Introduction
Managing diabetes requires a comprehensive understanding of dietary choices and lifestyle adjustments that support optimal health. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) diet serves as a guiding framework, emphasizing balanced nutrition, portion control, and the importance of whole foods.
This article delves into the key principles of the ADA diet:
- Balanced nutrition
- Portion control
- Importance of whole foods
Effective meal planning strategies, essential nutritional components, the role of physical activity, and the resources available for sustained success are also discussed.
By exploring these topics, individuals can gain valuable insights into managing their condition, enhancing their quality of life, and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Overview of the ADA Diet: Principles and Guidelines
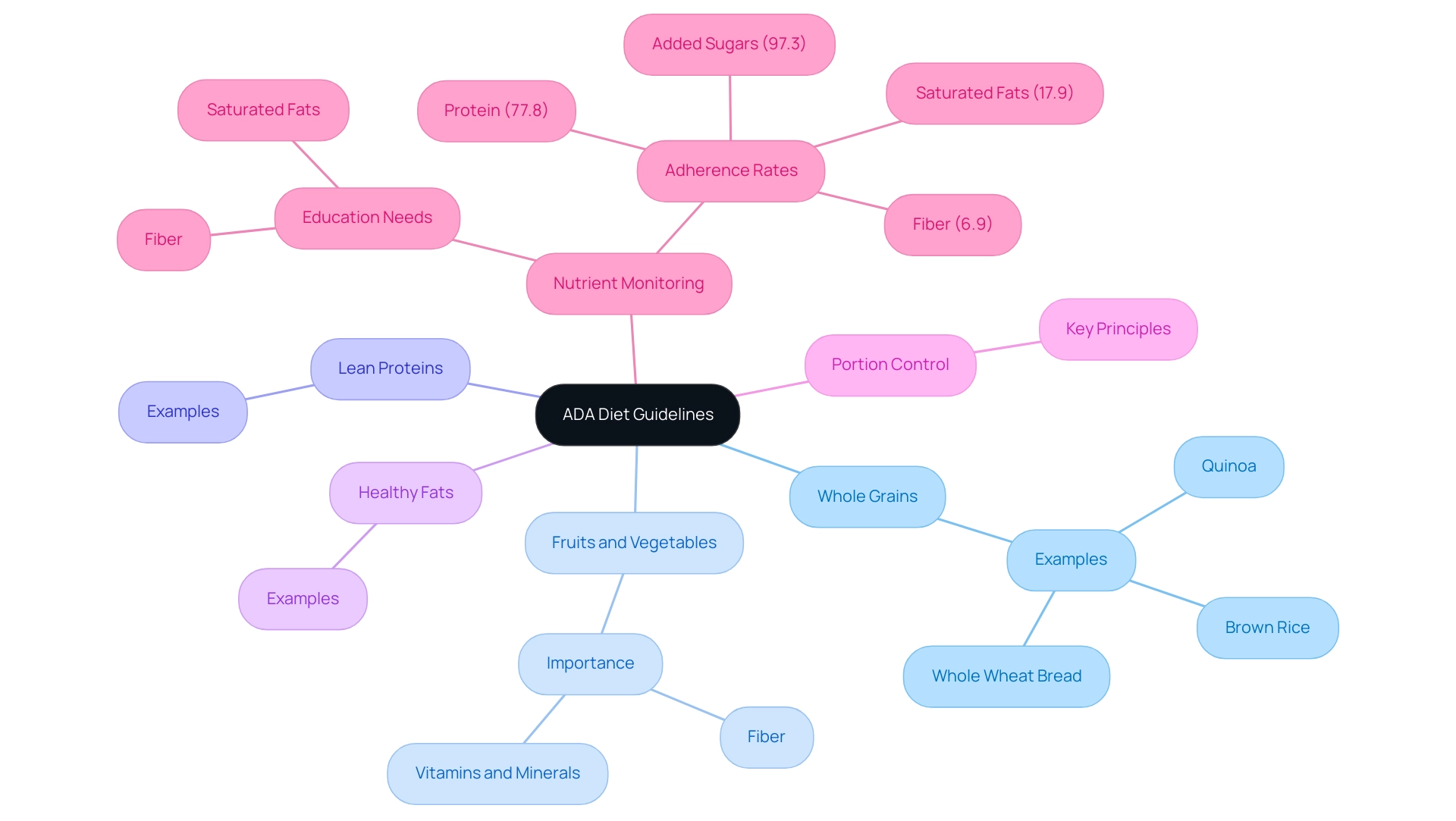
The ADA diet is meticulously crafted by the American Diabetes Association to support balanced nutrition and optimize sugar control for individuals managing diabetes. A crucial component of the ADA guidelines is the inclusion of a diverse range of foods, notably whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread. These grains are increasingly highlighted in menus at San Marcos eateries, as they assist in regulating sugar levels and offer sustained energy.
