Overview
The article focuses on the importance of understanding A1C formulas for effective diabetes management, highlighting their role in assessing average blood sugar levels over time. It emphasizes that maintaining an A1C level below 7% is crucial for reducing complications, supported by evidence showing that consistent monitoring and personalized care strategies can lead to better health outcomes for individuals with diabetes.
Introduction
Managing diabetes effectively hinges on understanding key metrics that influence health outcomes, with Hemoglobin A1C (A1C) standing out as a crucial indicator. This blood test provides a comprehensive view of average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, making it an essential tool for individuals with diabetes. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, awareness of A1C’s role in monitoring and managing the condition is more critical than ever.
This article delves into the significance of A1C testing, the methods for calculating and interpreting results, and the limitations that accompany its use. By exploring these facets, individuals can better navigate their diabetes management journey, making informed decisions that lead to improved health outcomes and reduced complications.
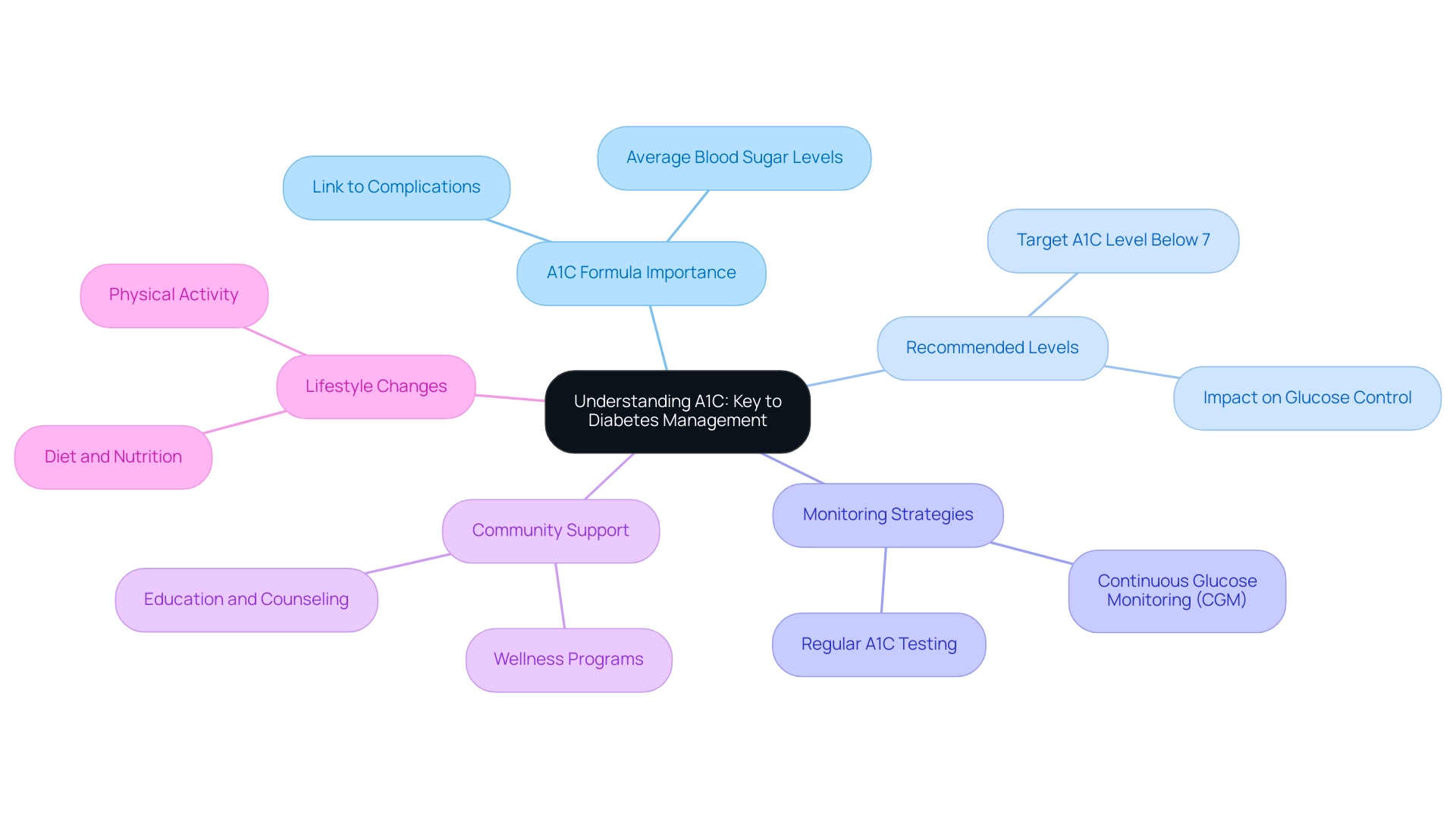
Understanding A1C: The Key to Diabetes Management
The a1c formula, commonly known as hemoglobin A1C, functions as an essential blood test that assesses the average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. This metric is especially crucial for managing type 2 conditions, as it provides a more extensive perspective on sugar regulation compared to daily tracking techniques. The American Diabetes Association suggests that adults with this condition strive to maintain an A1C level below 7%, as the A1C formula shows that reaching this target is linked to better glucose control and a lower risk of complications related to the illness.
