Overview
The ADA diet plan is a structured nutritional guide designed to optimize health outcomes for individuals managing type 2 diabetes through balanced nutrition, portion control, moderation, and mindful eating. The article supports this by detailing how these principles, along with specific food choices and personalized meal planning, can significantly improve blood sugar management and overall well-being.
Introduction
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) diet presents a comprehensive framework designed to empower individuals managing type 2 diabetes through informed dietary choices. With a focus on:
- Balanced nutrition
- Portion control
- Moderation
- Mindful eating
This structured approach aims not only to optimize health outcomes but also to address the growing diabetes epidemic. As the prevalence of prediabetes continues to rise, understanding the principles of the ADA diet becomes increasingly critical. This article delves into the key strategies and practical meal planning tips that can aid in effective diabetes management, while also highlighting the importance of personalizing dietary choices to meet individual health needs. By integrating fiber and healthy fats, and mastering carbohydrate control, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and take proactive steps toward reversing diabetes.
Overview of the ADA Diet Plan: Principles and Goals
The ada diet plan acts as a structured and balanced nutritional guide, aimed at optimizing wellness outcomes for individuals managing type 2 diabetes. This eating plan emphasizes four crucial methods that surpass traditional techniques to improve well-being and counteract diabetes. Key principles include:
- Balanced Nutrition: Emphasizing a diverse range of foods from all food groups ensures individuals receive the essential nutrients necessary for overall health. Research supports that a well-rounded diet, rich in vegetables, can significantly influence the management of blood sugar.
- Portion Control: Managing portion sizes is crucial to prevent excessive calorie intake and maintain stable blood sugar levels, especially as fewer than 4 in 10 adults with this condition utilize glucose-lowering medications.
- Moderation: The ADA advocates for the inclusion of diverse items in moderation, fostering flexibility while adhering to dietary restrictions, thus encouraging sustainable eating habits essential for long-term well-being.
- Mindful Eating: Developing greater awareness of eating habits and food choices can lead to improved dietary patterns, essential for effective diabetes management.
In addition to these strategies, consider exploring lesser-known power-plays that can further enhance your wellness journey, such as incorporating specific superfoods or engaging in community support initiatives.
The overarching aim of the ada diet plan is to empower individuals to make informed dietary choices that enhance their health and well-being. As Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, WHO Director-General, noted,
To bring the global health crisis related to blood sugar regulation under control, countries must urgently take action… This begins with implementing policies that promote healthy eating and physical activity.
The severity of the condition is emphasized by its reference as a cause of death in 399,401 certificates in 2021. With the increasing occurrence of prediabetes—estimated at 97.6 million adults in the U.S. alone—the ADA diet plan’s principles are becoming more significant in fighting the blood sugar epidemic. Moreover, case studies like ‘Impact of Lifestyle and Environment on Diabetes’ demonstrate how inactive habits and diets rich in processed items are primary drivers of elevated blood sugar rates, reinforcing the necessity of adopting the ADA diet plan to address these critical lifestyle factors.
If you’re prepared to take practical measures towards reversing the condition and improving your well-being, click to register for additional insights and resources.
Practical Meal Planning: Foods to Include and Avoid
When planning meals according to the ADA diet plan, it is essential to focus on both foods to include and those to avoid for optimal management. Research published in the British Journal of Nutrition (2007) supports the significance of dietary choices in managing diabetes and enhancing overall well-being.
Foods to Include:
- Non-Starchy Vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, and peppers are excellent choices as they are low in calories and packed with vital nutrients.
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread, which are abundant in fiber and vital nutrients, promoting overall digestive well-being.
- Lean Proteins: Incorporate protein sources like poultry, fish, beans, and legumes to promote muscle maintenance and overall well-being.
- Healthy Fats: Choose unsaturated fats found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, which provide heart-healthy benefits.
Foods to Avoid:
-
Sugary Beverages: Limit consumption of sodas and sweetened drinks, which can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
According to the ADA, “table sugar and other sugars in your diet don’t increase blood glucose levels any higher than other simple carbohydrates.”
-
Refined Carbohydrates: Steer clear of white bread, pastries, and sweets that offer minimal nutritional value and can adversely affect blood glucose control.
-
High-Fat Processed Items: Reduce consumption of fried dishes and processed snacks, as these can lead to negative wellness results and worsen weight gain.