Alongside whole grains, the guidelines advocate for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Vegetable-rich dishes play a vital role in supporting sugar regulation and overall health, offering essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Portion control remains a cornerstone of effective dietary regulation, with a strong emphasis on limiting added sugars and saturated fats.
Monitoring carbohydrate intake is vital for managing blood glucose effectively. Recent findings indicate high adherence rates for protein (77.8%) and added sugars (97.3%), but alarming lower rates for recommended saturated fats (17.9%) and fiber (6.9%), underscoring the necessity for ongoing education about these essential nutrients. Addressing common blood sugar management myths and understanding insulin resistance are also crucial for effective management and empowerment.
Additionally, prompt referral to a nephrologist is advised in cases of kidney disease uncertainties or rapid progression. By adhering to the ADA diet guidelines, individuals can achieve a healthy weight and significantly reduce their risk of diabetes-related complications, empowering them to manage their condition holistically and with confidence.
Effective Meal Planning Strategies for Diabetes Management
To effectively manage diabetes with the ada diet through meal planning, consider the following strategies:
-
Carbohydrate Counting: Monitoring total carbohydrate intake is essential for regulating glucose levels. Research indicates that the ada diet, particularly tracking carbohydrate consumption, is a key determinant of postprandial glucose levels in diabetic patients.
Notably, a study found an overall treatment difference in median estimation errors of −55% (−70 to −32), p < 0.001 at the end of the intervention, highlighting the effectiveness of carbohydrate counting. It is advisable to aim for a consistent carbohydrate intake throughout the day while following an ada diet to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
-
The Plate Method: This visual approach to meal planning involves dividing your plate into sections—half for non-starchy vegetables, one quarter for lean proteins, and one quarter for whole grains or starchy foods. As mentioned by Prof. Jennie C Brand-Miller, this method assists in portion control and encourages balanced nutrition, crucial for blood sugar regulation.
-
Meal Prepping: Preparing meals in advance ensures that healthy options are readily available, significantly reducing the temptation to opt for unhealthy alternatives. This strategy has been shown to increase the success rates of diabetes management by simplifying food choices in line with the ada diet.
-
Mindful Eating: Engaging in mindful eating practices enables people to pay attention to their hunger and fullness signals, which can prevent overeating and foster a more positive relationship with food. Additionally, a pilot study on carbohydrate counting in adolescents revealed that 50% of participants were able to count within 15 g of the actual carbohydrate amount, demonstrating practical outcomes of this approach. By incorporating these strategies into daily routines, individuals with Type 2 Diabetes can enhance their ability to manage their condition effectively while following an ada diet.
It is also important to recognize that V.P. and B.P.P. contributed equally to this work, underscoring the collaborative effort behind these findings.
Nutritional Components: What to Eat and Avoid
Adhering to the ADA diet involves a careful selection of nutritional components that can significantly impact diabetes management.