Recent studies underscore the significance of the A1C formula in managing blood sugar levels, revealing that consistent monitoring of this formula can lead to better health outcomes. As Chuck Henderson, CEO of the ADA, emphasizes, ‘At the ADA, we are focused on enhancing the quality of care for anyone who lives with this condition, prediabetes, or who is at risk of developing it.’ Significantly, 1 out of every 3 individuals you encounter will experience some type of blood sugar condition in their lifetime, highlighting the necessity for tailored community wellness programs that provide education, nutrition, and support.
Furthermore, the recommendation for the continuation of personal continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use in hospitalized individuals with this condition underscores the importance of effective A1C monitoring. A comprehensive grasp of the A1C formula is crucial for individuals with blood sugar issues, as it enables them to make informed choices about their health and control strategies. The latest statistics indicate that awareness and monitoring of A1C levels remain critical in addressing the challenges posed by the condition, particularly in light of emerging data linking situations such as COVID-19 with new cases of type 1.
This evolving landscape necessitates that patients utilize the a1c formula as a foundational element in their management plans, embracing effective lifestyle changes that promote holistic health and community support to better navigate their diabetes journey and minimize potential complications. Register now to discover real solutions and take control of your health.
Calculating A1C: Formulas and Methods for Accurate Monitoring
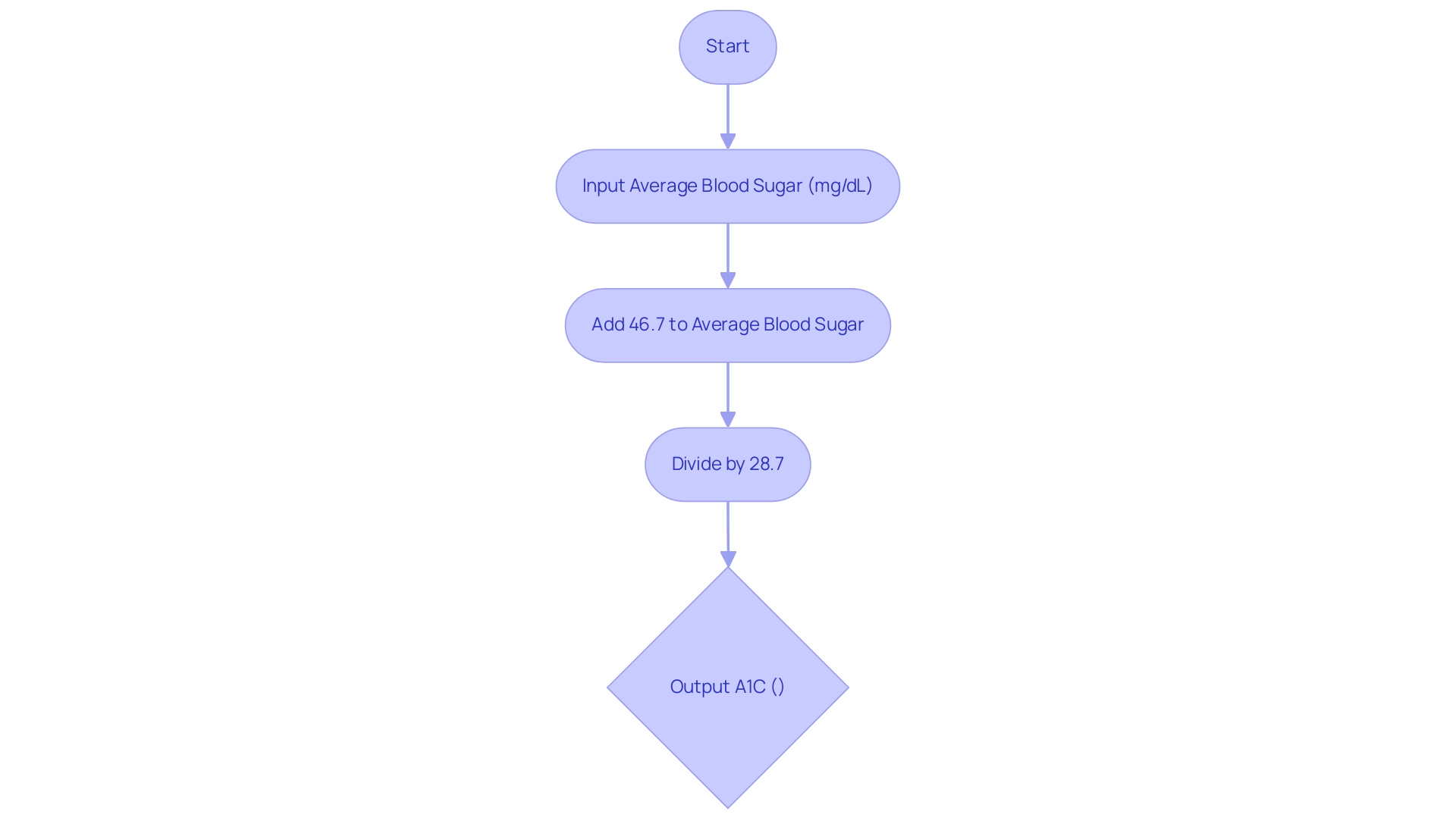
To determine the A1C percentage from average blood sugar levels, the A1C formula utilized is:
A1C (%) = (Average Blood Sugar (mg/dL) + 46.7) / 28.7.
For example, if an individual’s average blood sugar is recorded at 150 mg/dL, the calculation using the A1C formula would proceed as follows:
(150 + 46.7) / 28.7, resulting in an A1C value of approximately 6.84%.
This straightforward method enables Type 2 patients to monitor their condition effectively.
It’s essential to recognize that combining monitoring intervals achieved the lowest mean absolute error (95th percentile) of 6 mg/dL, highlighting the accuracy of the A1C formula. Insights from the case study titled ‘Clinical Implications of CGM and HbA Discrepancies’ emphasize that discrepancies between continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and HbA measurements can significantly impact treatment decisions. This emphasizes the significance of precise oversight in a comprehensive health strategy, which starts by reassessing the origin of the condition to tackle health at the fundamental level.
Furthermore, as pointed out by Vivian Fonseca in ‘Translating the hemoglobin A1C assay,’ comprehending the A1C formula is essential for effective control of blood sugar levels. By using different online calculators, patients can consistently carry out this calculation, enabling them to make informed modifications to their health plans. This proactive approach not only alleviates anxiety about potential complications but also fosters a deeper understanding of their health, aligning with the integrative philosophy at the Integrative Wellness Center and emphasizing the holistic regimen that supports overall well-being.