-
Excessive Sodium: Decrease high-sodium items to promote cardiovascular well-being, which is essential for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Additionally, a practical method for meal planning is calorie counting, as demonstrated in a case study showing that training in this method can enhance intake estimation and promote weight loss. By making informed choices about food, individuals can create balanced and satisfying meals that align with the ADA diet plan, ultimately enhancing their health and quality of life.
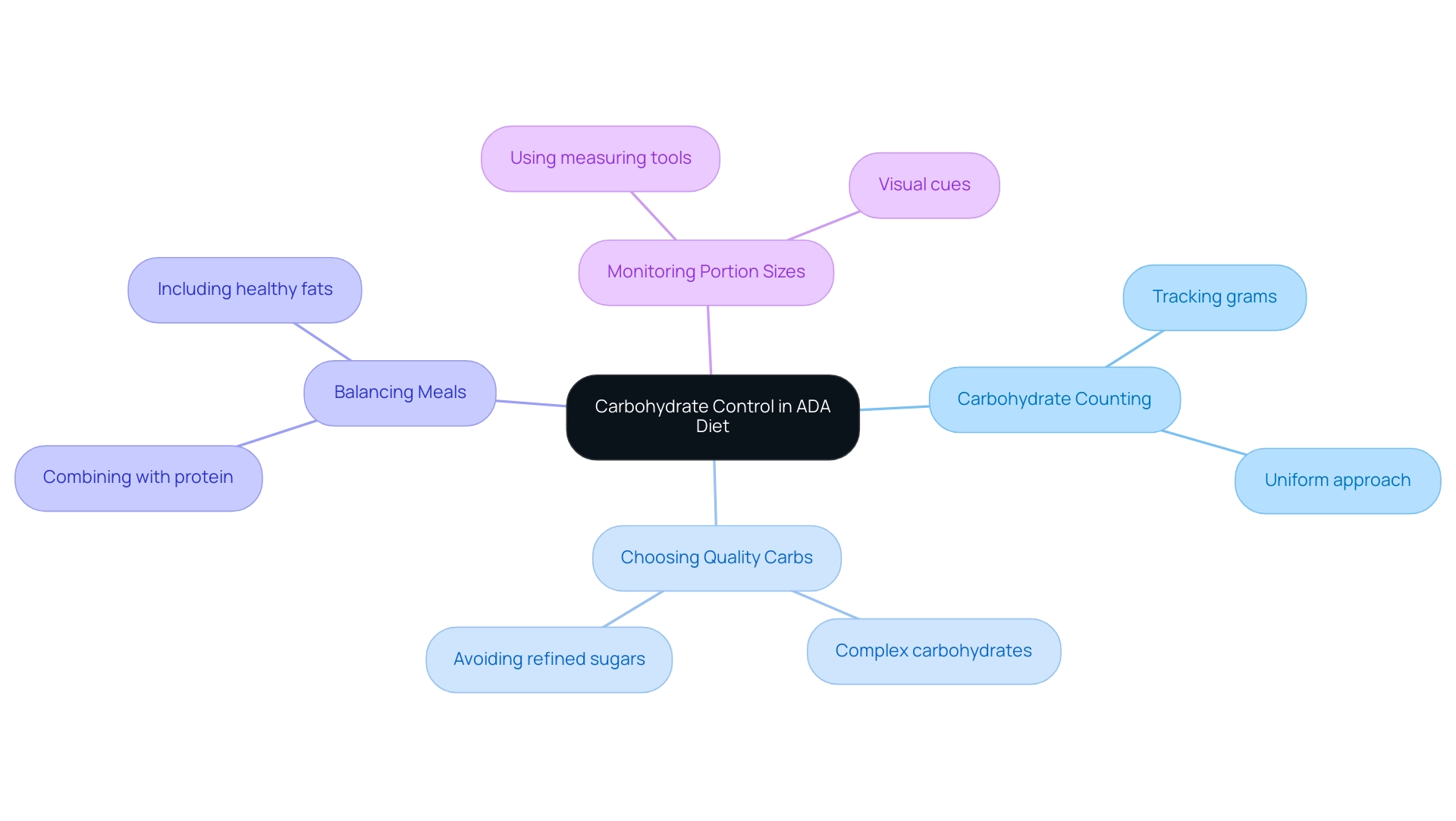
Understanding Carbohydrate Control in the ADA Diet
Carbohydrates play a pivotal role in regulating blood sugar levels, making effective management of their intake crucial for individuals with blood sugar issues, especially during pregnancy. Recent studies show that effective carbohydrate counting can reduce HbA1c levels by approximately 0.5% to 1%, significantly aiding in blood sugar management. Here are key strategies to help control carbohydrate consumption:
-
Carbohydrate Counting:
Tracking the grams of carbohydrates in meals is essential to maintain balanced blood sugar levels. Studies indicate that effective carbohydrate counting can significantly aid in blood sugar management. The American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee emphasizes, ‘Establishing a uniform approach to carbohydrate counting will benefit individuals with this condition and their caregivers.’
