Overview
Managing diabetes can be challenging, and it’s important to recognize the tools that can help. The Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) stands out as a crucial resource in diabetes management. Unlike traditional methods like HbA1c, GMI offers a more immediate assessment of average blood sugar levels, based on continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data. This means that you can receive timely treatment adjustments, empowering you to make informed health decisions.
Many patients find that having access to GMI significantly improves their glycemic control. It allows for a more responsive approach to managing blood sugar levels, ultimately leading to better overall management of diabetes. Imagine feeling more in control of your health—this is what GMI can help you achieve.
As you navigate your diabetes journey, consider how GMI can support you in making those crucial decisions. With this tool, you can take proactive steps towards a healthier lifestyle, paving the way for a fulfilling life. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to help you thrive.
Introduction
Understanding blood sugar management is crucial for individuals navigating the complexities of diabetes. It can often feel overwhelming, especially as new tools emerge to enhance this journey. The Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) stands out as a transformative metric, offering real-time insights that empower patients to take control of their health.
It’s important to recognize that with the introduction of GMI, a pressing question arises: how does this innovative approach compare to traditional methods like A1C? What implications does it hold for future diabetes management strategies? Many patients find that exploring these questions can lead to a deeper understanding of their health and well-being.
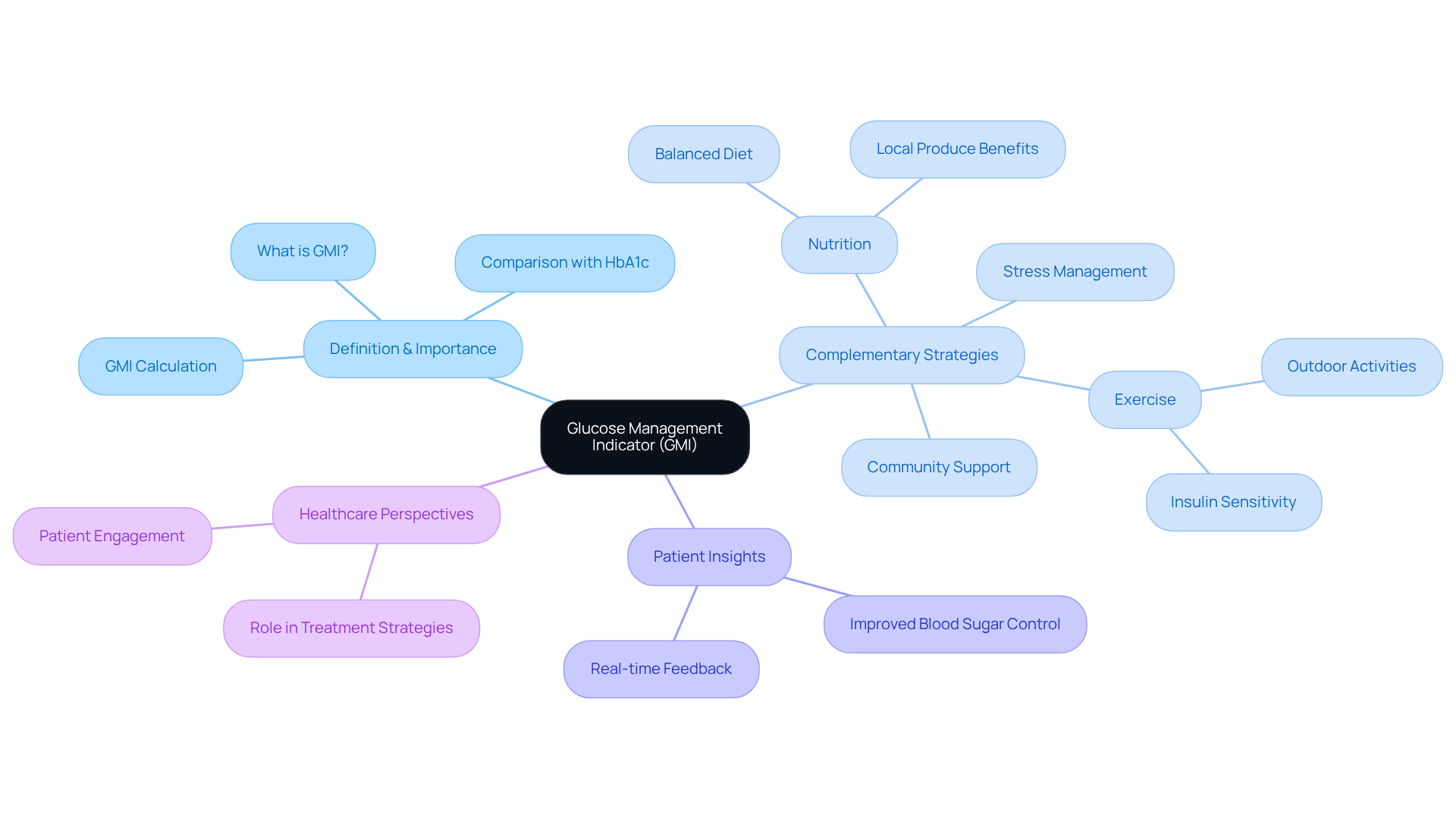
Define GMI: Understanding the Glucose Management Indicator
