Overview
This article highlights the importance of effectively using the DKA management algorithm, offering a structured approach to diagnosing and treating diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). It’s crucial to recognize the symptoms early, as this can lead to timely interventions. By following a step-by-step management algorithm, patients can feel more secure in their care journey. Additionally, integrating patient education and personalized care strategies not only improves health outcomes but also helps reduce complications associated with DKA. Many patients find that understanding their condition empowers them to take control of their health, leading to a more fulfilling life.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate attention. It is characterized by dangerously high blood sugar levels, the production of ketones, and metabolic acidosis. Many people may not realize that DKA often arises when insulin is in short supply, prompting the body to break down fat for energy. With diabetes being a leading cause of death in the United States, it’s crucial to understand DKA’s symptoms and management strategies to prevent severe complications.
This article aims to explore the complexities of DKA, delving into its pathophysiology, clinical signs, and the essential steps for effective management. It’s important to recognize that early identification and proactive patient education can make a significant difference. By understanding DKA better, both healthcare providers and patients can navigate the challenges posed by this critical condition more effectively. Together, we can work towards improving health outcomes and enhancing quality of life.
Understanding Diabetic Ketoacidosis: An Overview
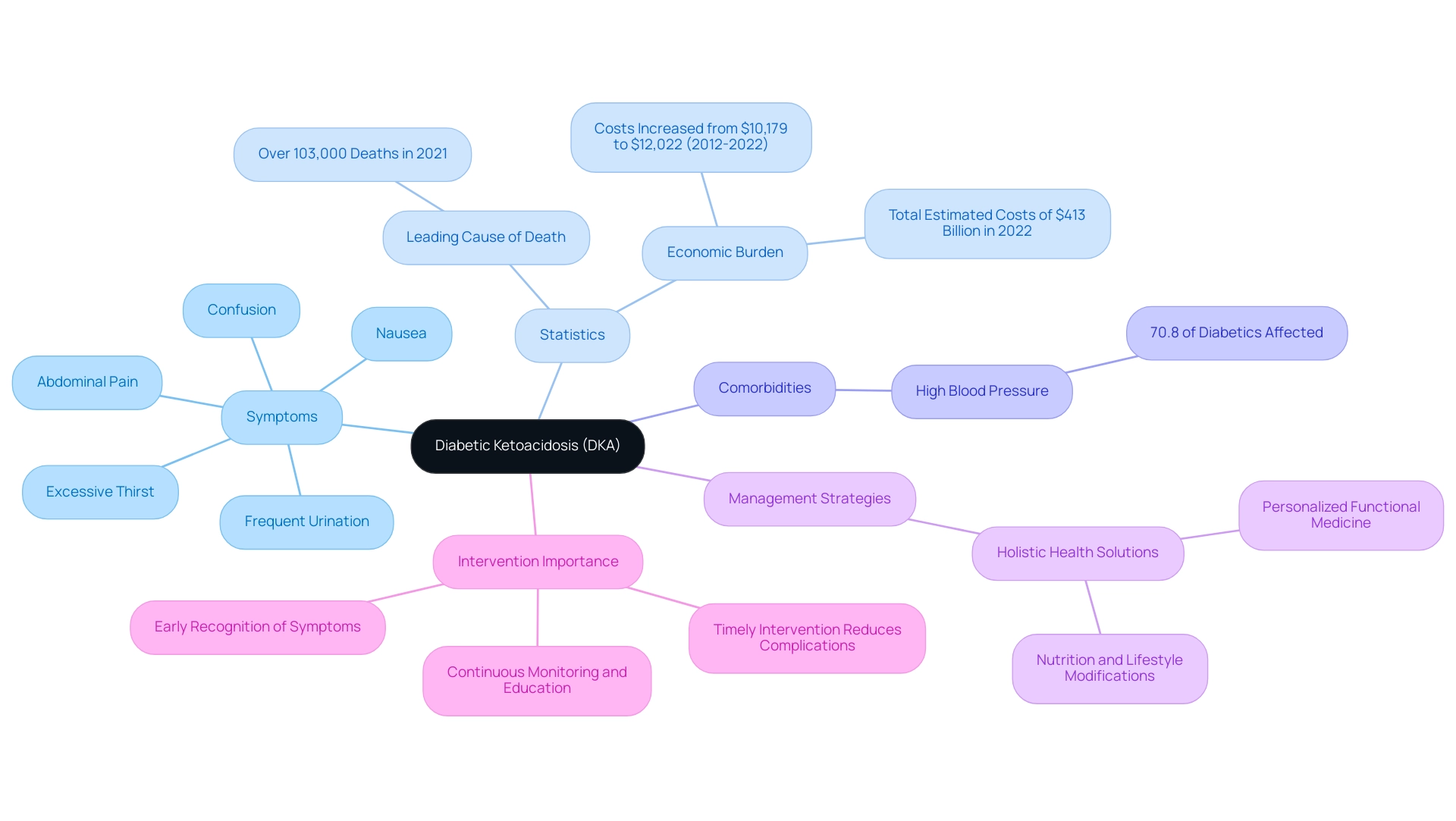
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious and potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes, characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, the production of ketones, and metabolic acidosis. This condition often arises when the body lacks sufficient insulin, leading to the breakdown of fat for energy and the accumulation of ketones in the bloodstream. It’s important to recognize the key symptoms of DKA, which include:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain
- Confusion—each requiring immediate attention.
Recent statistics highlight the urgency of addressing DKA. Did you know that diabetes was the eighth leading cause of death in the United States as of 2021, accounting for over 103,000 fatalities? Additionally, the economic burden associated with diabetes reached an estimated $413 billion in 2022, with excess medical costs per person rising from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022. This underscores the critical need for effective oversight strategies.
Alarmingly, 70.8% of U.S. adults diagnosed with diabetes also exhibit high blood pressure, a common comorbidity that can worsen DKA complications. Many patients find that understanding these connections can empower them to take proactive steps in managing their health.
The importance of early recognition of DKA cannot be overstated. Timely intervention can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications. Recent studies indicate that factors such as urban residence, the presence of infections, and poor glycemic control can determine DKA risk. For instance, individuals with a history of poor glycemic control were more likely to experience severe DKA complications, highlighting the necessity for continuous monitoring and education.
Expert opinions reinforce the critical nature of recognizing DKA symptoms early. Endocrinologists emphasize that understanding the signs of DKA can lead to quicker treatment and better outcomes. Dr. Jason Shumard, D.C., of Integrative Wellness Center, states, “By providing individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where they can reclaim their health and well-being.”
His approach emphasizes holistic health solutions, integrating personalized functional medicine strategies that focus on tailored nutrition and lifestyle modifications to manage diabetes effectively. It’s important to remember that you are not alone in this journey; support is available.
As the landscape of diabetes management evolves, ongoing research continues to shed light on the complexities of DKA, revealing new insights into its symptoms and management algorithms. By promoting awareness and education regarding DKA, healthcare providers can enhance care coordination and improve outcomes, ultimately reducing the prevalence and impact of this serious condition.
In examining the etiology of DKA, it is essential to summarize abnormal laboratory parameters that may indicate its onset, such as:
- Elevated blood glucose readings
- Increased ketone bodies
- Metabolic acidosis
Understanding these parameters is crucial for effective patient management and intervention, particularly in the context of holistic lifestyle strategies that emphasize nutrition, exercise, community support, and stress management. Remember, taking small steps can lead to significant changes in your health journey.
