Emphasizing Whole Foods: Prioritize the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, which serve as the foundation for a nutritious diet and play a crucial role in blood sugar regulation.
- Limiting Processed Foods: It is crucial to avoid foods that are high in added sweeteners and unhealthy fats, as these can cause significant spikes in glucose levels, potentially exacerbating insulin resistance.
- Focusing on Fiber: Including high-fiber foods is crucial, as they not only help regulate glucose levels but also enhance sensations of fullness, assisting in weight management and overall health.
- Monitoring Glycemic Index (GI): Choosing foods with a low to moderate glycemic index is essential to reduce sudden glucose fluctuations, thereby promoting stable levels.
- Personalization: Individualized meal planning is vital, allowing for the diet to be tailored to specific preferences and nutritional requirements, which enhances both sustainability and adherence. This approach empowers individuals to take control of their health management through informed dietary choices.
Alongside these principles, think about incorporating lesser-known strategies like mindful eating practices, which can improve awareness of hunger and fullness signals, and the addition of fermented foods to promote gut wellness, which may affect blood sugar regulation. Furthermore, regular physical activity, even in short bursts throughout the day, can significantly improve insulin sensitivity.
These principles emphasize the significance of informed dietary decisions that correspond with individual wellness goals and efficient management of blood sugar levels. Recent studies emphasize that adherence to the American Diabetes Association recommended diet is critical for achieving optimal health outcomes; however, it is concerning that many individuals with blood sugar issues do not receive structured education or nutrition therapy, with only about half reporting any form of education related to their condition. This highlights the need for comprehensive education to support effective management.
Additionally, a case study titled ‘Micronutrients and Herbal Supplements’ indicates that there is no clear evidence supporting vitamin or mineral supplementation for individuals with this condition without deficiencies. Routine use of antioxidants and certain micronutrients is not advised due to lack of efficacy and potential harm. Therefore, individualized meal planning is recommended to meet dietary needs, and patients should report supplement use to healthcare providers.
Furthermore, as stated by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, one elevated value can be used for diagnosis, emphasizing the importance of monitoring blood sugar levels. Grasping and implementing these dietary principles can greatly influence the management of this condition, promoting better health and well-being.