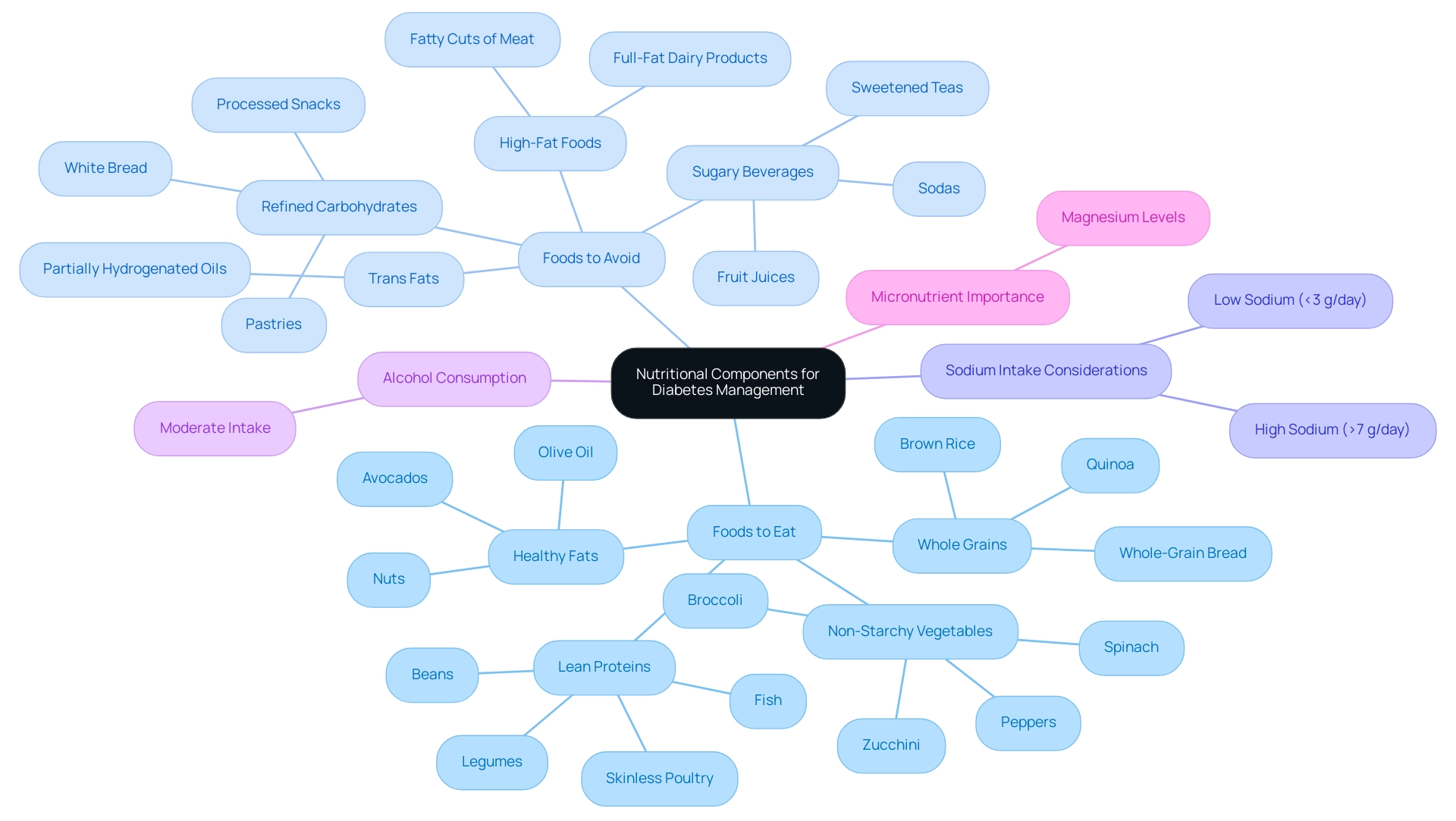
Foods to Eat:
- Non-Starchy Vegetables: Leafy greens such as spinach, broccoli, peppers, and zucchini are outstanding selections, offering vital vitamins and minerals without affecting glucose levels.
- Whole Grains: Foods like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-grain bread are recommended for their high fiber content, which can aid in sugar control and overall digestive health.