Interpreting A1C Results: What Do They Mean for Your Health?
The a1c formula indicates that A1C results serve as a critical indicator of blood sugar management. An A1C level below 5.7% is classified as normal, while levels ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% signify prediabetes. A diagnosis of the condition is indicated by an A1C of 6.5% or higher.
Current guidelines suggest that individuals with high blood sugar should aim for an A1C formula of less than 7%. However, it is essential to recognize that personalized targets may differ based on various factors, including age, health status, and individual risk profiles. At the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego, we concentrate on empowering patients by offering comprehensive insights and treatment options customized to their unique needs, which can result in transformative outcomes, including reversing type 2 conditions.
For instance, one of our patients, Jane, successfully reduced her A1C from 8.5% to 5.9% through our personalized care approach, which utilized the a1c formula, along with dietary changes and regular monitoring. Regular A1C monitoring using the A1C formula is essential, as it not only reflects average blood sugar levels over a three-month period but also provides a comprehensive view of how well blood sugar is being managed. This ongoing evaluation can prompt necessary adjustments in lifestyle or medication, ultimately enhancing health outcomes for individuals with blood sugar issues.
Significantly, recent research has emphasized that the chances of developing the condition are four times greater among individuals with both impaired fasting sugar levels and impaired sugar tolerance than either state alone, with odds ratios of 39.5 vs. 10.0 and 10.9, respectively. As policymakers and clinicians navigate the complexities of managing this condition, they will need to consider the trade-offs between performing both fasting plasma glucose (FPG) testing and the A1C formula testing alone or in combination to optimize patient outcomes. Furthermore, the economic expenses related to the condition in the U.S. reached $412.9 billion in 2022, highlighting the financial consequences of effective oversight and the essential role of the A1C formula in improving health results.
We invite you to explore our treatment options and see how we can help you achieve similar success.
Limitations of A1C Testing: Understanding Accuracy and Reliability
While the A1C formula acts as an important element in blood sugar control, it is vital to acknowledge its fundamental limitations. Certain medical conditions, such as anemia and hemoglobinopathies, can significantly skew A1C results, leading to inaccurate assessments of glycemic control. Moreover, the A1C test provides an average of blood sugar levels over the previous two to three months, which means it may not accurately reflect rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Incorporating daily blood glucose tracking along with A1C outcomes is essential for a thorough comprehension of a patient’s condition. The American Diabetes Association underscores this approach, recommending:
- A1C testing twice a year for stable patients
- A1C testing every three months for those experiencing medication changes or poor control
Significantly, a test needing only 2–10 µL of sample is essential for point-of-care (POC) A1C testing, improving its practicality and accessibility in blood sugar control.
Additionally, the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (IFCC) has developed a standardization approach that enhances the accuracy of A1C measurements, ensuring that manufacturers’ assays are traceable to primary reference materials. This progress enhances the National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program (NGSP) and highlights the necessity for a comprehensive strategy in health care, especially one that tackles underlying issues and empowers patients through a holistic approach. We begin by re-evaluating the origin of your condition, which is vital in tackling health at the root level and can assist in reducing the anxiety that comes with the concerns regarding the possible complications of your illness.
As noted by Elizabeth Selvin, the handling editor overseeing the manuscript review process, these insights are critical for ensuring precise management practices. Considering these factors, dependence only on the A1C formula can be deceptive; a comprehensive perspective that incorporates daily monitoring and an understanding of insulin resistance is essential for effective management. Furthermore, Klonoff DC et al. provide clinical practice guidelines that advocate for continuous blood sugar monitoring as an essential tool alongside A1C testing, aligning with the integrative wellness approach at Dr. Jason Shumard’s Integrative Wellness Center.