Practical Meal Planning Strategies for Diabetes Management
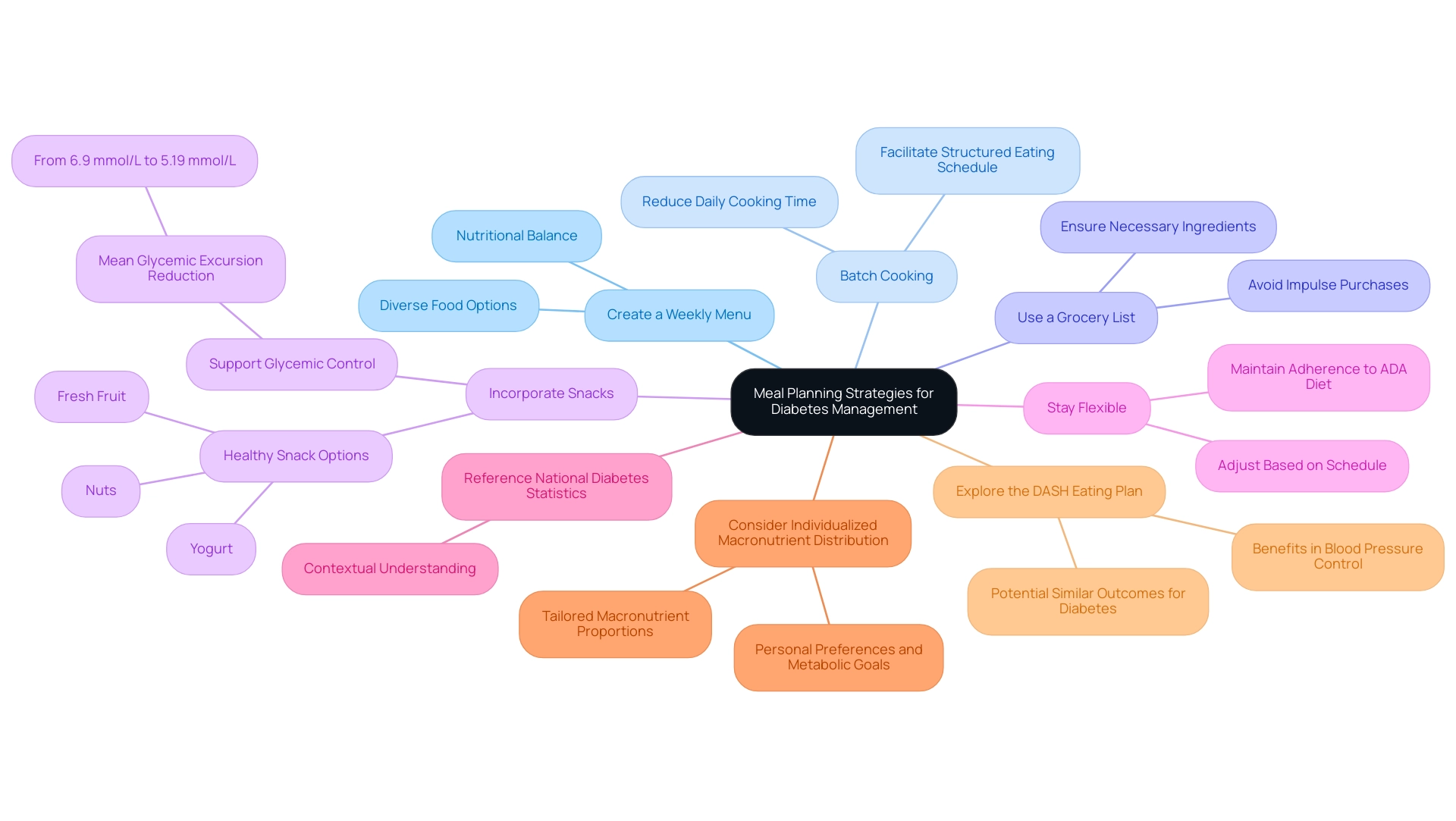
To effectively implement the American Diabetes Association (ADA) diet, consider the following meal planning strategies:
- Create a Weekly Menu: Outline meals for the week, ensuring a diverse array of foods that align with ADA principles. This approach not only aids in nutritional balance but also supports the American Diabetes Association recommended diet for more effective management of glycemic levels.
- Batch Cooking: Preparing large quantities of healthy meals in advance can significantly reduce daily cooking time and ensures access to nutritious options. Studies indicate that meal frequency and timing are crucial elements in managing blood sugar levels; therefore, having ready-made meals can facilitate adherence to a structured eating schedule.
- Use a Grocery List: Planning your grocery shopping around your menu is essential for avoiding impulse purchases and ensuring that all necessary ingredients are at hand. This strategy promotes mindful eating and is consistent with the American Diabetes Association recommended diet, which helps maintain dietary goals.
- Incorporate Snacks: It is beneficial to plan for healthy snacks, such as nuts, yogurt, or fresh fruit, which can help maintain energy levels and prevent blood sugar dips. Research shows that integrating planned snacking can further support glycemic control, as demonstrated by a reduction in the mean glycemic excursion amplitude from 6.9 mmol/L to 5.19 mmol/L with evening snacks.
- Stay Flexible: Allow for adjustments based on your daily schedule or cravings while maintaining adherence to the American Diabetes Association recommended diet. This flexibility is essential, as Roxana Paola Gomez-Ruiz highlights the importance of meal timing and frequency in managing type 2.
- Reference the National Diabetes Statistics Report: Understanding the broader context of prevalence and management strategies can reinforce the importance of meal planning in achieving better wellness outcomes.
- Consider Individualized Macronutrient Distribution: As emphasized in the case study titled ‘Macronutrient Distribution for Diabetes Management,’ there is no single ideal macronutrient distribution for all individuals with this condition. Tailoring macronutrient proportions based on personal preferences and metabolic goals can enhance dietary adherence and effectiveness.
- Explore the DASH Eating Plan: The DASH eating plan has demonstrated advantages in regulating blood pressure and may produce similar outcomes for individuals with blood sugar issues, highlighting the interconnectedness of dietary strategies in managing overall well-being.
By adopting these strategies, individuals can simplify their meal preparation process and enhance their commitment to the recommended dietary patterns, ultimately supporting better health outcomes.