Pathophysiology of DKA: How It Develops
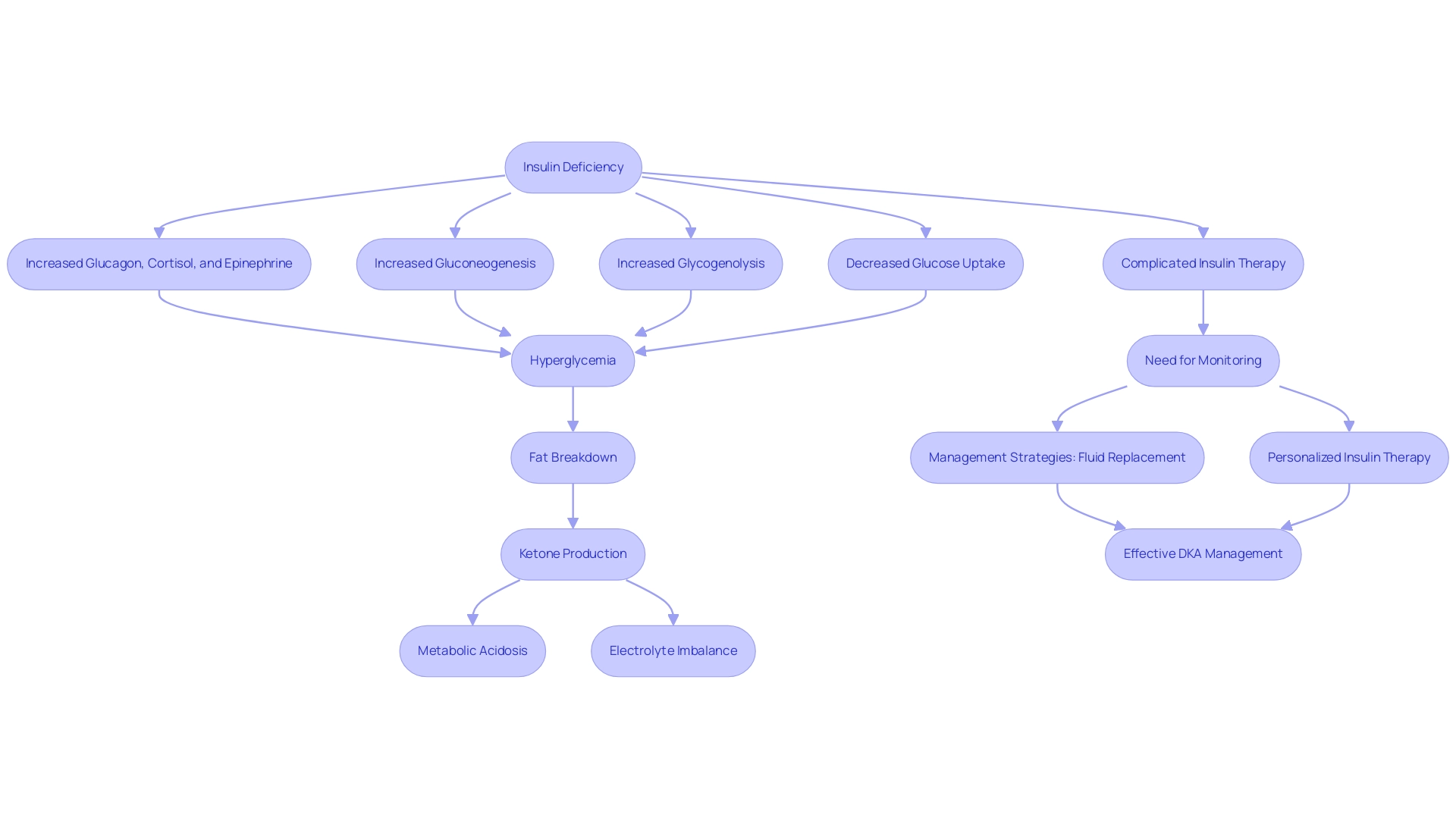
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) can feel overwhelming, arising from a complex interplay of insulin deficiency and increased amounts of counter-regulatory hormones like glucagon, cortisol, and epinephrine. This hormonal imbalance plays a significant role in increasing gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis, leading to hyperglycemia. As insulin levels drop, glucose struggles to enter cells, prompting the body to rely on fat as an alternative energy source.
The breakdown of fat results in the production of ketones, which can lead to metabolic acidosis and disrupt electrolyte balance, particularly causing hypokalemia. It’s important to recognize that recent research underscores the critical role of insulin deficiency in DKA’s pathophysiology, revealing that this deficiency not only worsens hyperglycemia but also triggers hormonal responses that complicate the situation further. Many patients find that the presence of counter-regulatory hormones can significantly hinder the effectiveness of insulin therapy, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and adjustments in treatment protocols.
Infection is a common trigger for DKA, making prompt antibiotic treatment essential if suspected. Effectively managing DKA requires a multifaceted approach, including hospitalization for fluid replacement, electrolyte oversight, and customized insulin therapy tailored to individual needs—especially for special groups like pregnant women and individuals with renal failure. Revised guidelines emphasize the importance of education regarding insulin dosing and recognizing early symptoms to prevent recurrence.
Statistics show that timely intervention, such as introducing an IV glucose 10% infusion when blood glucose is <14 mmol/L, can drastically reduce both morbidity and mortality associated with DKA. This underscores the necessity for healthcare providers to remain vigilant in identifying and treating this condition promptly.
Understanding the pathophysiology of DKA is essential for developing an effective management algorithm. By addressing the underlying causes of insulin deficiency and hormonal imbalance, healthcare professionals can better equip individuals with the knowledge and tools necessary for effective diabetes management. This is where the Integrative Wellness Center’s personalized approach shines, as it emphasizes functional medicine strategies that consider each individual’s unique health profile.
Specific strategies employed by the Integrative Wellness Center include comprehensive assessments, dietary modifications, and lifestyle interventions tailored to individual needs. As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By offering individuals actionable insights and practical tools, the center cultivates an environment where they can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to enhanced quality of life and decreased dependence on conventional medical interventions.” This holistic approach to educating and empowering individuals is crucial in managing DKA effectively with the management algorithm, enabling them to set SMART goals and track their progress using tools such as fitness apps and journals, thereby enhancing their overall health management journey.
Recognizing the Clinical Signs of DKA
Recognizing the common clinical signs of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is critical for early intervention and support. These signs include:
- Polyuria: Frequent urination occurs as the body tries to eliminate excess glucose, leading to osmotic diuresis.
- Polydipsia: Patients often experience excessive thirst, a response to fluid loss, signaling dehydration.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms may come with abdominal pain, indicating metabolic distress.
- Kussmaul Breathing: This deep, labored breathing pattern arises as the body attempts to correct acidosis by expelling carbon dioxide.
- Fruity-Smelling Breath: A distinctive odor from acetone, a byproduct of fat metabolism, is often noted in individuals with DKA.
It’s important to recognize these signs early, as timely medical intervention can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications. Many patients find that awareness of DKA symptoms remains a challenge, highlighting the need for improved education and training in symptom recognition. For instance, a study revealed that many individuals fail to identify early signs of DKA, which can delay treatment and worsen outcomes.
Furthermore, statistics indicate that the incidence of type 2 diabetes has significantly increased among all racial and ethnic groups from 2002 to 2018, with non-Hispanic Black children having the highest rates. This underscores the importance of awareness in diverse populations.
Healthcare professionals emphasize a proactive approach in managing symptoms using the DKA management algorithm. Regular education on recognizing these clinical signs is advocated, as early intervention can lead to better management outcomes. Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the Integrative Wellness Center fosters an environment where people can reclaim their health and well-being.”
Additionally, the latest clinical guidelines recommend that healthcare providers routinely evaluate individuals for these symptoms, especially in those with type 2 diabetes, to facilitate prompt and effective treatment using the DKA management algorithm.
To further empower individuals, incorporating effective strategies for progress tracking and goal-setting can enhance overall health management. Utilizing methods such as fitness apps, journals, and pedometers, individuals can set SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. For example, aiming to increase daily walking steps or gradually extending exercise duration can significantly boost motivation and accountability.
Research indicates that structured goal-setting can enhance performance, making it essential for individuals to regularly review their progress and adjust their goals as necessary. This holistic approach not only aids in managing DKA symptoms but also fosters a sense of achievement and engagement in their health journey. Moreover, it is crucial to recognize that severe starvation occurs after 2 or 3 days of fasting, further emphasizing the urgency of recognizing DKA symptoms.
