Overview
Managing diabetes can be a challenging journey, and understanding how to navigate it is crucial. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) has established important criteria for diagnosing diabetes, which serves as a guiding light for many. By recognizing the significance of accurate identification, we can take meaningful steps toward managing this chronic condition effectively.
Key diagnostic tests, such as the A1C test, fasting plasma glucose, and oral glucose tolerance test, play a vital role in this process. It’s important to recognize that early diagnosis can lead to better health outcomes. Many patients find that when they are diagnosed promptly, they can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications associated with diabetes.
As you consider these insights, remember that you are not alone in this. Many individuals share similar struggles, and there is support available. Taking action towards understanding diabetes can lead to a healthier, more fulfilling life. If you’re interested, the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program offers a compassionate approach to making positive changes. Together, we can work towards a brighter future.
Introduction
In a world where diabetes impacts millions, it’s essential to understand this complex condition more than ever. As a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels, diabetes manifests in various forms, each requiring unique management strategies. From the autoimmune nature of Type 1 diabetes to the lifestyle-related challenges of Type 2, the implications of this disease reach far beyond individual health, affecting public health systems and economies.
It’s important to recognize that with rising prevalence rates and staggering costs associated with diabetes care, the need for early diagnosis and effective management has never been more pressing. Many patients find that understanding their condition empowers them to take control of their health. This article delves into the key concepts and classifications of diabetes, the critical role of the American Diabetes Association’s diagnostic criteria, and the importance of continuous monitoring and early intervention. Together, we can navigate this journey toward better health and well-being.
Define Diabetes: Key Concepts and Classifications
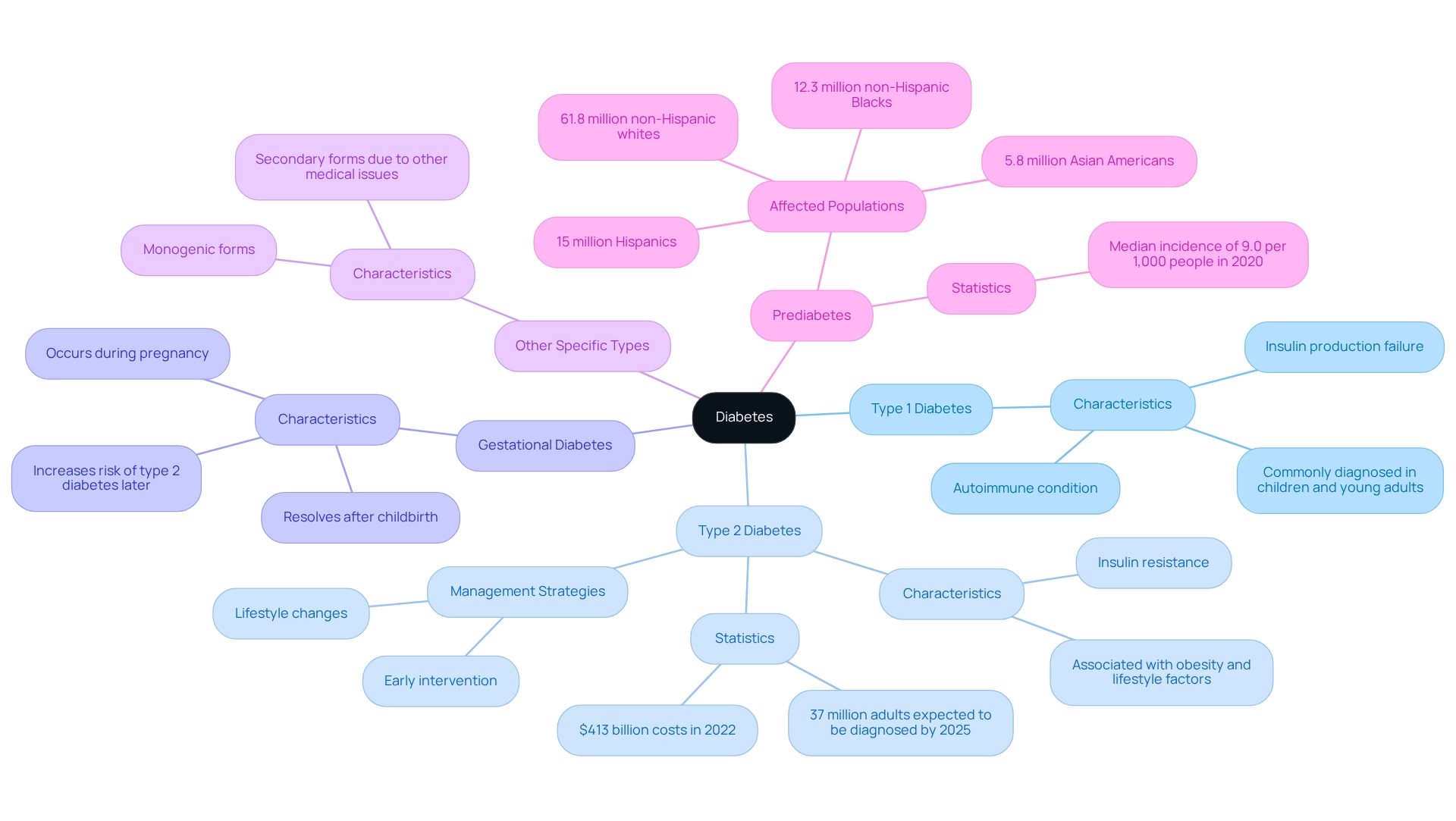
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that can feel overwhelming, characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to issues with insulin secretion or action. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recognizes several key types of diabetes that are important to understand:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune condition occurs when the body cannot produce insulin, often diagnosed in children and young adults.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, typically linked to insulin resistance and often associated with obesity and lifestyle factors. As we look towards 2025, approximately 37 million adults in the U.S. are expected to be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, underscoring a significant public health challenge. In 2022, the direct and indirect costs of diabetes-related conditions in the United States reached a staggering $413 billion, highlighting the urgent need for action.