Managing Carbohydrates: Choosing the Right Foods
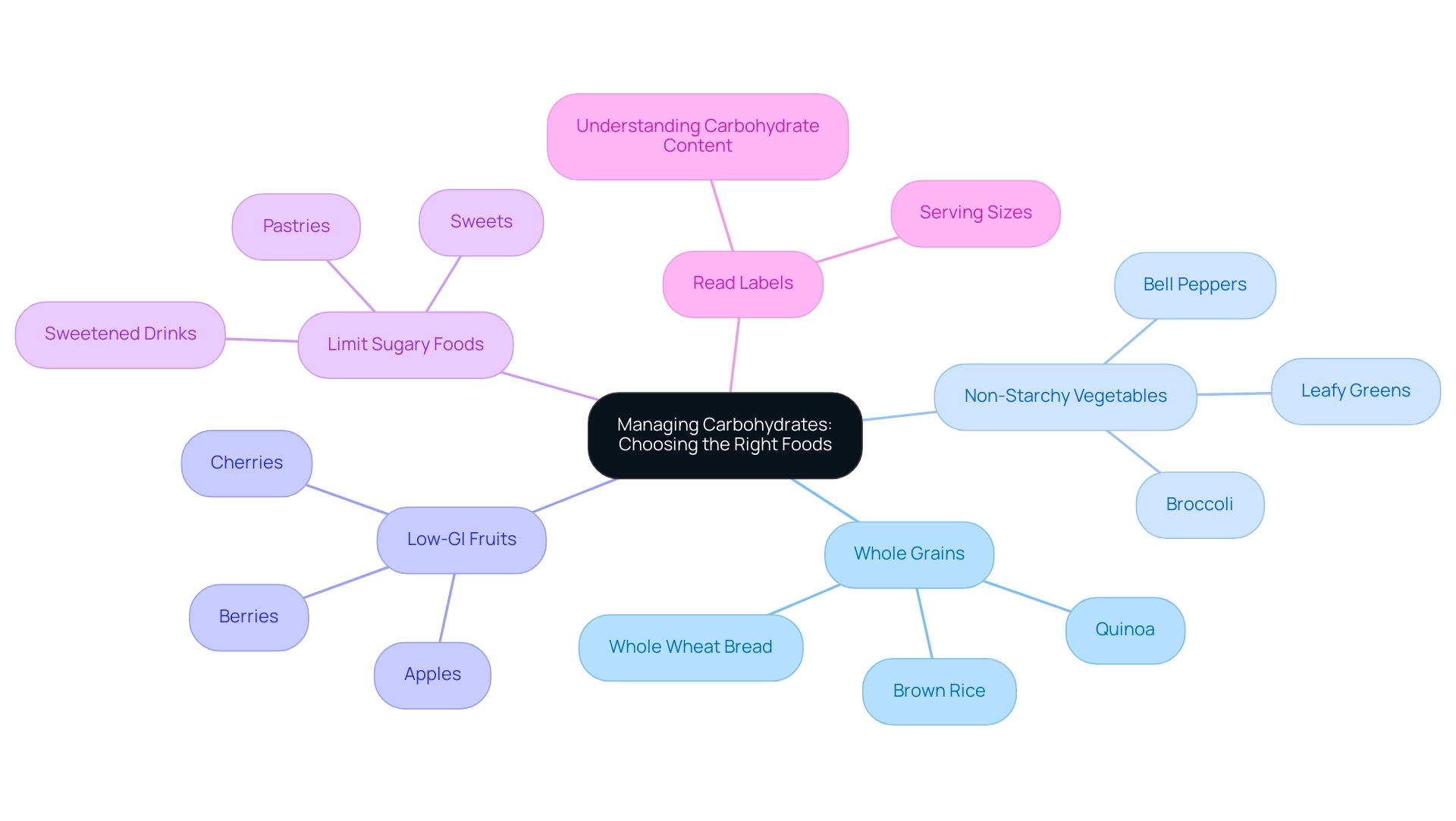
Effectively managing carbohydrates is a key component of the American Diabetes Association recommended diet, which requires not only counting them but also making informed choices regarding the types consumed. The following guidelines can assist individuals with type 2 diabetes in making healthier dietary selections:
- Opt for Whole Grains: Emphasize whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread instead of refined grains. Whole grains offer vital nutrients and fiber that aid in improved glucose regulation.
- Incorporate Non-Starchy Vegetables: Prioritize non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, and bell peppers. These options are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, assisting in maintaining stable glucose levels.