-
Choosing Quality Carbs:
Emphasizing complex carbohydrates—such as those found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables—over simple sugars from refined sources is vital for health.
-
Balancing Meals:
Combining carbohydrates with protein and healthy fats can slow digestion and reduce the likelihood of blood sugar spikes.
-
Monitoring Portion Sizes:
Utilizing measuring tools or visual cues can help individuals keep their portion sizes in line with dietary goals, ensuring carbohydrate intake is appropriate.
Additionally, it is crucial to understand insulin resistance and its implications for managing blood sugar conditions. Conventional therapies may present dangers, and early identification of risk is essential. For instance, a study on screening for type 1 condition risk found that nearly 70% of children with multiple autoantibodies developed type 1 condition within 10 years, highlighting the importance of proactive dietary management.
By mastering these principles, individuals can use an ADA diet plan to make informed food choices, enhancing their ability to maintain stable blood sugar levels and improve overall well-being, particularly during pregnancy.
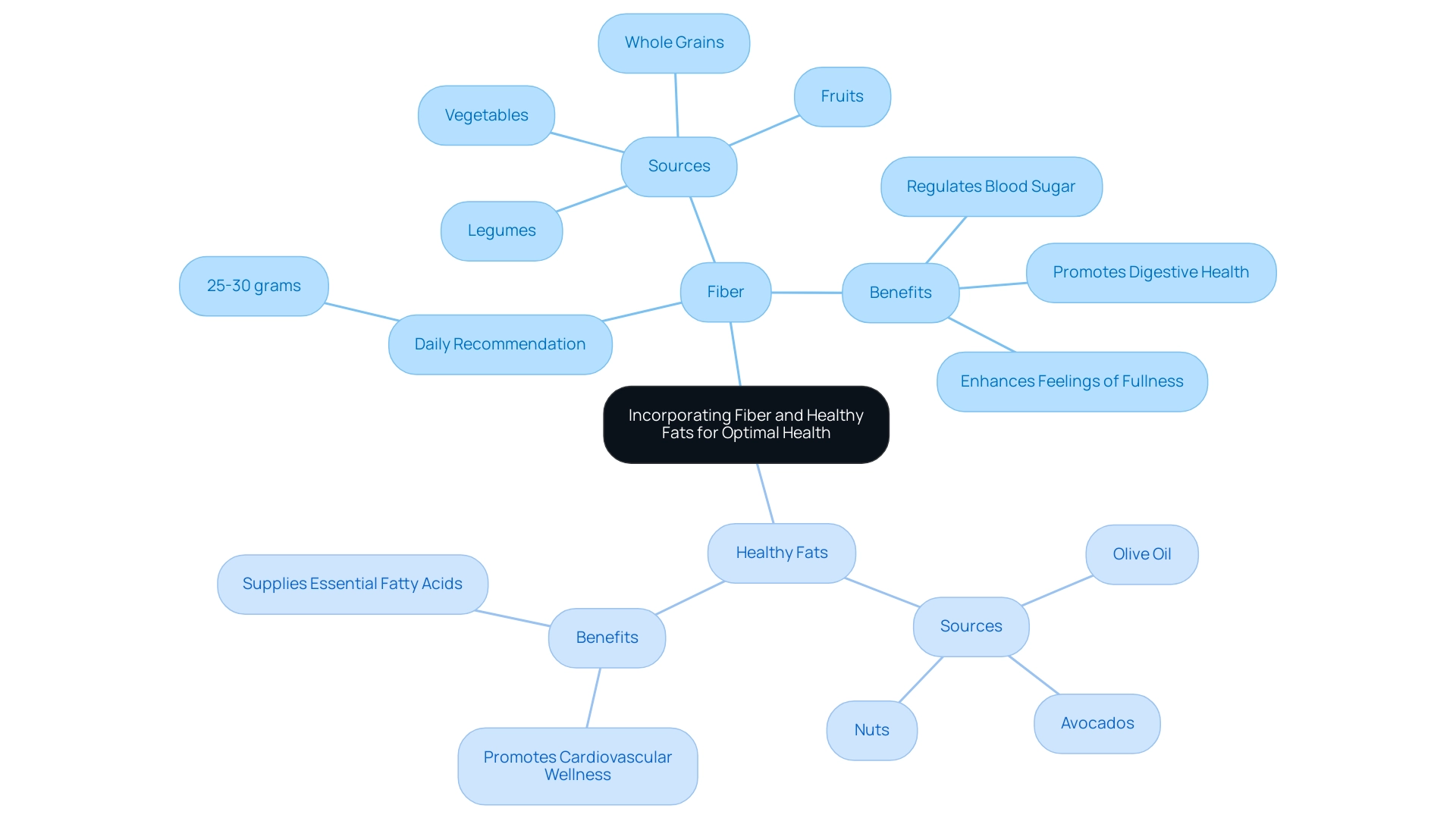
Incorporating Fiber and Healthy Fats for Optimal Health
Including fiber and nutritious fats in the ADA diet plan provides considerable advantages, especially within a comprehensive approach focused on reversing the condition.
Fiber: It is recommended to consume at least 25-30 grams of fiber daily, sourced from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Fiber plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels, enhancing feelings of fullness, and promoting digestive health.
Recent studies suggest that individuals who emphasize high-fiber carbohydrate sources instead of processed foods may achieve better glycemic control, highlighting the significance of fiber in managing blood sugar. A study published in Diabetes Care (2014;37(Supplement 1):S120-S43) highlights that a fiber-rich diet can significantly improve metabolic parameters in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Healthy Fats: It is vital to include sources of unsaturated fats—such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts—while minimizing saturated fats typically found in red meat and full-fat dairy products.