- Gestational Diabetes: This type arises during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth, but it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Other Specific Types: This includes conditions such as monogenic and secondary forms that arise due to other medical issues.
Understanding these classifications is vital for recognizing the appropriate diagnostic criteria, specifically the American Diabetes Association criteria for diagnosis of diabetes, and treatment approaches. It’s important to recognize that early intervention and lifestyle changes can significantly improve outcomes, especially for those at risk of developing type 2 diabetes. In San Marcos, CA, individuals can embrace holistic lifestyle strategies, such as enjoying outdoor activities, focusing on a balanced diet rich in local produce, and participating in community wellness programs. These approaches not only help manage blood sugar levels but also enhance overall well-being.
Many patients find that adopting these strategies can be life-changing. Recent statistics reveal that the median county-level incidence of diagnosed blood sugar disorders was 9.0 per 1,000 people in 2020, emphasizing the need for effective management strategies as we approach 2025. Expert insights stress the importance of understanding these conditions, as they directly impact treatment choices and personal education. For instance, Dr. Sharita E. Warfield notes, “Embracing these behavioral modifications early in life aids in enhancing life quality and averting the emergence of prediabetes, which ultimately results in Type 2 if no action is taken.” By providing patients with information about their condition, healthcare providers can foster a proactive approach to managing diabetes.
It is also crucial to acknowledge the populations affected by prediabetes, which include 61.8 million non-Hispanic whites, 15 million Hispanics, 12.3 million non-Hispanic Blacks, and 5.8 million Asian Americans. The World Health Organization highlights the global burden of this condition, reinforcing the need for comprehensive strategies to address this growing health concern.
Explore the American Diabetes Association Diagnostic Criteria
The essential diagnostic criteria for diabetes provided by the American Diabetes Association criteria for diagnosis of diabetes play a vital role in accurately identifying and managing this condition. It’s important to recognize that these criteria can significantly impact your health journey. They include:
- A1C Test: An A1C value of 6.5% or above indicates a condition, reflecting average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. Many patients appreciate this test for its convenience and reliability.