- Select Low-GI Fruits: Choose fruits with a lower glycemic index (GI), such as berries, cherries, and apples. Unlike tropical fruits such as bananas and pineapples, these options can assist in minimizing glucose spikes.
- Limit Sugary Foods: It is essential to decrease the intake of sweets, pastries, and sweetened drinks. These items can cause rapid increases in blood sugar levels, which may be detrimental to diabetes management.
- Read Labels: Becoming familiar with nutrition labels is essential for understanding carbohydrate content and serving sizes. This knowledge empowers individuals to make better dietary choices, and by following the American Diabetes Association recommended diet principles, individuals can significantly improve their carbohydrate management, thereby enhancing glycemic control.
Significantly, research indicates a relationship between carbohydrate intake and wellness outcomes; a study reported a mortality incidence of 7.2 per 1000 person-years among individuals consuming 77.2% of their energy from carbohydrates. The authors of this study, Seidelmann et al., noted a U-shaped curve between carbohydrate intake and mortality, emphasizing the need for balanced consumption. Furthermore, findings from a dietary assessment revealed that diabetic patients had a higher daily intake of grains, particularly Basmati rice, which accounted for 43.1% of the total carbohydrate intake. This underscores the importance of dietary modifications for better health outcomes, particularly the reduction of Basmati rice consumption among these patients.
Portion Control and the Plate Method for Balanced Meals
The Plate Method serves as an effective tool for visualizing and managing portion sizes, crucial for individuals with blood sugar concerns. This approach is not only straightforward but also encourages balanced meal composition, crucial for regulating glucose levels and reducing the risk of complications. For instance, M.L., a patient who has been diabetic for 10 years, shared, ‘When I started this program, the Doctor gave great personal attention and care in helping fix my condition.’
M.L. experienced remarkable results after adopting the Plate Method as part of a comprehensive program at the Integrative Wellness Center. They lost 55 lbs, and their A1C improved from 9.1 to 5.7, with fasting glucose dropping from 133 to 85, showcasing the potential for reversing type 2 diabetes through personalized care.