Differential Diagnosis: Distinguishing DKA from Other Conditions
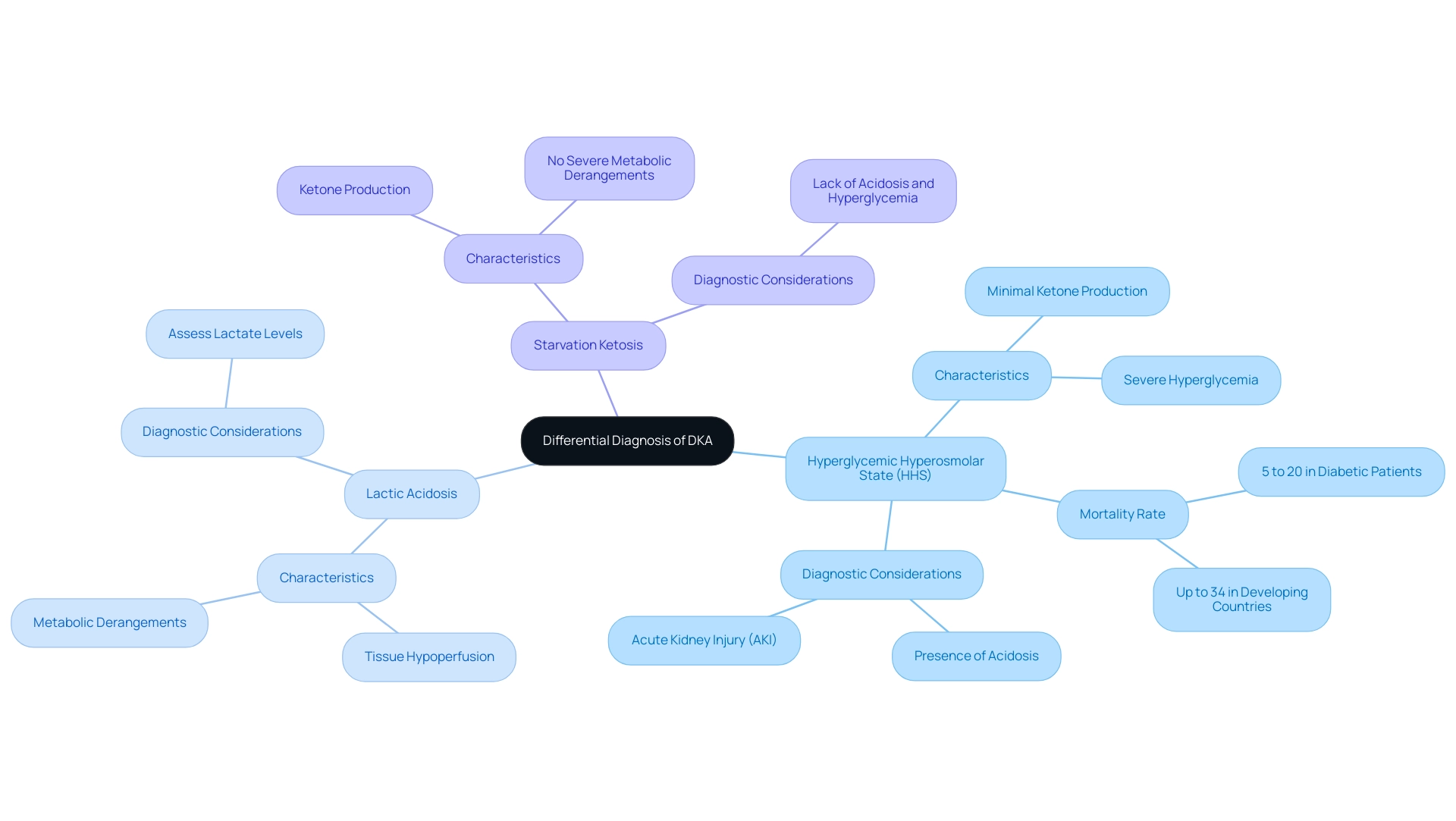
When diagnosing diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), it’s important to recognize the challenges you may face in distinguishing it from other conditions that present with similar symptoms. Here are some key conditions to consider:
-
Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State (HHS): This condition often arises in individuals with type 2 diabetes and is marked by severe hyperglycemia, frequently exceeding 600 mg/dL, without significant ketone production. It’s crucial to understand that, unlike DKA, HHS carries a higher mortality rate, especially in developing countries, where it can reach up to 34%. Recent statistics indicate that the mortality rate of diabetic patients who develop hyperglycemic emergencies ranges from 5% to 20%, highlighting the urgency of accurate diagnosis.
-
Lactic Acidosis: This condition can mimic DKA symptoms but is primarily caused by tissue hypoperfusion and metabolic derangements unrelated to insulin deficiency. Assessing lactate levels is essential to effectively distinguish between these two conditions.
-
Starvation Ketosis: This occurs in individuals without diabetes and is characterized by ketone production without the severe metabolic derangements typically seen in DKA. Patients may show elevated ketones but lack the acidosis and hyperglycemia associated with DKA.
Accurate diagnosis is critical for effective management, especially when utilizing the DKA management algorithm. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment strategies. A case study illustrates this point: an individual initially diagnosed with DKA was later found to have lactic acidosis, resulting in a significant delay in receiving appropriate treatment. This underscores the importance of a thorough differential diagnosis process, which aligns with Dr. Jason Shumard’s holistic approach to health, focusing on personalized care and education.
Experts emphasize the value of utilizing clinical guidelines and the DKA management algorithm to distinguish DKA from other hyperglycemic states effectively. Diabetes care specialists advocate this method to enhance outcomes for individuals and reduce the risk of complications linked to misdiagnosis. As Dr. Shumard states, “By providing individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where they can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.”
Additionally, patients with pure HHS can be categorized based on the presence of acidosis and acute kidney injury (AKI) according to KDIGO guidelines, further enriching the discussion on differential diagnosis.
Diagnostic Testing for DKA: Key Assessments
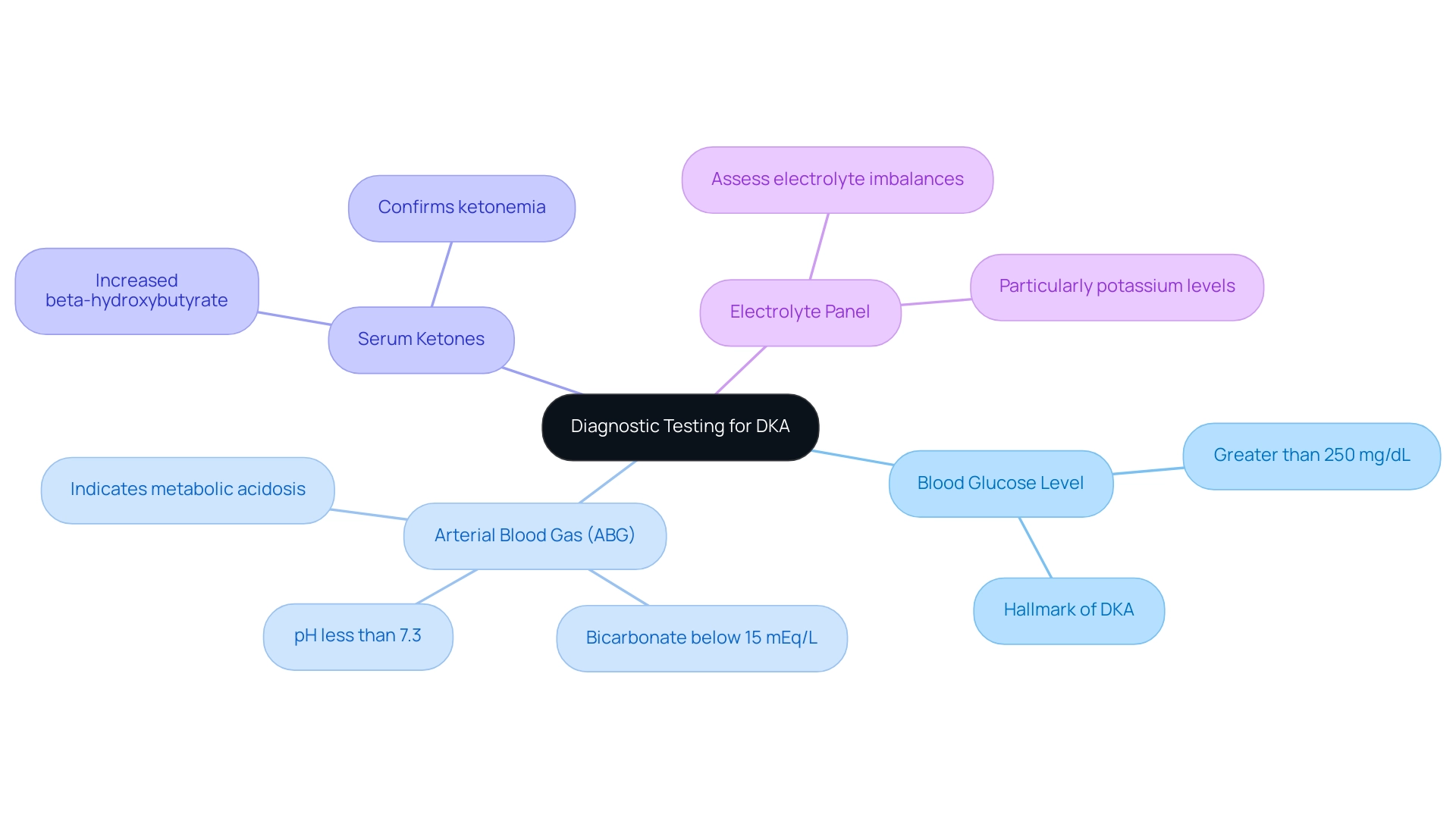
Key diagnostic tests for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) are essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. It’s important to recognize that these tests can significantly impact your health journey. They include:
- Blood Glucose Level: A hallmark of DKA, blood glucose levels are typically greater than 250 mg/dL, indicating significant hyperglycemia.