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG): A fasting blood sugar measurement of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or higher confirms the condition. This test requires fasting overnight, making it a straightforward option for diagnosis.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): A 2-hour plasma sugar concentration of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or greater during an OGTT suggests a diabetic condition. This test assesses how your body reacts to sugar and is particularly useful for detecting insulin resistance.
- Random Plasma Glucose: A random blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher, accompanied by typical symptoms of hyperglycemia, verifies the condition. This test can be performed at any time, allowing for flexibility in diagnosis.
These criteria are crucial for ensuring that individuals receive the appropriate care tailored to their unique situations. Recent statistics reveal that approximately 5.8 million Asian Americans are diagnosed with prediabetes, underscoring the urgent need for effective diagnostic strategies. Furthermore, a 2021 study highlighted that 97.6 million U.S. adults had prediabetes, emphasizing the importance of early detection and intervention to prevent progression to type 2 diabetes. By utilizing these diagnostic methods, healthcare providers can better support individuals in managing their health and working toward remission.
Jason Shumard emphasizes the significance of providing individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, fostering an environment where people can reclaim their health and well-being. When selecting diagnostic examinations, it’s essential to consider risk factors and convenience, ensuring a personalized approach to diagnosing the condition. Additionally, insights from specialists highlight the importance of the A1C and FPG tests in understanding and managing the condition effectively. As we look toward 2025, it is vital for both patients and healthcare providers to stay informed about the latest American Diabetes Association criteria for diagnosis of diabetes.
Understanding the Importance of Early Diagnosis
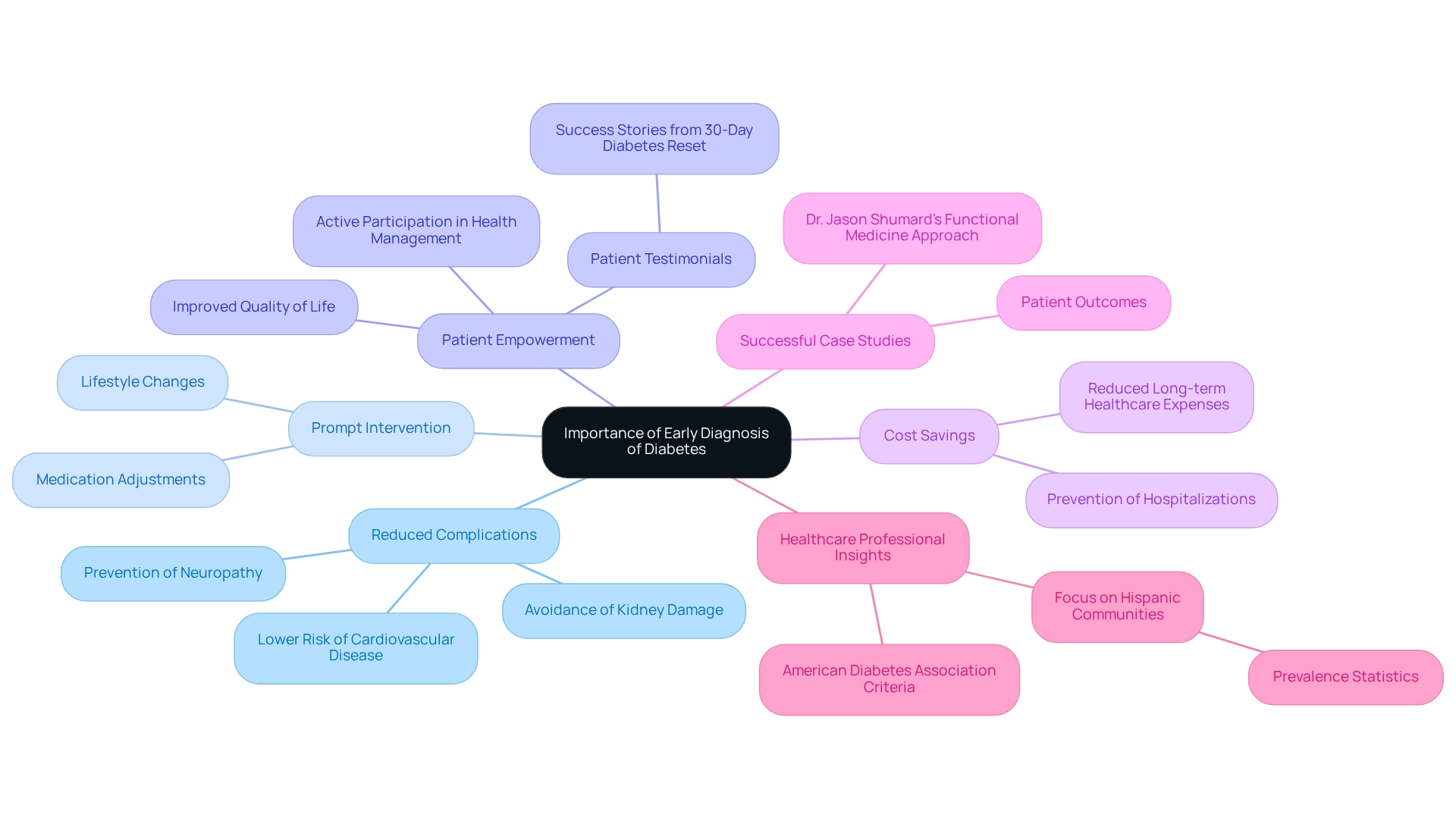
Early diagnosis of diabetes is crucial for several compelling reasons:
-
It’s important to recognize that timely identification of diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications, including cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage. Research shows that early intervention can lower the occurrence of these conditions, ultimately enhancing outcomes for individuals.
-
Many patients find that an early diagnosis facilitates prompt intervention strategies, such as lifestyle changes and medication adjustments, essential for maintaining blood glucose levels within target ranges. This proactive approach can lead to better long-term health management.
-