Here’s how to implement the Plate Method:
-
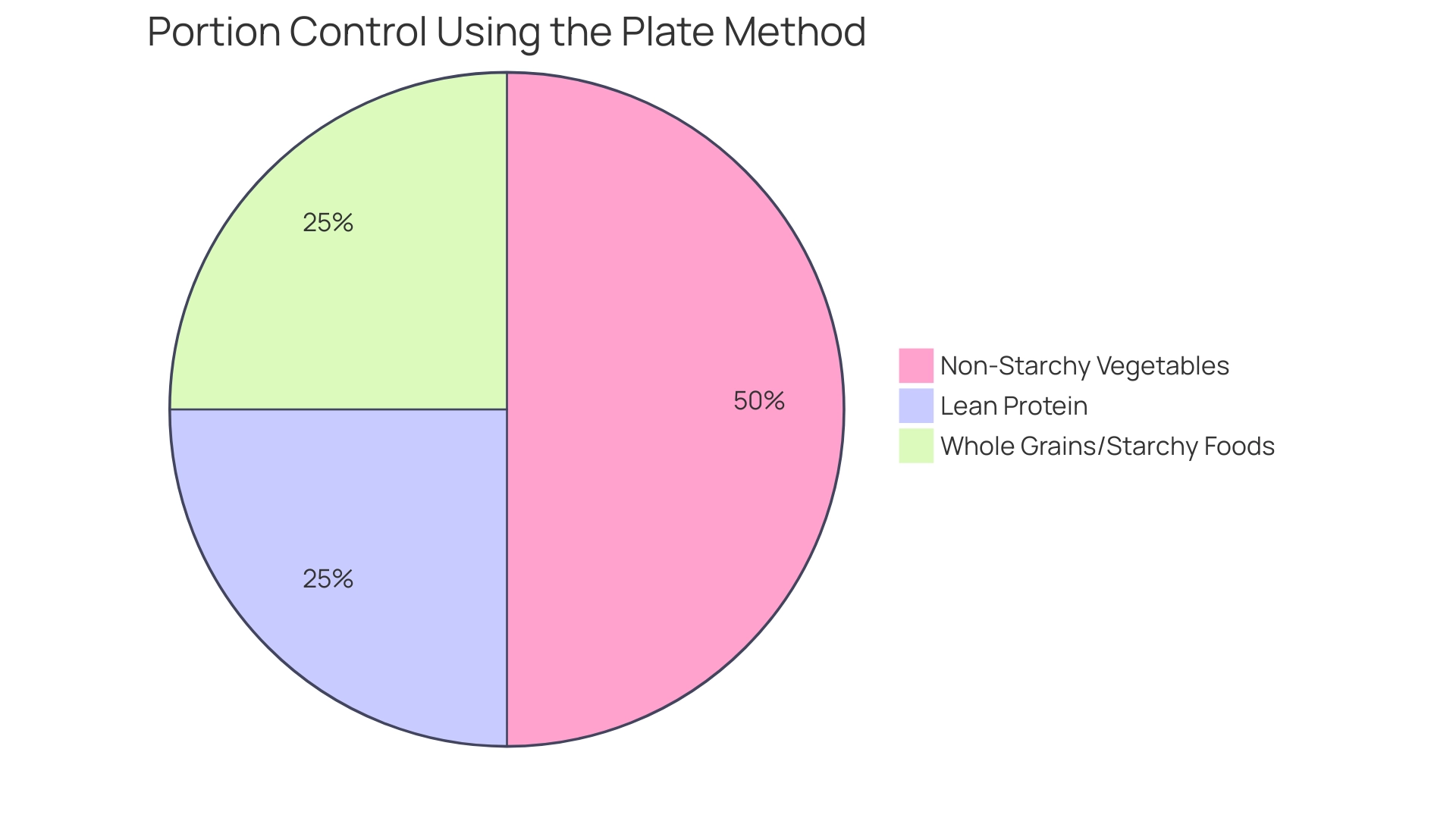
Divide Your Plate: Utilize a standard dinner plate and section it as follows:
-
50% Non-Starchy Vegetables: Fill half of your plate with a colorful array of non-starchy vegetables such as leafy greens, peppers, and broccoli.
This ensures a low-calorie, nutrient-dense portion that aids in blood sugar management.
-
25% Lean Protein: Dedicate a quarter of your plate to lean protein sources, which can include chicken, fish, tofu, or legumes. Protein is vital for satiety and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
-
25% Whole Grains/Starchy Foods: Reserve the remaining quarter for whole grains or starchy vegetables like brown rice or sweet potatoes. These provide essential carbohydrates that should be consumed in moderation.
-
-
Mindful Eating: It is essential to remain attuned to hunger cues and eat slowly, allowing your body to signal when it is satisfied.
This practice not only enhances enjoyment but also helps prevent overeating.
-
Avoid Distractions: During meals, minimize distractions such as television or smartphones to focus entirely on your food and portion sizes. This approach encourages a more mindful eating experience, which is associated with improved management of blood sugar levels.
By utilizing the Plate Method, individuals can create meals that align with the American Diabetes Association recommended diet while enjoying a variety of foods. This approach is particularly relevant given that the awareness of prediabetes among certain demographics is increasing; from 2017 to 2020, the awareness rate among Hispanic adults was reported at 20.9%. As Dr. T A Wadden, a consultant with BMIQ, observes, ‘The Plate Method is a practical approach that aids individuals with blood sugar issues in understanding portion sizes and making healthier food choices.’
Moreover, incorporating effective portion control techniques, such as the Plate Method, in accordance with the American Diabetes Association recommended diet, can greatly influence overall wellness results for individuals managing blood sugar levels. M.L. concluded, ‘The personal attention I received made all the difference in my journey towards better health.