To understand what is gmi blood sugar, the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) serves as a vital tool for assessing average blood sugar levels over time, based on continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. Unlike traditional methods such as HbA1c, which reflect average blood sugar over a two to three-month period, GMI offers a more immediate snapshot of sugar levels, expressed as a percentage. This percentage comes from a specific formula that aligns mean glucose readings with expected HbA1c values, enabling a more dynamic assessment of glycemic control.
It’s important to recognize that managing type 2 diabetes can feel overwhelming, especially in communities like San Marcos, CA. However, GMI can be complemented by holistic lifestyle strategies that emphasize:
- Nutrition
- Exercise
- Community support
- Stress management
Many patients find that embracing the local outdoor lifestyle through regular exercise in scenic parks and trails enhances insulin sensitivity and helps control weight—both crucial for effective diabetes management. Additionally, focusing on a balanced diet rich in local produce, such as avocados and berries, supports overall health and aids in regulating blood sugar levels.
Healthcare professionals and individuals alike benefit from GMI’s immediate insights into what is gmi blood sugar level variations, allowing for prompt interventions and adjustments to treatment strategies. For instance, patients using GMI have shared their experiences of improved blood sugar control, as it empowers them to respond swiftly to fluctuations in their glucose levels. This prompt feedback is particularly beneficial in managing health effectively, enabling individuals to make informed choices about their well-being.
Specialists in blood sugar management emphasize what is gmi blood sugar as a significant aspect of contemporary health practices. As one expert noted, GMI provides a clearer view of an individual’s glycemic control, paving the way for improved treatment strategies. By integrating GMI into diabetes management, along with personalized functional medicine approaches and community wellness programs, healthcare providers can enhance patient engagement and optimize treatment outcomes. This marks a significant shift in how diabetes is monitored and managed, especially looking ahead to 2025.