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG): This test reveals metabolic acidosis, characterized by a pH less than 7.3 and bicarbonate amounts below 15 mEq/L, which are critical indicators of DKA.
- Serum Ketones: Increased amounts of beta-hydroxybutyrate are indicative of ketonemia, confirming the presence of ketones in the bloodstream.
- Electrolyte Panel: This panel is vital for assessing electrolyte imbalances, particularly potassium levels, which can fluctuate significantly in individuals with DKA.
These diagnostic tests are not only crucial for confirming the diagnosis of DKA but also play a pivotal role in guiding the DKA management algorithm for treatment decisions. Many patients find that recent advancements in continuous ketone monitoring (CKM) systems have shown promise in improving adherence to monitoring practices, thereby reducing the incidence of DKA, especially in individuals at high risk. A case study titled “Rationale for Continuous Ketone Monitoring” highlighted the limitations of current monitoring methods and advocated for CKM technology, emphasizing the importance of educating individuals in managing their condition effectively.
Furthermore, expert opinions underscore the necessity of these assessments in the clinical setting. For instance, endocrinologists emphasize that timely and accurate diagnostic testing is fundamental to employing the DKA management algorithm for managing DKA and preventing complications. By integrating these key assessments into routine practice, healthcare providers can enhance outcomes and empower individuals to take control of their health.
Alongside these diagnostic measures, applying effective strategies for progress tracking and goal setting can significantly empower individuals in their diabetes management journey. Utilizing SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—can help you set realistic targets for your health, such as monitoring your blood glucose levels or adhering to a walking program. Specific tracking methods, including fitness apps, journals, and pedometers, can further enhance this process.
Regularly reviewing progress not only fosters accountability but also allows for the adaptation of goals in response to changing health conditions. As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the Integrative Wellness Center fosters an environment where people can reclaim their health and well-being.
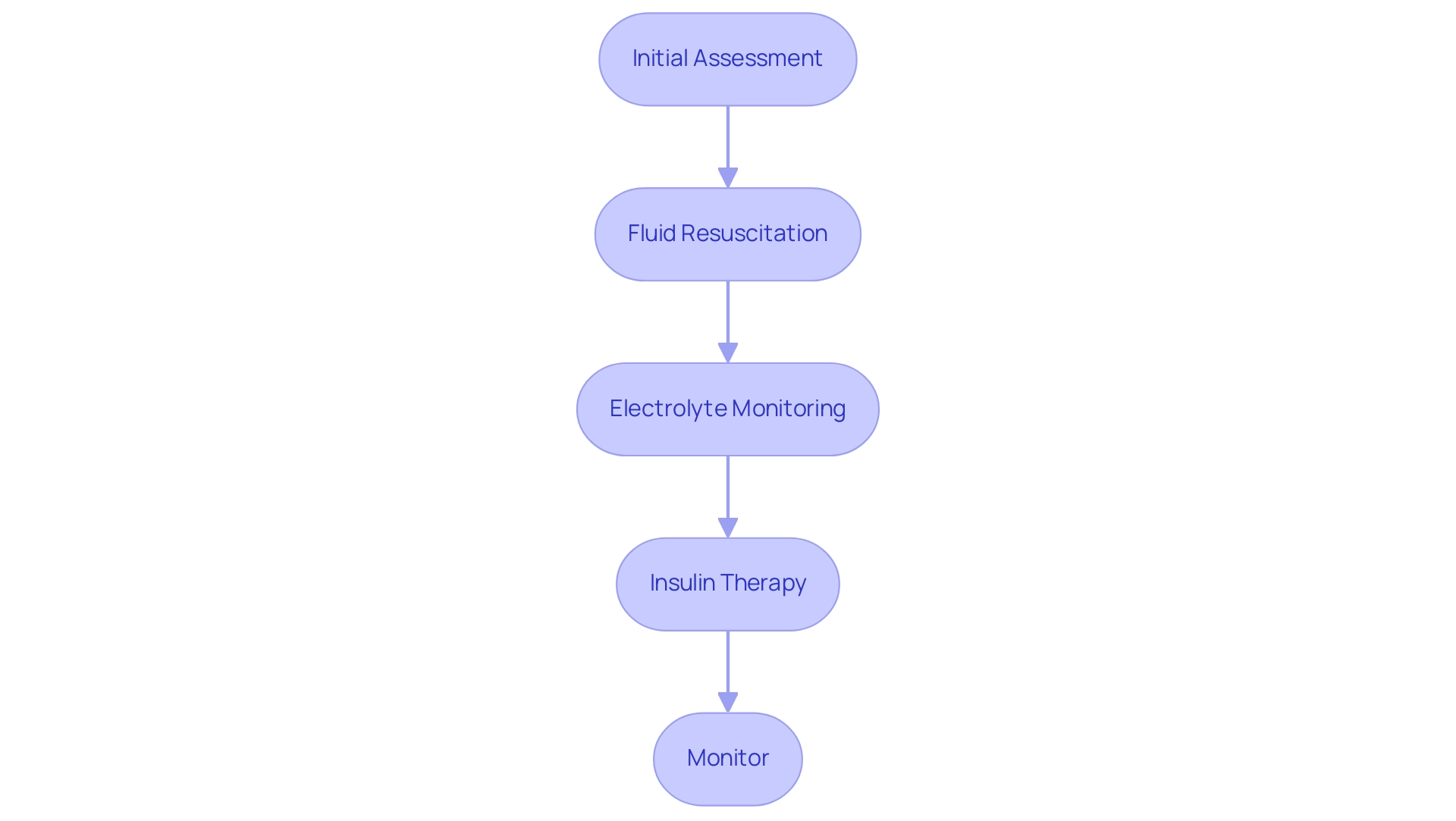
Step-by-Step DKA Management Algorithm
Managing diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is critical, and it’s essential to follow a structured DKA management algorithm that ensures comprehensive care while respecting patient rights and privacy. Let’s explore the steps together:
- Initial Assessment: It’s important to begin by evaluating vital signs, state of consciousness, and hydration status. This foundational step is crucial for determining the severity of the condition and guiding subsequent interventions.
- Fluid Resuscitation: Administer isotonic saline (0.9% NaCl) at a rate of 15-20 mL/kg for the first hour. Effective fluid resuscitation is vital to restore intravascular volume and improve renal perfusion, which is essential for the excretion of ketones and glucose.
- Electrolyte Monitoring: Regularly check potassium concentrations, as hypokalemia can occur with insulin therapy. Replacing electrolytes as necessary helps avoid complications related to rapid changes in potassium concentrations.
- Insulin Therapy: Initiate a continuous intravenous (IV) insulin infusion at a rate of 0.1 units/kg/hour. This step is critical for reducing blood glucose concentrations and halting ketogenesis, addressing the underlying metabolic derangements of DKA.
- Monitor: Continuously assess blood glucose, ketone levels, and electrolytes to guide treatment adjustments. Frequent monitoring allows for timely interventions and helps prevent potential complications.
Following the DKA management algorithm not only ensures effective oversight of DKA but also aligns with recent findings that emphasize the importance of an interprofessional approach in emergency settings. Many patients find that streamlined protocols have significantly reduced morbidity and mortality rates associated with DKA in developed countries. Interestingly, the mean total insulin dosage administered to individuals with DKA within their first 48 hours of treatment did not differ between preimplementation and postimplementation periods, indicating the effectiveness of established protocols.
However, challenges remain in developing regions, where socioeconomic factors contribute to higher mortality rates. The case study titled “Deterrence and Patient Education in Diabetes Management” highlights the crucial role of education on diabetes, including complications and treatment compliance, emphasizing the need for an interprofessional team in managing DKA effectively.
Incorporating expert insights into the DKA management algorithm underscores the necessity of ongoing education for healthcare providers and individuals alike. Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By offering individuals actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where they can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.” This approach not only empowers individuals to take control of their health but also ensures that their rights to privacy and personalized care are upheld, including the right to request special privacy protections and the right to inspect and copy their health information.