- Lean Proteins: Incorporating skinless poultry, fish, beans, and legumes supports muscle health while keeping calorie intake in check, essential for maintaining a healthy weight.
- Healthy Fats: Sources of unsaturated fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, contribute to cardiovascular health, an important consideration for individuals with blood sugar concerns.
Foods to Avoid:
- Sugary Beverages: It is advisable to limit consumption of sodas, fruit juices, and sweetened teas, as these can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Refined Carbohydrates: Foods such as white bread, pastries, and many processed snacks should be avoided due to their low fiber content, which can negatively affect glycemic control.
- High-Fat Foods: Reducing intake of saturated fats found in fatty cuts of meat and full-fat dairy products is crucial for lowering the risk of heart disease, which is heightened in individuals with blood sugar issues.
- Trans Fats: It is also important to steer clear of partially hydrogenated oils commonly present in processed foods, as they can exacerbate cardiovascular risks.
In terms of sodium intake, it is important to note that both low (<3 g/day) and high (>7 g/day) sodium excretions are associated with increased mortality in individuals with type 2, highlighting the need for balanced sodium consumption.
Furthermore, moderate alcohol intake has minimal acute and/or long-term harmful effects on blood glucose levels in people with the condition, which can guide dietary choices. Finally, sustaining a balanced consumption of food sources for essential nutrients is vital, as evidence indicates a possible connection between magnesium levels and the risk of diabetes-related conditions, highlighting the significance of micronutrients in the care of such issues. By making informed food choices, individuals can better manage their condition and enhance overall health.
Integrating Lifestyle Changes: The Role of Physical Activity
Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine is vital for effective management of blood sugar levels. The American Diabetes Association recommends engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, which can include activities such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Furthermore, it is advisable to perform strength training exercises at least twice a week, as these exercises enhance muscle mass and improve glucose metabolism.
Research indicates that physical activity not only aids in lowering sugar levels but also reduces insulin resistance, contributing to overall well-being. Significantly, the median county-level prevalence of diagnosed conditions related to blood sugar increased from 6.3% in 2004 to 8.3% in 2021, underscoring the importance of managing these issues through lifestyle changes such as exercise. A recent study emphasizes that resistance training can reduce fasting blood glucose levels in individuals with impaired fasting glucose, underscoring its significance in managing blood sugar.
As Ann L Albright, PHD, RD from the CDC states, ‘Physical activity is a cornerstone of controlling blood sugar that can lead to significant health improvements.’ To enhance the effectiveness of your physical activity, it is essential to re-examine the root causes of your condition, which may include factors such as:
- ADA diet
- Stress
- Lifestyle choices
By tackling these fundamental concerns through a comprehensive approach, people can enhance their ability in their health journey.
To maintain motivation, consider:
- Partnering with a workout buddy
- Joining local exercise groups
- Setting realistic goals
- Tracking your progress
These strategies can foster a sense of achievement, encouraging continued commitment to your fitness journey. By adhering to these guidelines and integrating a holistic approach, individuals with this condition can significantly improve their health outcomes and quality of life.
Resources and Support for Sustaining the ADA Diet
To effectively sustain the ada diet, it is essential to utilize a variety of resources and support networks. First, Registered Dietitians play a pivotal role; seeking guidance from certified dietitians who specialize in blood sugar control can provide personalized meal planning and tailored advice, which is crucial for achieving optimal health outcomes. Research indicates that support for Diabetes Self-Management Education (DSME) can yield a significant reduction in HbA1c levels, with an absolute effect of −1.05%±0.58, underscoring the importance of professional assistance in dietary adherence.
Significantly, a randomized controlled trial involving 516 participants highlighted the effectiveness of DSME in improving management of the condition. Additionally, Education Programs related to blood sugar management are available through hospitals and community centers, offering comprehensive education on managing the condition. These programs have demonstrated effectiveness, particularly in improving glycemic control and lipid profiles, as evidenced by statistical significance observed between intervention and control groups in recent studies.