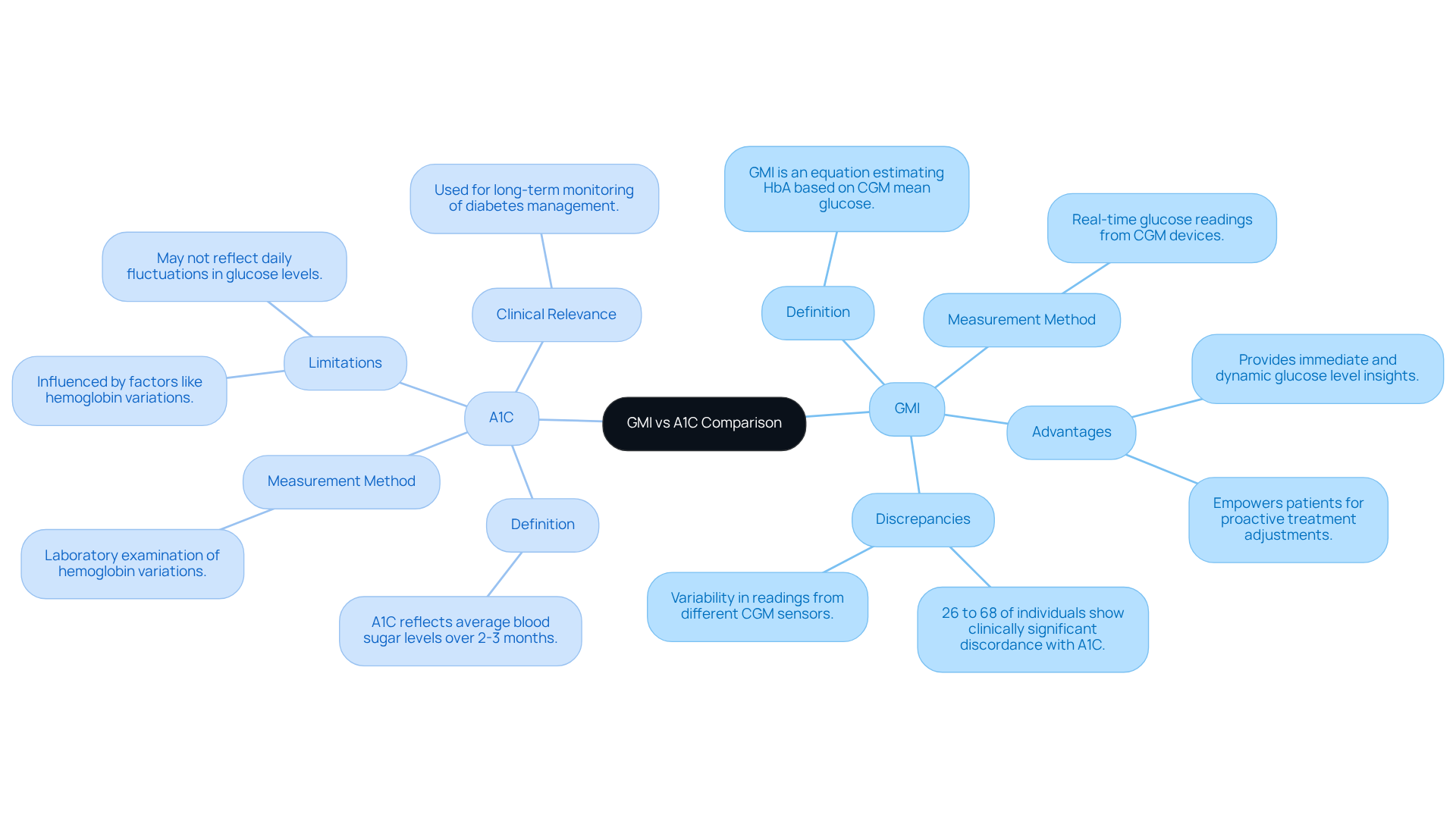
Compare GMI and A1C: Key Differences and Implications
What is GMI blood sugar, and how does it differ from A1C as both are essential indicators of sugar regulation, yet they offer different insights and methods? A1C is a laboratory examination that reflects average blood sugar levels over two to three months, influenced by factors like hemoglobin variations. In contrast, what is GMI blood sugar refers to measurements derived from real-time glucose readings obtained through continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices, providing a more immediate and dynamic view of glucose levels. This real-time data allows for timely treatment adjustments, highlighting what is GMI blood sugar and its benefits for patients facing significant daily fluctuations.
It’s important to recognize that recent studies have highlighted the effectiveness of GMI compared to A1C. Findings reveal that 26% to 68% of individuals experience clinically significant discordance between the two metrics. For instance, a study involving participants with type 2 sugar intolerance demonstrated that GMI readings from Abbott Libre and Dexcom G4 sensors often showed discrepancies of about 0.3 %-points. Such variability underscores the importance of understanding both measures in diabetes management.
Many patients find that understanding what is GMI blood sugar helps empower them during the transition from A1C to GMI monitoring. They report feeling more informed about their glucose levels, enabling proactive adjustments to their treatment plans. Expert opinions suggest that GMI’s ability to deliver continuous data can lead to more personalized and effective management strategies for blood sugar.