The Integrative Wellness Center implements these rights through specific programs that support individual empowerment and education, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and quality of life.
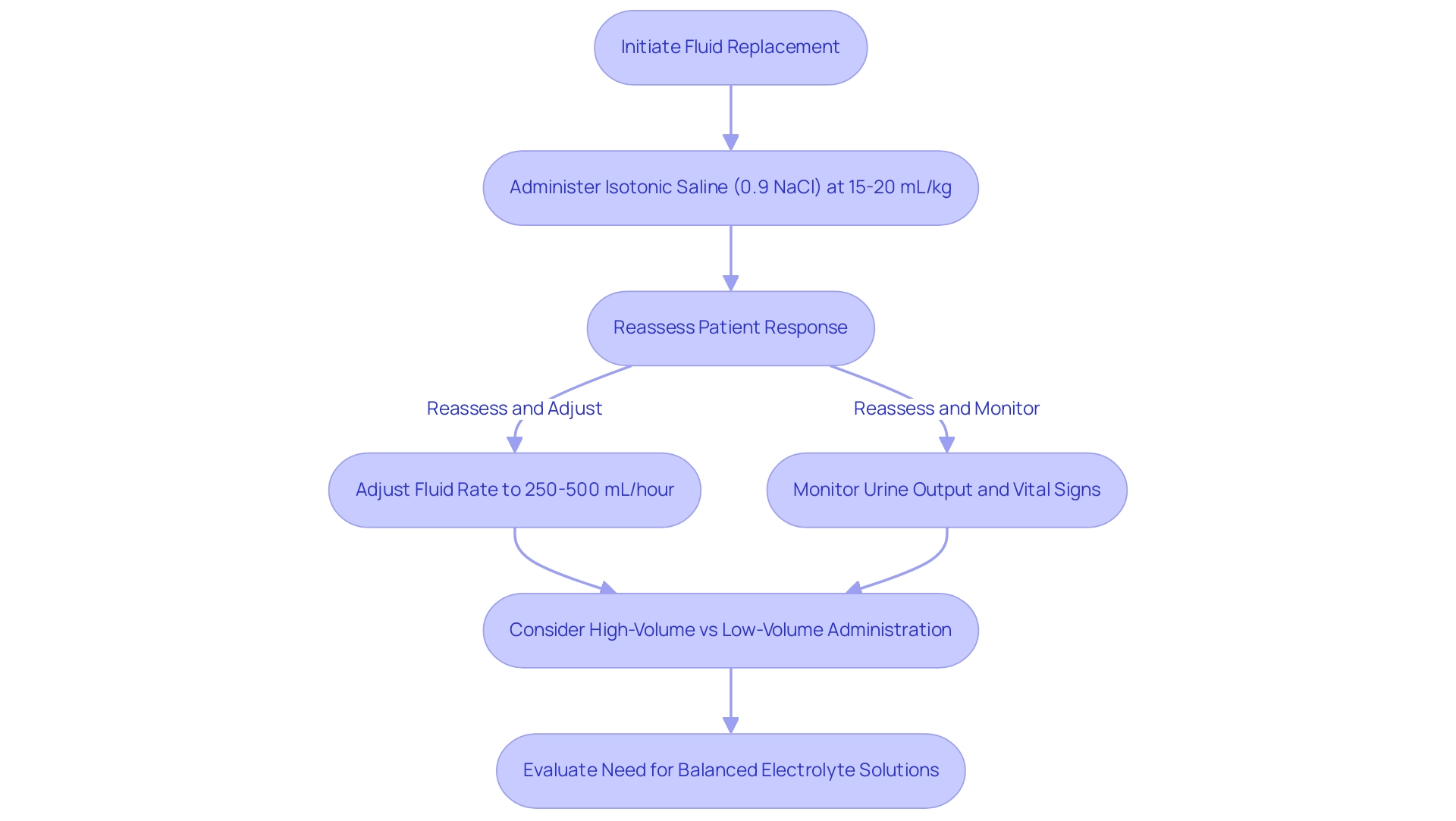
Fluid Replacement Strategies in DKA Management
Managing diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) can be daunting, and it’s important to recognize that fluid replacement is critical for correcting dehydration and restoring electrolyte balance. Initially, healthcare professionals typically recommend administering isotonic saline (0.9% NaCl) at a rate of 15-20 mL/kg for the first hour. This initial bolus is essential for rapid rehydration, allowing for a thorough reassessment to tailor subsequent fluid therapy based on how each individual responds.
After this initial resuscitation, fluid rates may be adjusted to 250-500 mL/hour, depending on ongoing needs and losses. Continuous monitoring of urine output and vital signs is vital to guide fluid therapy effectively. Many patients find that high-volume fluid administration can lead to faster metabolic normalization and shorter treatment durations, although it’s worth noting that the quality of evidence remains low.
A study by Bakes in 2016 highlighted the benefits of high-volume versus low-volume fluid administration in patients with type 1 diabetes experiencing DKA, favoring high volume for achieving metabolic normalization. Current research indicates a shift in the DKA management algorithm, advocating for balanced electrolyte solutions (BES) over traditional 0.9% saline for fluid resuscitation. This change is supported by emerging data suggesting improved outcomes with BES, though further trials are necessary to solidify these recommendations.
When calculating the total volume for rehydration, it’s helpful to assume a 10% deficit plus maintenance fluid, providing a clearer understanding of the fluid approach. In practice, the DKA management algorithm emphasizes effective fluid control, which not only addresses dehydration but also plays a crucial role in correcting electrolyte imbalances, particularly hyperglycemia and acidosis. Isotonic saline remains a key component in DKA treatment, as it helps maintain hemodynamic stability while facilitating the safe administration of insulin and other necessary interventions.
As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where they can reclaim their health and well-being.”
By following these best practices and employing evidence-based strategies, healthcare providers can significantly improve patient outcomes using the DKA management algorithm. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; support is available, and together we can navigate towards better health.
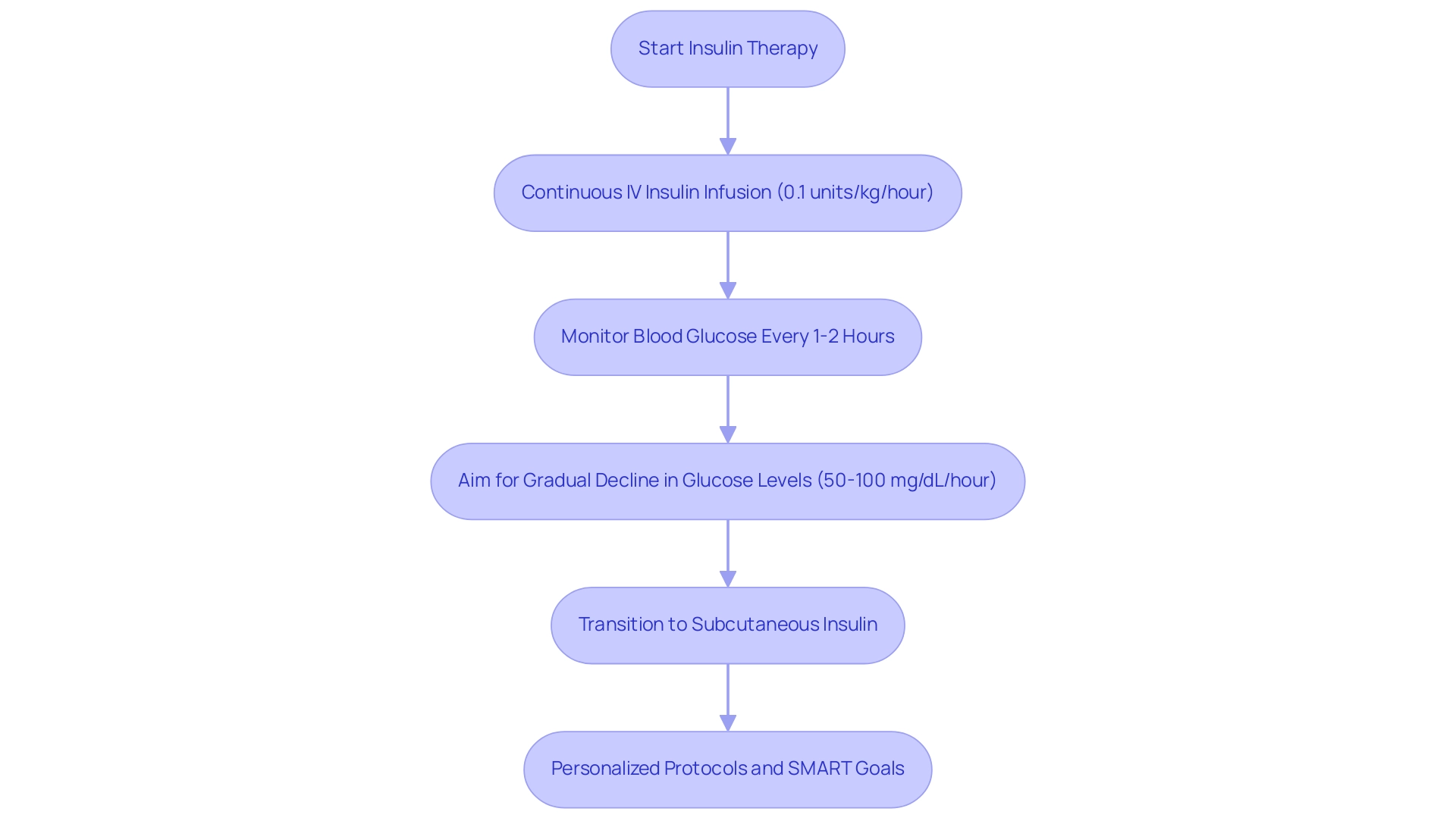
Insulin Therapy: Administration and Monitoring
Insulin therapy is a cornerstone in the management of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and adhering to a structured protocol is vital for effective care. It’s important to recognize that a standard protocol typically includes several key components:
- Continuous IV Insulin Infusion: Treatment begins with an infusion rate of 0.1 units/kg/hour. This rate should be adjusted based on frequent blood glucose monitoring to ensure optimal control.