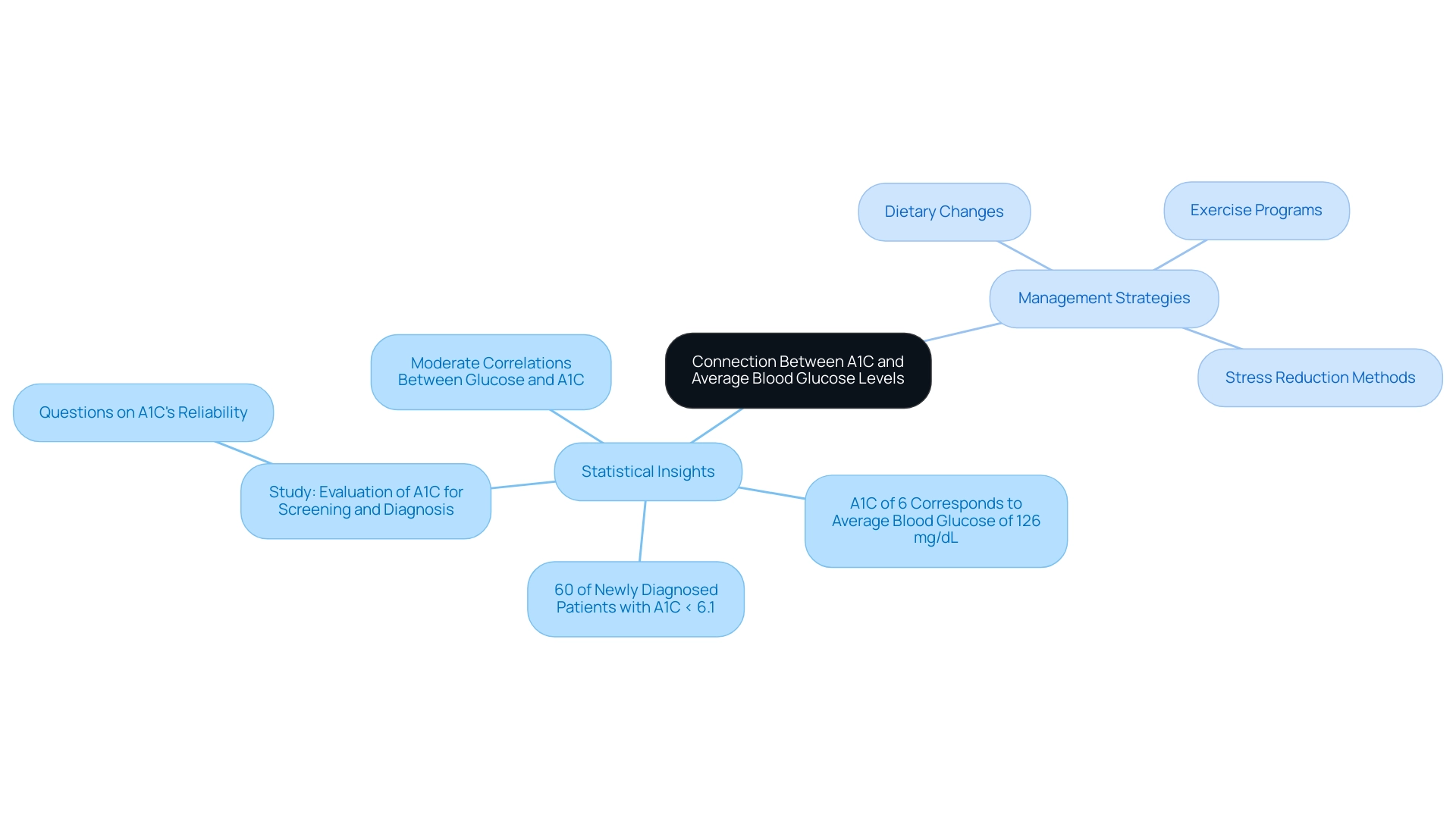
The Connection Between A1C and Average Blood Glucose Levels
The established connection between the a1c formula and average blood sugar levels is essential for effective management of the condition. Notably, 60% of patients with newly diagnosed diabetes had A1C levels <6.1%, highlighting the importance of understanding the a1c formula in assessing the population. Specifically, the A1C formula indicates that an A1C of 6% typically corresponds to an average blood glucose level of around 126 mg/dL.