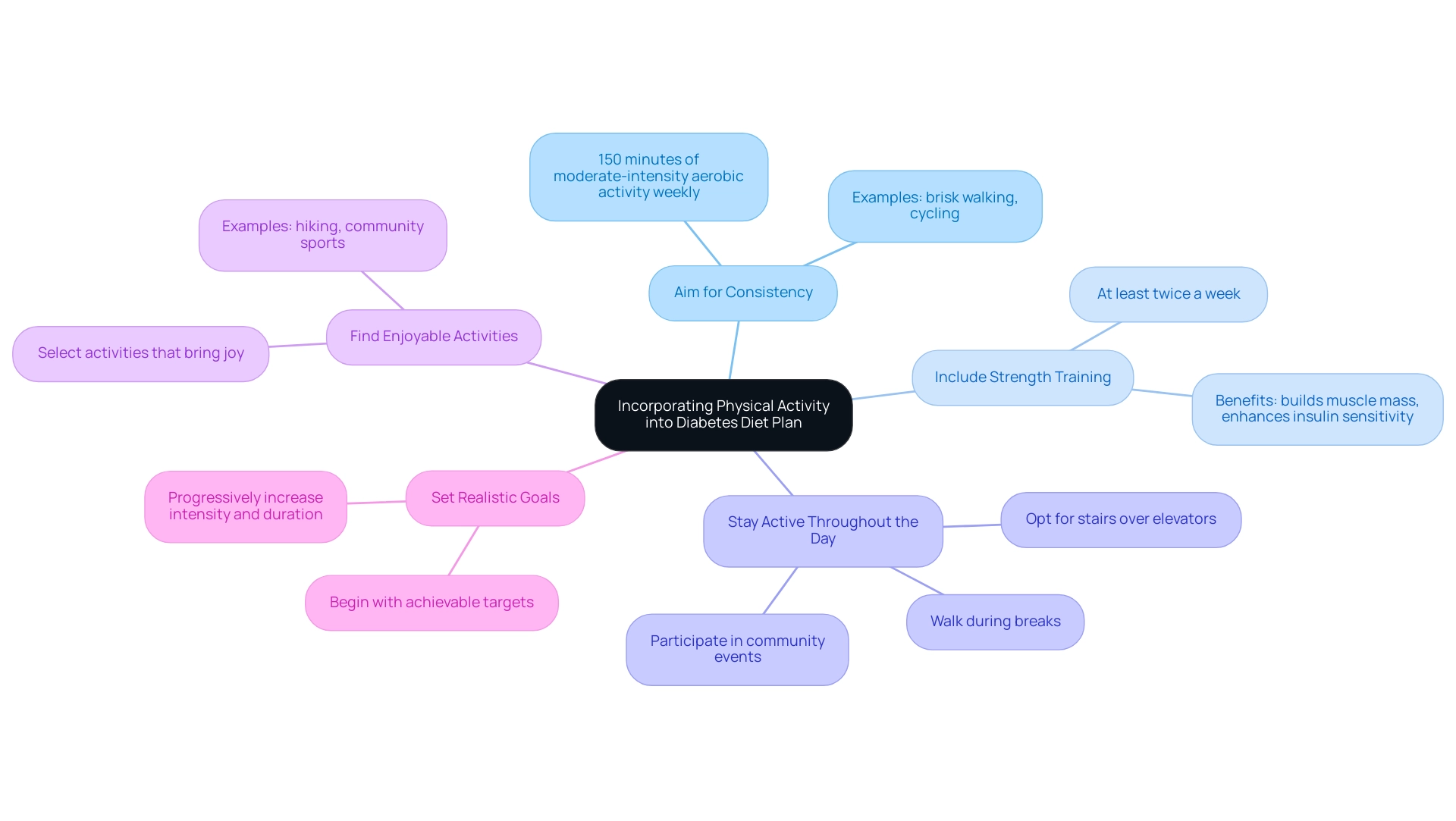
Incorporating Physical Activity into Your Diabetes Diet Plan
Incorporating regular physical activity is essential for effective health management, especially in communities like San Marcos, CA, where outdoor fitness opportunities abound. Here are several strategies to consider, including some lesser-known power-plays that can enhance your approach to reversing blood sugar issues:
- Aim for Consistency: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, such as brisk walking in local parks or cycling along scenic routes, to reap the metabolic benefits crucial for glycemic control.
- Include Strength Training: Undertaking strength training exercises at least twice a week is vital for building muscle mass and enhancing insulin sensitivity, both of which are key factors in managing blood sugar levels.
- Stay Active Throughout the Day: Seek opportunities to increase daily activity levels, such as opting for stairs over elevators, walking during breaks, or performing household chores, to maintain an active lifestyle. Community events and group exercises can also foster a supportive environment.
- Find Enjoyable Activities: Selecting physical activities that bring enjoyment, such as hiking local trails or participating in community sports, can significantly improve adherence to exercise routines, making it easier to maintain consistency over time.
- Set Realistic Goals: Begin with achievable targets and progressively increase both the intensity and duration of your workouts as your fitness level improves, promoting long-term success and sustainability.