- Monitoring: Blood glucose readings should be assessed every 1-2 hours at the outset of treatment. This frequent monitoring allows for timely adjustments to the insulin infusion rate, aiming for a gradual decline in glucose levels of approximately 50-100 mg/dL/hour. Many patients find that consistent monitoring is crucial, as studies indicate that inadequate monitoring can lead to complications and prolonged hospital stays. Additionally, current testing methods for ketone monitoring are often seen as inconvenient and costly, highlighting the challenges encountered in DKA oversight.
- Transitioning to Subcutaneous Insulin: Once DKA is resolved, a careful transition to subcutaneous insulin regimens is necessary. This transition should be tailored to the individual needs of each person, taking into account their previous insulin requirements and current metabolic status. Recent research underscores the importance of individualized insulin therapy protocols within the DKA management algorithm. For instance, a retrospective cohort study involving 93 individuals analyzed transitions from intravenous to subcutaneous insulin, revealing that successful transitions are critical to preventing recurrence of DKA. Transition failure, defined as the re-initiation of intravenous insulin within 24 hours, underscores the need for careful monitoring during this phase.
Expert insights from endocrinologists emphasize that effective monitoring of insulin treatment in DKA is not only about managing blood glucose but also about understanding the underlying metabolic derangements. This comprehensive approach aligns with Dr. Jason Shumard’s philosophy of addressing the root causes of diabetes through functional medicine, empowering individuals with the knowledge and tools necessary for long-term health management. By implementing SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—patients can enhance their focus and motivation in managing their diabetes.
For example, setting a goal to reduce blood glucose levels by a certain percentage within a specified timeframe can foster accountability and engagement in their treatment plan. As Dr. Shumard states, “By providing individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where they can reclaim their health and well-being.”
In summary, the DKA management algorithm incorporates continuous monitoring, personalized insulin protocols, and a focus on education as essential components of effective DKA care. This ultimately leads to improved outcomes and a reduced risk of complications. Dr. Shumard’s innovative methodologies provide actionable insights and practical tools for individuals, reinforcing the center’s commitment to empowering them in their health journey.
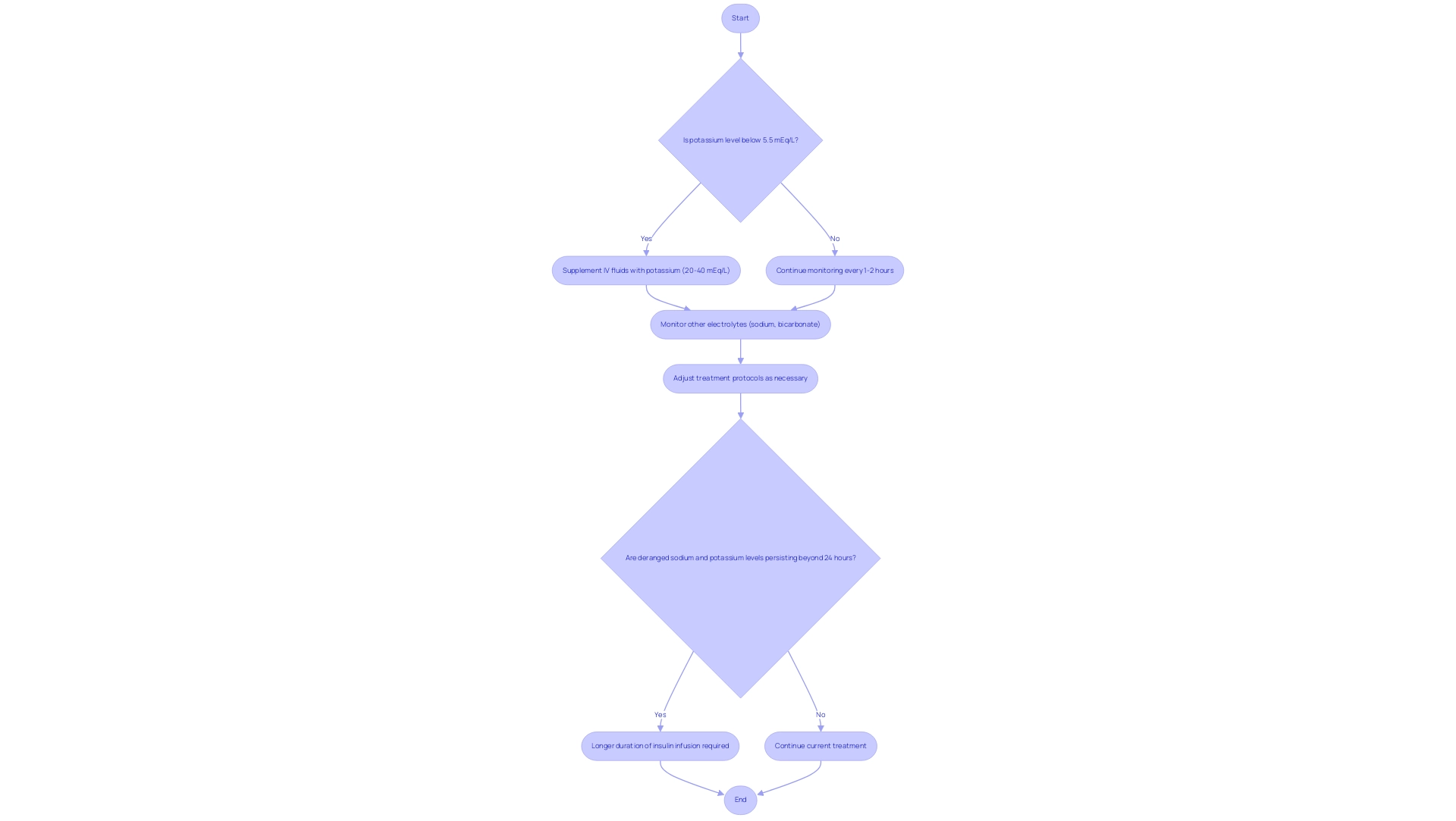
Managing Electrolytes: Potassium and Beyond
Effective electrolyte management is crucial in treating diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), especially regarding potassium concentrations. It’s important to recognize that monitoring serum potassium is essential, as fluctuations can significantly affect patient outcomes. When potassium levels drop below 5.5 mEq/L, healthcare providers typically recommend supplementing intravenous (IV) fluids with potassium, usually at a concentration of 20-40 mEq/L. This proactive step helps prevent complications associated with hypokalemia, which can occur due to insulin therapy that drives potassium into cells.
Many patients find that regular monitoring of potassium concentrations is vital, with checks occurring every 1-2 hours during treatment. This frequent assessment allows for timely adjustments to therapy, ensuring potassium levels remain within a safe range. Additionally, it’s crucial to monitor other electrolytes, such as sodium and bicarbonate, adjusting treatment protocols as necessary to correct any imbalances that may arise.