When individuals comprehend their condition at an early stage, they are more inclined to actively participate in their health management. This empowerment not only enhances their quality of life but also fosters a sense of control over their health journey. As one patient from Dr. Jason Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program shared, “I was on two different meds that weren’t working and was told that I needed insulin. After joining this program, I lost 55 lbs, and my A1C dropped from 9.1 to 5.7. I feel so much better and don’t need my meds anymore!” Such testimonials highlight the significant improvements in health and well-being that can follow early intervention.
-
Moreover, early treatment can lead to considerable cost savings by reducing long-term expenses linked to managing complications related to the condition. For example, recent statistics indicate that early diagnosis can lower healthcare expenses by preventing hospitalizations and extensive treatments associated with advanced complications.
-
Numerous case studies from Dr. Jason Shumard’s Functional Medicine Approach illustrate patients who have successfully prevented complications through early diagnosis and intervention. These individuals often report enhanced health results and a greater capacity to manage their condition effectively.
-
Healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of early diagnosis based on the American Diabetes Association criteria for diagnosis of diabetes in preventing complications. Their insights underline that proactive screening and awareness can lead to better health trajectories for individuals at risk. Furthermore, considering the increased occurrence of this condition among Hispanic adults—13.3% being Puerto Rican, 11.1% Mexican or Mexican American—highlights the necessity for focused early diagnosis initiatives in various communities.
By identifying the signs and symptoms of this condition and pursuing prompt diagnosis, individuals can greatly improve their health results and lower the chances of serious complications. For those keen on taking proactive measures towards improved health, the Integrative Wellness Center provides extensive services aimed at assisting individuals in their journey to effectively managing their condition.
The Role of Continuous Monitoring in Diabetes Management
Continuous monitoring is essential for effective diabetes management, encompassing several key components:
-
Blood Sugar Monitoring: Consistently assessing blood sugar readings helps you understand how your diet, physical activity, and medications affect your control. It’s important to recognize that around 31.9% of adults with high blood sugar are physically inactive, which can negatively impact blood glucose levels. This highlights the need for increased awareness and action in promoting physical activity as part of diabetes management. Many patients find that participating in a structured walking program, as detailed in our user manual, can greatly improve their physical activity levels. Start by evaluating your current fitness level and setting realistic goals, such as committing to a daily walk of 10-15 minutes. This gradual method aids in improved sugar management and overall health.