Furthermore, according to Pillay and colleagues, “Supporting the DSME program can result in a greater benefit, especially for programs with less than 10 hours of contact time.” Participating in support groups—whether local or online—allows people to share experiences and strategies, fostering a sense of community among those facing similar challenges. Finally, accessing Educational Materials from the American Diabetes Association, including meal planning tools, recipes, and the latest research findings, can provide indispensable knowledge and ongoing support for the ada diet.
These resources are crucial for individuals striving to maintain their dietary commitments and manage their diabetes effectively.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes effectively hinges on a well-rounded approach that prioritizes balanced nutrition, portion control, and the consumption of whole foods, as outlined by the American Diabetes Association (ADA). The principles of the ADA diet emphasize the importance of selecting nutrient-dense foods, such as whole grains, lean proteins, and a variety of fruits and vegetables, while simultaneously limiting intake of added sugars and unhealthy fats. By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can achieve better blood sugar control and enhance their overall health.
Incorporating effective meal planning strategies, such as carbohydrate counting and the plate method, can further streamline the management process. These approaches not only simplify food choices but also promote mindful eating habits that contribute to a healthier relationship with food. Additionally, regular physical activity complements dietary efforts, playing a crucial role in reducing insulin resistance and improving glucose metabolism.
Access to resources, including registered dietitians and diabetes education programs, can provide the necessary support for individuals navigating their diabetes management journey. Engaging with community support groups and utilizing educational materials from reputable organizations can empower individuals to stay committed to their dietary and lifestyle changes.
Ultimately, by embracing the ADA diet and the associated lifestyle adjustments, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. This holistic approach fosters a sense of control over one’s health and well-being, enabling individuals to manage diabetes with confidence and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ADA diet and who created it?
The ADA diet is a nutrition plan developed by the American Diabetes Association to support balanced nutrition and optimize sugar control for individuals managing diabetes.
What types of foods are emphasized in the ADA diet?
The ADA diet emphasizes a diverse range of foods, particularly whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread, as well as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Why are whole grains important in the ADA diet?
Whole grains help regulate sugar levels and provide sustained energy, making them a crucial component of the ADA diet.
What role do vegetables play in the ADA diet?
Vegetable-rich dishes are vital for supporting sugar regulation and overall health, offering essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
What is the significance of portion control in the ADA diet?
Portion control is essential in effectively regulating dietary intake, with a strong emphasis on limiting added sugars and saturated fats.
Why is monitoring carbohydrate intake important for diabetes management?
Monitoring carbohydrate intake is vital for effectively managing blood glucose levels and preventing spikes in sugar levels.
What are the adherence rates for various dietary components according to recent findings?
Recent findings show high adherence rates for protein (77.8%) and added sugars (97.3%), but alarmingly low rates for recommended saturated fats (17.9%) and fiber (6.9%).
What should individuals do if they have uncertainties regarding kidney disease?
Individuals should seek prompt referral to a nephrologist if there are uncertainties or rapid progression of kidney disease.
What are some effective meal planning strategies for managing diabetes with the ADA diet?
Effective meal planning strategies include carbohydrate counting, using the plate method, meal prepping, and practicing mindful eating.
How does carbohydrate counting help in diabetes management?
Carbohydrate counting helps regulate glucose levels and has been shown to significantly improve the accuracy of carbohydrate intake estimation in diabetic patients.
What is the plate method in meal planning?
The plate method involves dividing a plate into sections: half for non-starchy vegetables, one quarter for lean proteins, and one quarter for whole grains or starchy foods, promoting balanced nutrition and portion control.
How does meal prepping benefit individuals following the ADA diet?
Meal prepping ensures that healthy food options are readily available, reducing the temptation to choose unhealthy alternatives and supporting diabetes management.
What is mindful eating and how does it help in diabetes management?
Mindful eating involves paying attention to hunger and fullness signals, which can prevent overeating and foster a healthier relationship with food, aiding in diabetes management.