Additionally, consider incorporating mindfulness practices and community engagement as part of your routine. Recent studies have shown that just seven days of vigorous aerobic exercise can lead to meaningful improvements in glycemic control for adults with type 2 conditions, regardless of weight changes. Participants in such studies demonstrated decreased fasting plasma insulin levels and a remarkable 45% increase in insulin-stimulated glucose disposal, showcasing the immediate benefits of exercise for insulin sensitivity. However, it is important to note that the metabolic benefits from exercise are short-lived, fading within 48 to 96 hours, highlighting the necessity of ongoing exercise programs. In a study involving 1,446 participants with severe uncontrolled type 2 condition, these findings underscore the critical role of consistent physical activity in managing the illness. As Ann L Albright, PhD, RD, from the Division of Diabetes Translation at the CDC, states, ‘Regular physical activity is essential for controlling blood sugar levels and enhancing overall well-being.’ By integrating physical activity into their diabetes management plan and following the American Diabetes Association recommended diet, individuals can enhance their overall health and effectively control their condition.
Conclusion
Navigating diabetes management through diet is a crucial aspect that can significantly influence health outcomes. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) diet provides a comprehensive framework centered on whole foods, fiber intake, and personalized meal planning, empowering individuals to make informed dietary choices. Key principles include:
- Emphasizing whole foods
- Limiting processed options
- Focusing on fiber
- Monitoring the glycemic index
All of which contribute to better blood sugar control.
Practical meal planning strategies, such as:
- Creating weekly menus
- Batch cooking
- Utilizing the Plate Method
Enhance adherence to the ADA diet. These approaches simplify meal preparation while ensuring balanced nutrition. Additionally, effective carbohydrate management is essential; opting for whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, and low-GI fruits can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Incorporating regular physical activity is equally vital. Engaging in consistent aerobic and strength training exercises not only improves insulin sensitivity but also supports overall well-being. By integrating these dietary and physical activity strategies, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing their diabetes effectively.
Ultimately, understanding and applying these principles is essential for achieving optimal health outcomes. Comprehensive education and personalized care play a pivotal role in empowering those living with diabetes to take charge of their health, leading to improved quality of life and better management of their condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the foundation of the American Diabetes Association recommended diet?
The diet is centered on whole foods, nutrient density, and moderation, emphasizing the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Why is it important to limit processed foods in this diet?
Processed foods often contain high levels of added sweeteners and unhealthy fats, which can cause significant spikes in glucose levels and potentially worsen insulin resistance.
How does fiber play a role in managing blood sugar levels?
High-fiber foods help regulate glucose levels and enhance feelings of fullness, contributing to weight management and overall health.
What is the significance of monitoring the glycemic index (GI) in food choices?
Choosing foods with a low to moderate glycemic index helps reduce sudden glucose fluctuations, promoting stable blood sugar levels.
How can meal planning be personalized for individuals?
Individualized meal planning allows the diet to be tailored to personal preferences and nutritional needs, enhancing sustainability and adherence to the dietary guidelines.
What are some additional strategies to consider alongside the main dietary principles?
Incorporating mindful eating practices, adding fermented foods for gut health, and engaging in regular physical activity can further improve blood sugar regulation and overall health.
What is the importance of education regarding the American Diabetes Association diet?
Many individuals with blood sugar issues lack structured education or nutrition therapy, which is crucial for effective management and achieving optimal health outcomes.
Is there evidence supporting the use of vitamin or mineral supplements for individuals with diabetes?
There is no clear evidence supporting routine vitamin or mineral supplementation without deficiencies, and the use of certain antioxidants and micronutrients is not advised due to lack of efficacy and potential harm.
What are some recommended meal planning strategies for following the ADA diet?
Recommended strategies include creating a weekly menu, batch cooking, using a grocery list, incorporating healthy snacks, staying flexible, understanding diabetes statistics, tailoring macronutrient distribution, and exploring the DASH eating plan.
How can batch cooking benefit individuals following the ADA diet?
Batch cooking allows for preparing large quantities of healthy meals in advance, reducing daily cooking time and ensuring access to nutritious options, which supports adherence to a structured eating schedule.
Why is it beneficial to plan for snacks in the ADA diet?
Planning for healthy snacks helps maintain energy levels and prevent blood sugar dips, contributing to better glycemic control.
What does the DASH eating plan offer for individuals managing blood sugar issues?
The DASH eating plan has shown advantages in regulating blood pressure and may provide similar benefits for individuals with blood sugar concerns, highlighting the interconnectedness of dietary strategies.