This correlation is essential as it empowers individuals to set realistic and achievable goals for their blood sugar control within a holistic framework. Tackling the unease that comes with worries about possible complications of the condition is also essential, as it can greatly improve patient empowerment and health oversight. By incorporating a thorough strategy that targets the underlying factors of the illness, including particular holistic routines such as:
- Dietary changes
- Exercise programs
- Stress reduction methods
patients can handle their condition more efficiently.
However, studies, such as the one titled ‘Evaluation of A1C for Screening and Diagnosis,’ have raised questions about the reliability of the A1C formula as an indicator of sugar levels, especially in individuals with normal or moderately elevated levels. By regularly monitoring both the a1c formula and average blood glucose, patients gain a comprehensive understanding of their management strategies for the condition. This dual approach facilitates informed decision-making regarding dietary choices, exercise regimens, and necessary adjustments in medication.
Roopa Naik, a diabetes expert, emphasizes the importance of these measurements within a holistic context in optimizing diabetes care and improving overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively managing diabetes requires a comprehensive grasp of key metrics, with Hemoglobin A1C (A1C) emerging as a vital indicator of average blood sugar levels over time. This article has explored the significance of A1C testing, detailing how it serves not only as a benchmark for diabetes control but also as a critical tool for decision-making in treatment plans. With A1C levels guiding recommendations for lifestyle changes and medication adjustments, consistent monitoring can lead to improved health outcomes and a reduction in diabetes-related complications.
Calculating and interpreting A1C results is essential for individuals managing diabetes. The straightforward formulas and methods discussed provide clarity, enabling patients to track their progress and make informed adjustments. However, awareness of the limitations of A1C testing is equally crucial. Factors such as medical conditions and the nature of blood sugar fluctuations can affect accuracy, underscoring the need for a holistic approach that combines A1C testing with daily glucose monitoring.
In conclusion, the relationship between A1C levels and average blood glucose is pivotal for tailoring diabetes management strategies. By recognizing the importance of A1C as part of a broader health framework, individuals can take proactive steps towards better diabetes control. Embracing a multifaceted approach that includes dietary changes, regular monitoring, and professional support will empower patients to navigate their diabetes journey effectively, ultimately leading to enhanced health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C formula and why is it important?
The A1C formula, or hemoglobin A1C, is a blood test that measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes as it provides a broader view of sugar regulation compared to daily blood sugar tracking.
What A1C level is recommended for adults with type 2 diabetes?
The American Diabetes Association recommends that adults with type 2 diabetes strive to maintain an A1C level below 7%, as this is associated with better glucose control and a lower risk of complications.
How does consistent monitoring of A1C levels affect health outcomes?
Recent studies have shown that consistent monitoring of A1C levels can lead to improved health outcomes for individuals managing blood sugar levels.
What is the significance of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in relation to A1C?
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is recommended for hospitalized individuals with diabetes, highlighting its importance in effective A1C monitoring and management of blood sugar levels.
How do you calculate the A1C percentage from average blood sugar levels?
The A1C percentage can be calculated using the formula: A1C (%) = (Average Blood Sugar (mg/dL) + 46.7) / 28.7. For example, if the average blood sugar is 150 mg/dL, the A1C value would be approximately 6.84%.
What is the accuracy of the A1C formula in monitoring blood sugar?
Combining monitoring intervals has shown the lowest mean absolute error of 6 mg/dL, indicating the accuracy of the A1C formula in assessing blood sugar levels.
Why is understanding the A1C formula essential for diabetes management?
Understanding the A1C formula is vital for effective blood sugar control, allowing patients to make informed decisions about their health and treatment plans, thereby reducing anxiety about potential complications.
How can patients utilize online calculators for A1C?
Patients can use various online calculators to consistently calculate their A1C values, which helps them make informed modifications to their health plans and enhances their understanding of their condition.