-
A1C Testing: This essential examination should be performed at least twice a year to assess long-term sugar management and enable necessary modifications to treatment strategies. Regularly monitoring A1C values is crucial for evaluating your overall blood sugar management.
-
Monitoring for Complications: Routine check-ups for potential complications, including eye exams and foot assessments, are vital for early detection and intervention, helping to prevent serious health issues.
-
Employing Technology: Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) signify a major improvement in diabetes management. These devices provide real-time information on sugar concentrations, allowing you to make prompt changes to your treatment. For example, case studies have shown that individuals using CGMs experienced enhanced blood glucose management, with some research suggesting a decrease in A1C levels by as much as 1.5% within three months of usage. This illustrates their effectiveness in improving patient outcomes. As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By offering individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where people can reclaim their health and well-being.”
By incorporating ongoing observation into your daily practices, you can actively engage in your health management, resulting in enhanced health outcomes and an improved quality of life. Additionally, seeking community support and engaging in local wellness programs can further empower you on your journey. As diabetes educators emphasize, the benefits of consistent blood glucose monitoring cannot be overstated, as it fosters a proactive approach to managing this chronic condition.
Conclusion
Understanding diabetes is vital in a world where its prevalence continues to rise. It’s important to recognize that many individuals face challenges in managing this condition. This article has explored the classifications of diabetes, emphasizing the differences between Type 1, Type 2, gestational, and other specific types. Recognizing these distinctions is crucial for proper diagnosis and management, as each type requires tailored strategies to effectively control blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Many patients find that the role of the American Diabetes Association’s diagnostic criteria cannot be overstated. By utilizing tests such as the A1C, fasting plasma glucose, and oral glucose tolerance tests, healthcare providers can accurately identify diabetes early, which is essential for effective management. Early diagnosis not only empowers patients but also plays a significant role in preventing complications and reducing healthcare costs associated with advanced diabetes.
Continuous monitoring further enhances diabetes management, allowing patients to engage actively in their health. Regular blood glucose checks and A1C testing, along with the use of technology like continuous glucose monitors, provide valuable insights that can lead to better health outcomes. By fostering a proactive approach and encouraging lifestyle changes, individuals can take control of their diabetes journey, improving their quality of life.
In conclusion, as the global burden of diabetes continues to grow, the importance of early diagnosis, effective management strategies, and continuous monitoring becomes increasingly clear. By equipping individuals with the knowledge and tools they need, it is possible to navigate the complexities of diabetes and pave the way for healthier futures. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and with the right support and information, a healthier life is within reach.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to issues with insulin secretion or action.
What are the main types of diabetes recognized by the American Diabetes Association (ADA)?
The main types of diabetes recognized by the ADA are Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, Gestational Diabetes, and Other Specific Types.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune condition that occurs when the body cannot produce insulin, often diagnosed in children and young adults.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 Diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, typically linked to insulin resistance and often associated with obesity and lifestyle factors. It is projected that approximately 37 million adults in the U.S. will be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes by 2025.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational Diabetes arises during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth, but it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
What are Other Specific Types of diabetes?
Other Specific Types of diabetes include conditions such as monogenic and secondary forms that arise due to other medical issues.
Why is it important to understand the classifications of diabetes?
Understanding these classifications is vital for recognizing the appropriate diagnostic criteria and treatment approaches, which can significantly improve outcomes, especially for those at risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
What lifestyle strategies can help manage diabetes?
Holistic lifestyle strategies, such as engaging in outdoor activities, focusing on a balanced diet rich in local produce, and participating in community wellness programs, can help manage blood sugar levels and enhance overall well-being.
What is the significance of early intervention in diabetes management?
Early intervention and lifestyle changes can significantly improve outcomes and help prevent the emergence of prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes.
What populations are affected by prediabetes?
Populations affected by prediabetes include 61.8 million non-Hispanic whites, 15 million Hispanics, 12.3 million non-Hispanic Blacks, and 5.8 million Asian Americans.