Current research continues to explore the accuracy of GMI versus A1C. Findings indicate that the accuracy of CGM sensors can vary, potentially impacting GMI calculations. Factors such as individual red blood cell turnover and the timing of measurements can contribute to discrepancies between GMI and A1C. Therefore, healthcare providers are encouraged to use both metrics together to enhance management of the condition and improve outcomes for individuals.
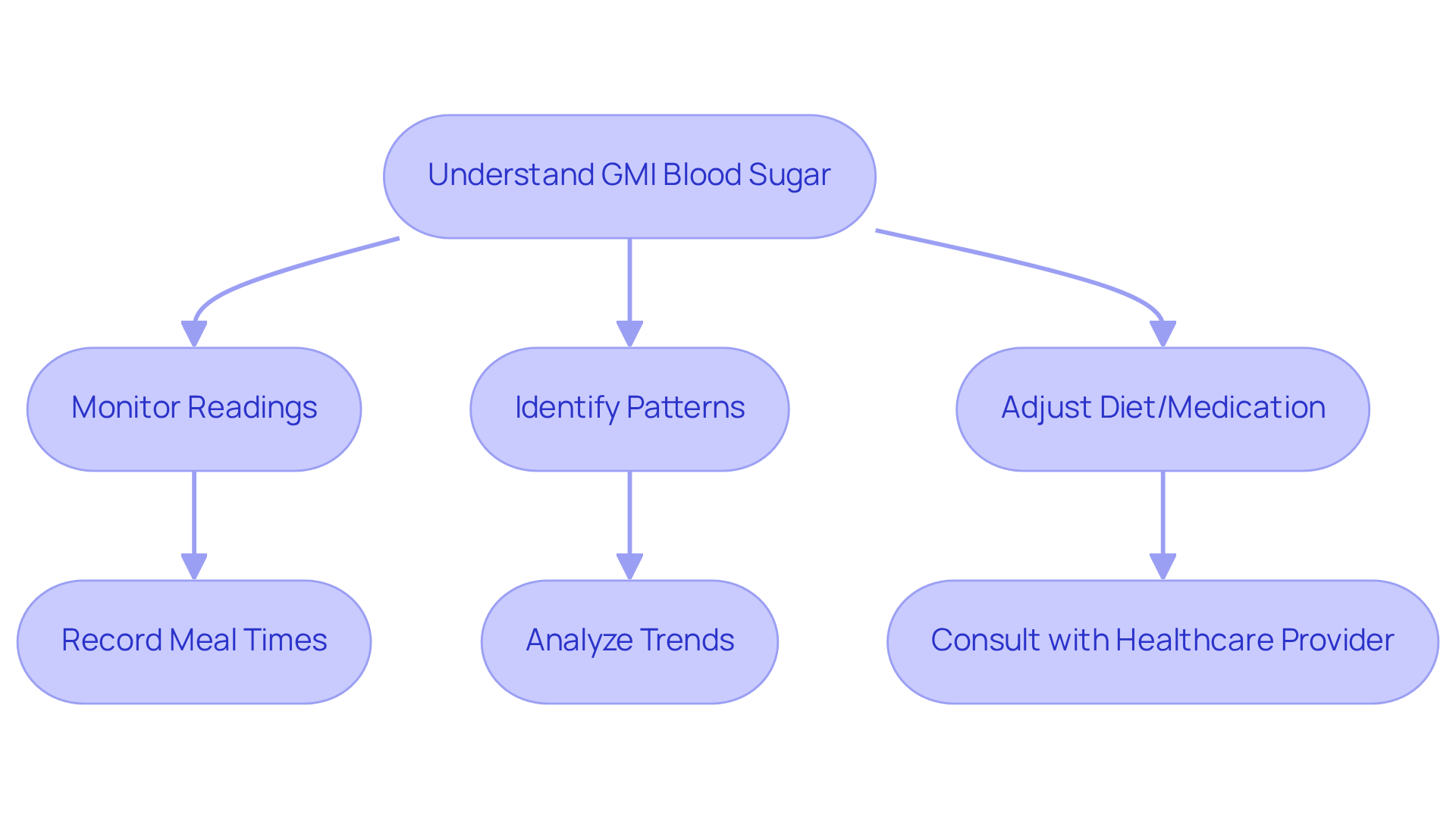
Utilize GMI in Daily Management: Practical Applications and Benefits
Managing diabetes can be challenging, but knowing what is GMI blood sugar and incorporating it into your daily routine can truly make a difference in controlling blood sugar levels. By understanding what is GMI blood sugar through your readings, you can identify patterns in your blood sugar, empowering you to make informed choices about your diet, exercise, and medication. For instance, if you notice a spike in GMI after certain meals, you can adjust your carbohydrate intake or medication timing. This proactive approach not only helps you set achievable management goals but also fosters a sense of empowerment and responsibility in your health journey.