Current guidelines emphasize the importance of addressing electrolyte imbalances promptly. Persistence of deranged sodium and potassium concentrations beyond 24 hours is linked to significantly longer durations of insulin infusion requirements. This highlights the need for an interprofessional team approach in managing DKA, where effective fluid resuscitation, insulin therapy, and electrolyte replacement work together to reduce morbidity and mortality rates. As noted in the Journal of Pediatric Critical Care, “persistence of deranged sodium and potassium levels beyond 24 hours is associated with significantly longer duration of insulin infusion requirement.”
Recent findings underscore the importance of potassium regulation in DKA treatment. For instance, case studies have shown that timely potassium replacement strategies can lead to improved outcomes for individuals. Healthcare professionals advocate for a structured approach to electrolyte oversight, emphasizing that careful monitoring and replacement of potassium are integral to the DKA management algorithm.
By following these protocols, healthcare providers can enhance the safety and effectiveness of DKA treatment, ultimately improving the quality of care for individuals. The primary objectives of fluid replacement in DKA are to restore circulatory volume, eliminate ketones, and correct electrolyte imbalances, further supporting the comprehensive handling of this critical condition.
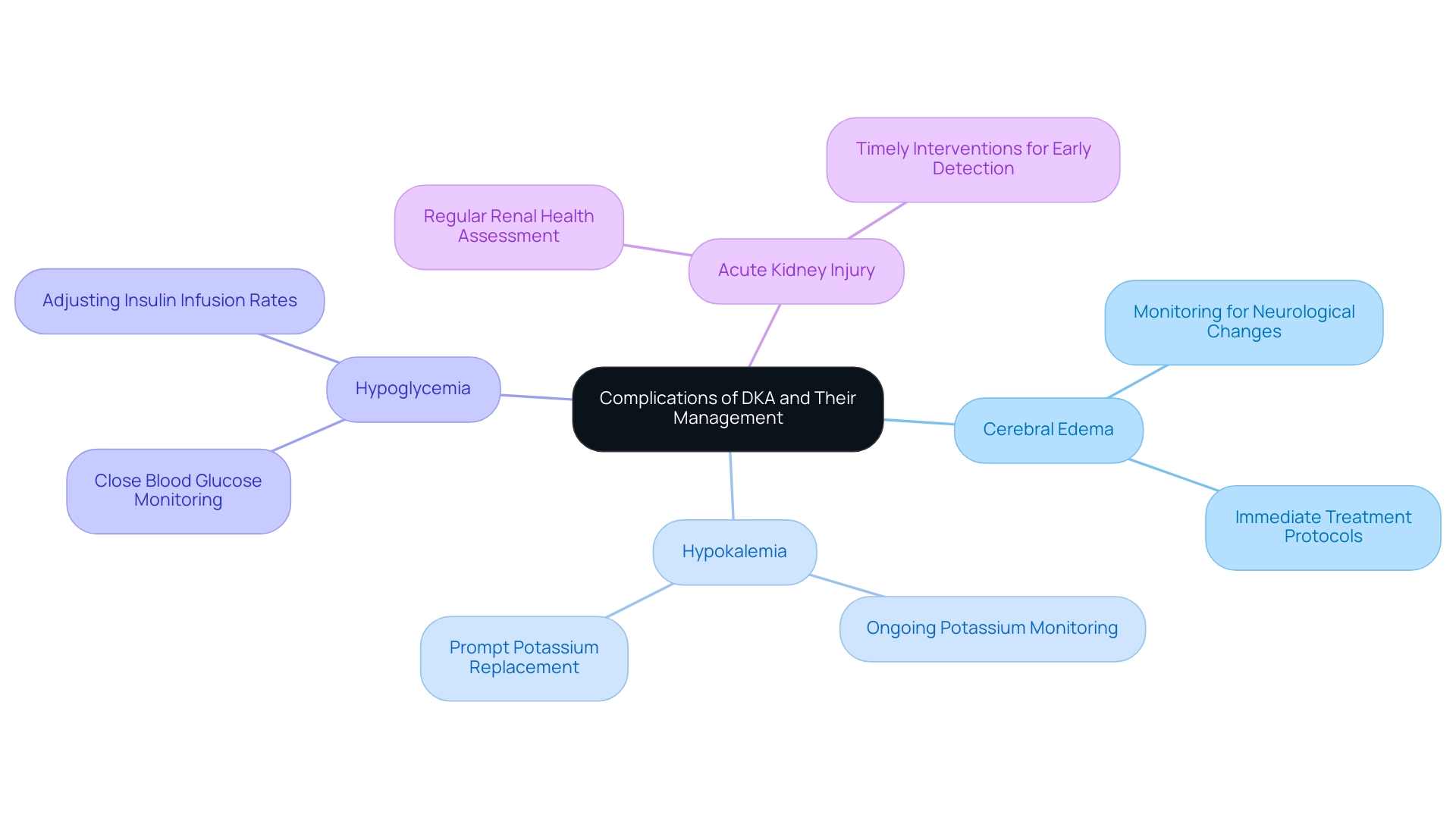
Complications of DKA and Their Management
Complications of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) can significantly influence outcomes and necessitate the use of a DKA management algorithm for vigilant monitoring. It’s important to recognize that these complications can be daunting, but understanding them can empower patients and caregivers alike. Key complications include:
-
Cerebral Edema: This rare but serious complication is particularly concerning in pediatric patients. Close observation for neurological changes is essential, and immediate treatment is critical if cerebral edema is suspected. Recent studies indicate that the incidence of cerebral edema in DKA patients, especially children, remains a pressing concern. This highlights the need for heightened awareness and prompt intervention, ensuring that every child receives the care they deserve.
-
Hypokalemia: Often a consequence of insulin therapy, hypokalemia can lead to severe cardiac and muscular complications. Ongoing observation of potassium concentrations is crucial, and prompt replacement is required to avoid negative effects. Many patients find that understanding these risks can help them feel more in control of their treatment.
-
Hypoglycemia: Rapid drops in blood glucose levels can occur, particularly if insulin infusion rates are not carefully adjusted. It’s vital to monitor blood glucose closely and modify insulin delivery to mitigate the risk of hypoglycemia. Remember, being proactive can make a significant difference in managing your health.
-
Acute Kidney Injury: DKA can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, which may adversely affect renal function. Regular assessment of renal health is vital, as early detection of acute kidney injury can facilitate timely interventions and improve patient outcomes. Taking charge of your health includes being aware of these potential complications.
Statistics indicate that hospitalization rates for DKA have increased significantly, especially among individuals below 45 years of age. This underscores the urgency of effective treatment strategies. Furthermore, 39.5% of adults with diabetes had a non-HDL amount of 130 mg/dL or higher, indicating cardiovascular disease risk. This is a critical consideration in managing DKA complications.
A comprehensive review of immediate care for severe DKA management algorithms is essential to synthesize current research findings and provide evidence-based recommendations for practitioners. It’s important to know that you are not alone in this journey; support is available.
Case studies have shown that despite the availability of urine ketone testing for over 50 years, its limitations can lead to an underestimation of DKA severity. Blood ketone meters, while offering more accurate measurements, are not universally accessible. This indicates a need for improved education on DKA symptoms and better access to reliable testing methods. As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By offering individuals actionable insights and practical tools, the center cultivates an environment where they can reclaim their health and well-being, ultimately leading to enhanced quality of life and decreased dependence on conventional medical interventions.”
This gap in resources highlights the significance of providing healthcare providers and individuals with the knowledge and tools required for effective DKA management algorithm implementation. Together, we can work towards better health outcomes and a brighter future.