Nutritious fats promote cardiovascular wellness and supply essential fatty acids that enhance overall well-being. Nutrition specialists stress that these dietary selections not only assist in managing blood sugar levels but also improve cardiovascular wellness, underscoring the necessity for a balanced approach to nutrition. Moreover, a comprehensive approach that tackles the underlying factors of this condition can help reduce the stress linked to possible complications, enabling individuals to take control of their well-being.
By focusing on these dietary strategies, individuals can significantly enhance their health while effectively managing type 2 diabetes through an ADA diet plan. Moreover, it is essential to recognize the dangers of traditional treatments, which may not address the underlying issues of insulin resistance. Instead, combining acarbose, an amylase inhibitor, with a fiber-rich meal represents a promising therapeutic approach for identified T2DM patients.
Encouraging high-fiber carbohydrate sources over processed foods can improve glycemic control, with specific serving recommendations tailored to individual needs, thus promoting better glucose control and flexibility in food choices.
Personalizing Your ADA Diet: Tailoring Nutrition to Individual Needs
Customizing the ada diet plan requires a thoughtful approach that considers individual health conditions, preferences, and lifestyles, while also addressing the anxiety that often accompanies concerns about potential complications of diabetes. Here are key steps to effectively tailor your diet:
-
Assessing Dietary Preferences: Begin by identifying foods you enjoy and those you dislike.
This step is essential in creating a more satisfying and sustainable eating experience, which is crucial for long-term adherence.
-
Consulting with Healthcare Professionals: Engaging with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider is vital.
They can assist in creating a personalized meal plan that aligns with specific wellness needs, ensuring that nutritional choices are both beneficial and enjoyable.
Recent studies indicate that 50% to 70% of women who experience gestational conditions may develop type 2 health issues later in life, underscoring the importance of tailored dietary strategies.
Additionally, it’s important to note that more American men (41%) than women (39%) have prediabetes, highlighting the necessity for personalized dietary strategies for a broader audience.
By re-examining the root causes of your diabetes, healthcare professionals can assist in creating a holistic regimen that supports patient empowerment and wellness improvement.
-
Setting Realistic Goals: Establish achievable dietary goals that resonate with your personal wellness objectives, whether it’s weight management, improved blood sugar control, or overall well-being.