It’s important to recognize that recent studies suggest that what is GMI blood sugar may provide a more accurate representation of average blood sugar levels compared to traditional A1C tests, particularly under varying lab conditions. With an average mean CGM glucose of 162 mg/dL reported in a study with 641 participants, the potential for GMI to guide your dietary choices becomes clear. Regularly monitoring your GMI allows you to take charge of your health, leading to improved well-being and a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications. Many patients find that utilizing GMI helps them to learn what is GMI blood sugar, which enhances their daily blood sugar control and makes it an invaluable tool in managing diabetes.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Embracing these strategies can lead to a healthier, more fulfilling life. Let’s take these steps together toward better health!
Conclusion
The Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) marks a significant advancement in diabetes management, offering individuals a dynamic and immediate way to assess their blood sugar levels. It’s important to recognize that by integrating GMI into daily routines, patients can move beyond traditional metrics like A1C, gaining a clearer and more actionable understanding of their glycemic control. This shift not only enhances personal health management but also empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their diet, exercise, and medication.
Many patients find that key insights highlight the differences between GMI and A1C, emphasizing GMI’s real-time data capabilities and its role in facilitating timely adjustments to treatment plans. The compelling evidence suggests that GMI can lead to better patient engagement and improved health outcomes, particularly for those facing daily fluctuations in glucose levels. Moreover, the holistic strategies surrounding GMI—such as nutrition, exercise, and community support—underscore its comprehensive approach to diabetes management.
Embracing GMI is not merely about tracking numbers; it is about fostering a proactive mindset towards health. As individuals become more educated about their glucose levels, they can take meaningful steps towards better diabetes management. The future of diabetes care lies in leveraging innovative tools like GMI, encouraging patients to actively participate in their health journey and ultimately leading to a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI)?
The Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) is a tool used to assess average blood sugar levels over time, based on continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. It provides a more immediate snapshot of sugar levels compared to traditional methods like HbA1c.
How does GMI differ from HbA1c?
Unlike HbA1c, which reflects average blood sugar over a two to three-month period, GMI offers a dynamic assessment of glycemic control expressed as a percentage derived from mean glucose readings aligned with expected HbA1c values.
What lifestyle strategies can complement GMI in managing diabetes?
Holistic lifestyle strategies that can complement GMI include nutrition, exercise, community support, and stress management.
How can exercise impact diabetes management?
Regular exercise, particularly in scenic areas, can enhance insulin sensitivity and help control weight, both of which are crucial for effective diabetes management.
What dietary recommendations support blood sugar regulation?
A balanced diet rich in local produce, such as avocados and berries, supports overall health and aids in regulating blood sugar levels.
How does GMI benefit patients and healthcare professionals?
GMI provides immediate insights into blood sugar level variations, allowing for prompt interventions and adjustments to treatment strategies, which can improve blood sugar control.
What is the significance of GMI in contemporary health practices?
GMI offers a clearer view of an individual’s glycemic control, paving the way for improved treatment strategies and enhancing patient engagement in diabetes management.
What future implications does GMI have for diabetes management?
Integrating GMI into diabetes management, along with personalized functional medicine approaches and community wellness programs, marks a significant shift in how diabetes is monitored and managed, especially looking ahead to 2025.