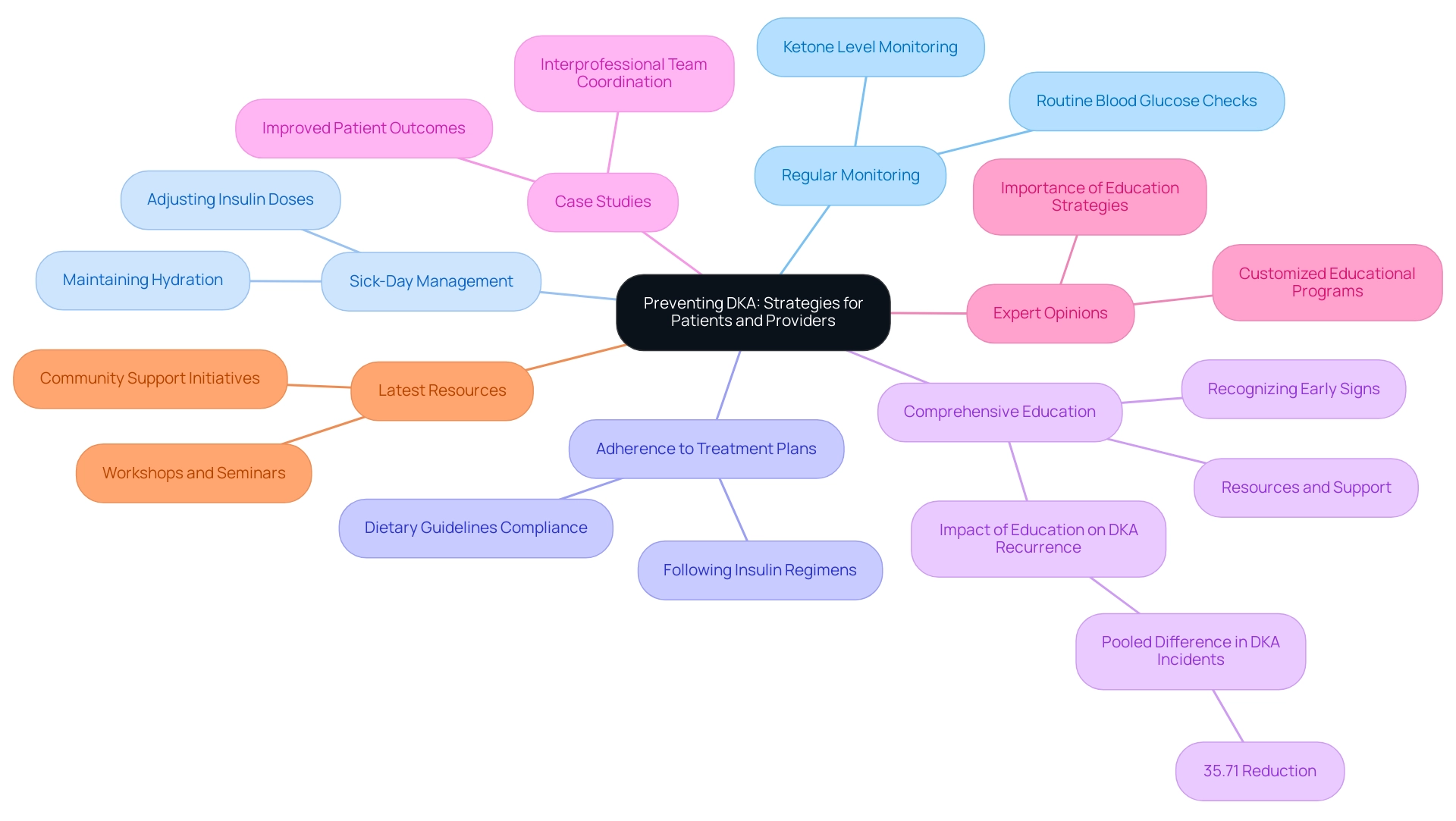
Preventing DKA: Strategies for Patients and Providers
Preventing diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) requires a compassionate, multifaceted approach that combines patient education with proactive management strategies. It’s crucial to address hospital safety concerns, where 7,000 incorrect medications are given to patients and 80,000 infections are acquired in hospitals each year.
-
Regular Monitoring: It’s important to encourage patients to routinely check their blood glucose and ketone levels, especially during times of illness or stress. This practice is essential, as prompt identification of increased amounts can prevent progression to the DKA management algorithm.
-
Sick-Day Management: Many patients find it vital to understand how to adjust their insulin doses and maintain adequate hydration during illness. This knowledge empowers them to manage their condition effectively, reducing the risk of DKA.
-
Adherence to Treatment Plans: Emphasizing the importance of following prescribed insulin regimens and dietary guidelines is essential for maintaining stable blood glucose levels. Non-compliance with treatment plans significantly contributes to the DKA management algorithm, making adherence a key focus in education efforts.
-
Comprehensive Education: Providing individuals with resources and support to understand their condition is critical. Recognizing early signs of the DKA management algorithm can lead to timely intervention. Studies indicate that effective education can significantly reduce DKA recurrence rates, with intervention campaigns showing a pooled difference in DKA incidents reaching 35.71%. This statistic underscores the effectiveness of targeted educational initiatives.
-
Case Studies: Insights from case studies highlight the importance of interprofessional team coordination in managing DKA. For instance, a recent initiative demonstrated that collaborative efforts among healthcare providers led to improved outcomes for individuals, showcasing how a team-based approach directly enhances the DKA management algorithm.
-
Expert Opinions: Diabetes educators emphasize that education strategies for individuals are paramount in preventing DKA. They promote customized educational programs that cater to individual needs, ensuring that individuals are well-informed and equipped to manage their diabetes effectively with the DKA management algorithm.
-
Latest Resources: Current educational materials, including workshops and seminars offered by Dr. Jason Shumard’s center, enhance understanding of DKA prevention. These initiatives not only provide valuable information but also foster a supportive community for individuals managing diabetes. As Dr. Shumard states, “By providing individuals with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where they can reclaim their health and well-being.”
By concentrating on these strategies, healthcare providers can significantly reduce the risk of DKA through the implementation of a DKA management algorithm. This ultimately results in better health outcomes and an enhanced quality of life for individuals. Furthermore, addressing safety concerns in hospitals through effective patient education and management strategies is essential to prevent the adverse effects of incorrect medications and infections.
Conclusion
Timely recognition and management of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) are crucial in preventing the severe complications associated with this life-threatening condition. It’s important to recognize that understanding DKA’s pathophysiology, identifying its clinical signs, and implementing effective management strategies can make a significant difference. Early symptom identification, such as polyuria and nausea, along with structured treatment protocols involving fluid resuscitation and insulin therapy, are all essential for improving patient outcomes.
Many patients find that education plays a vital role in their journey. Empowering individuals with knowledge about DKA, its triggers, and effective diabetes management contributes significantly to preventing episodes of DKA. The integration of holistic approaches, as advocated by compassionate healthcare professionals like Dr. Jason Shumard, highlights the importance of personalized care in diabetes management.
In summary, the fight against DKA requires a collaborative effort between healthcare providers and patients. Focusing on education, proactive monitoring, and tailored treatment plans fosters a supportive environment. By nurturing awareness and understanding of DKA, the healthcare community can work towards reducing its incidence and enhancing the quality of life for those affected by diabetes. Prioritizing these strategies will pave the way for better health outcomes and a more resilient approach to diabetes management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious and potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, the production of ketones, and metabolic acidosis, often occurring when the body lacks sufficient insulin.
What are the key symptoms of DKA?
Key symptoms of DKA include excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea, abdominal pain, and confusion. Each of these symptoms requires immediate attention.
What are the recent statistics regarding diabetes and DKA?
As of 2021, diabetes was the eighth leading cause of death in the United States, accounting for over 103,000 fatalities. The economic burden of diabetes reached an estimated $413 billion in 2022, with excess medical costs per person rising from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022.
How does high blood pressure relate to DKA?
Approximately 70.8% of U.S. adults diagnosed with diabetes also exhibit high blood pressure, a common comorbidity that can worsen DKA complications.
Why is early recognition of DKA important?
Early recognition of DKA is crucial as timely intervention can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications. Factors such as urban residence, infections, and poor glycemic control can influence DKA risk.
What laboratory parameters indicate the onset of DKA?
Abnormal laboratory parameters indicating the onset of DKA include elevated blood glucose readings, increased ketone bodies, and metabolic acidosis.
What triggers the onset of DKA?
DKA can be triggered by insulin deficiency, infections, and hormonal imbalances that increase gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis, leading to hyperglycemia.
What are the management strategies for DKA?
Effective management of DKA requires hospitalization for fluid replacement, electrolyte oversight, and customized insulin therapy tailored to individual needs, along with education on insulin dosing and recognizing early symptoms.
What role does education play in preventing DKA?
Education regarding insulin dosing and recognizing early symptoms is essential to prevent the recurrence of DKA and improve patient outcomes.
What holistic strategies are recommended for managing diabetes and DKA?
Holistic strategies include personalized functional medicine approaches focusing on tailored nutrition, lifestyle modifications, and support systems to empower individuals in managing their health effectively.