Setting practical targets fosters a sense of accomplishment and encourages ongoing commitment to dietary changes.
-
Monitoring Progress: Regularly assess the impact of dietary adjustments on your wellness metrics.
This ongoing assessment allows for timely modifications to your ADA diet plan, optimizing its effectiveness in managing diabetes.
Personalizing your ADA diet plan empowers you to take charge of your health journey, facilitating adherence to your plan and aiding in the achievement of desired health outcomes.
The latest trends in nutrition for managing blood sugar emphasize the importance of personalized meal plans, which have shown a beneficial effect on control.
As the field evolves with new research and advancements, such as innovative meal planning tools and personalized nutrition apps, staying informed and working collaboratively with healthcare professionals remains essential for successful dietary management.
Remember, addressing the root causes of diabetes through a holistic approach can significantly alleviate the anxiety associated with managing your condition.
Conclusion
In summary, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) diet provides a structured and effective framework for managing type 2 diabetes through informed dietary choices. By adhering to key principles such as:
- Balanced nutrition
- Portion control
- Moderation
- Mindful eating
Individuals can significantly enhance their health outcomes. Incorporating fiber-rich foods and healthy fats further supports blood sugar regulation and overall well-being, while mastering carbohydrate control is essential for effective diabetes management.
Practical meal planning strategies that focus on foods to include and avoid play a crucial role in this dietary approach. Foods to prioritize include:
- Non-starchy vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats
Sugary beverages and refined carbohydrates should be minimized. Personalizing the ADA diet to fit individual health needs and preferences is vital, enabling a sustainable and enjoyable eating experience that fosters long-term adherence.
Ultimately, embracing the ADA diet is a proactive step toward reversing diabetes and improving overall health. As the prevalence of prediabetes continues to rise, understanding and implementing these dietary principles becomes increasingly important. By taking control of dietary choices, individuals can empower themselves on their health journey, paving the way for better health outcomes and a higher quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ADA diet plan?
The ADA diet plan is a structured and balanced nutritional guide designed to optimize wellness outcomes for individuals managing type 2 diabetes. It emphasizes balanced nutrition, portion control, moderation, and mindful eating.
What are the key principles of the ADA diet plan?
The key principles include: 1. Balanced Nutrition: A diverse range of foods from all food groups for essential nutrients. 2. Portion Control: Managing portion sizes to prevent excessive calorie intake and maintain stable blood sugar levels. 3. Moderation: Including diverse items in moderation to foster flexibility and sustainable eating habits. 4. Mindful Eating: Developing awareness of eating habits and food choices for better dietary patterns.
Why is balanced nutrition important in the ADA diet plan?
Balanced nutrition ensures individuals receive essential nutrients necessary for overall health and can significantly influence the management of blood sugar levels.
What foods should be included in the ADA diet plan?
Foods to include are: 1. Non-Starchy Vegetables: Such as leafy greens, broccoli, and peppers. 2. Whole Grains: Like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread. 3. Lean Proteins: Including poultry, fish, beans, and legumes. 4. Healthy Fats: Unsaturated fats from avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
What foods should be avoided in the ADA diet plan?
Foods to avoid include: 1. Sugary Beverages: Such as sodas and sweetened drinks. 2. Refined Carbohydrates: Including white bread, pastries, and sweets. 3. High-Fat Processed Items: Such as fried dishes and processed snacks. 4. Excessive Sodium: High-sodium items should be reduced for cardiovascular health.
How does portion control help in managing diabetes?
Portion control is crucial to prevent excessive calorie intake and maintain stable blood sugar levels, especially since many individuals with diabetes may not use glucose-lowering medications.
What is the significance of mindful eating in the ADA diet plan?
Mindful eating helps individuals develop greater awareness of their eating habits and food choices, leading to improved dietary patterns essential for effective diabetes management.
What additional strategies can enhance the ADA diet plan?
Exploring lesser-known strategies, such as incorporating specific superfoods or engaging in community support initiatives, can further enhance wellness during the diabetes management journey.
How does the ADA diet plan address the increasing occurrence of prediabetes?
The principles of the ADA diet plan are becoming increasingly significant in combating the blood sugar epidemic, especially with the rising number of individuals diagnosed with prediabetes in the U.S.