Overview
The article provides a detailed guide on converting fructosamine levels to HbA1c percentages, which is essential for diabetes management as it allows for both short-term and long-term blood glucose monitoring. The step-by-step conversion formula and the discussion on the implications of these measurements underscore their importance in tailoring personalized treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes in diabetes care.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, understanding the nuances of blood sugar markers is essential for effective care. Fructosamine and HbA1c are two pivotal indicators that provide insights into glucose control over different time frames, enabling both patients and healthcare providers to tailor management strategies.
While HbA1c offers a long-term view of average blood glucose levels, fructosamine serves as a valuable tool for short-term monitoring, making it particularly useful in dynamic situations where immediate adjustments are necessary.
As the prevalence of type 2 diabetes continues to rise, a comprehensive approach that integrates these markers can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health, ultimately improving their quality of life.
In communities like San Marcos, CA, where outdoor activities and local resources abound, the potential for personalized diabetes care is significant, merging clinical insights with lifestyle adjustments for optimal results.
Understanding Fructosamine and HbA1c: Key Blood Sugar Markers
Fructosamine to A1C serve as critical indicators for evaluating blood glucose control over varying durations, which is essential for managing type 2 conditions effectively. HbA1c indicates the average blood glucose concentrations over the past 2-3 months, providing a long-term view on management, while another marker offers insights into glucose concentrations over the last 2-3 weeks, making it especially beneficial for short-term modifications. This distinction is crucial in scenarios where HbA1c may not accurately reflect glycemic control, such as in patients with hemoglobin variants or recent blood loss.
In the supportive environment of San Marcos, CA, understanding these differences empowers patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding diabetes care. Participating in outdoor pursuits such as hiking at Lake San Marcos or strolling the paths at Discovery Lake can greatly influence blood sugar levels, enhancing the knowledge obtained from measurements of HbA1c. Recent studies have demonstrated that a specific compound and glycated albumin have associations with complications like retinopathy and chronic kidney disease that mirror those seen with HbA1c, underscoring their complementary roles in risk stratification.
Incorporating these indicators into personalized management strategies, tailored through functional medicine approaches, can lead to more effective care that considers individual lifestyle factors, nutrition, and community support. For instance, participating in local wellness programs or shopping at farmers’ markets for fresh produce can enhance overall health and support blood sugar regulation. As one expert succinctly summarized, these results suggest the complementary nature of fructosamine to A1C and glycated albumin for risk stratification for blood sugar issues and its microvascular complications.
With the occurrence of type 2 conditions increasing among all racial and ethnic groups, it is becoming more essential to monitor blood glucose readings thoroughly. By incorporating both markers into comprehensive health strategies and utilizing local resources, patients can attain more tailored and effective care, ultimately improving their overall well-being and quality of life.
How Fructosamine and HbA1c Tests Are Conducted
Fructosamine to A1C tests provide important information about average blood glucose readings over the previous 2-3 weeks, making them an effective tool for short-term oversight of health conditions related to blood sugar. The procedure entails drawing a blood sample, typically from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. In contrast, tests that compare fructosamine to A1C assess the percentage of glycosylated hemoglobin, reflecting average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
These tests can be performed using blood samples obtained either from a vein or through a finger prick, making them accessible and straightforward. Both testing methodologies provide essential data on fructosamine to A1C that can significantly impact management strategies, empowering patients to monitor their progress effectively and set achievable health goals. Significantly, at a cut-off level >3325 μg/L for serum ferritin, β-TM patients are more prone to develop mellitus, highlighting the importance of these tests in this patient group.
Given the nuances in individual health profiles, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider to determine which test is most appropriate, allowing for personalized functional medicine approaches tailored to each patient’s needs. Moreover, a major promise of these tests is their ability to predict which pre-diabetic patients may progress to clinical conditions, potentially leading to significant lifestyle and pharmacological interventions to prevent the onset of this illness and its complications. Recent advancements in these testing methods underline their importance, particularly in identifying pre-diabetic patients and guiding timely interventions, as highlighted by experts in the field.
Furthermore, awareness of potential assay limitations, such as the impact of temperature changes and the presence of reducing substances in serum, is essential for accurate interpretation of results, especially in relation to the reliability of fructosamine to A1C assays as noted in case studies. By merging these testing approaches with comprehensive lifestyle modifications—such as balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and community support—patients in San Marcos can effectively manage their type 2 condition and enhance their overall well-being. To further enhance progress tracking, individuals are encouraged to utilize various methods, including fitness apps, journals, and pedometers, to monitor their daily activities and set SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound.
For example, a patient might aim to walk 10,000 steps daily or incorporate more vegetables into their meals each week. Participating in community wellness programs can also offer crucial support, assisting individuals in remaining accountable and motivated in their diabetes care journey.
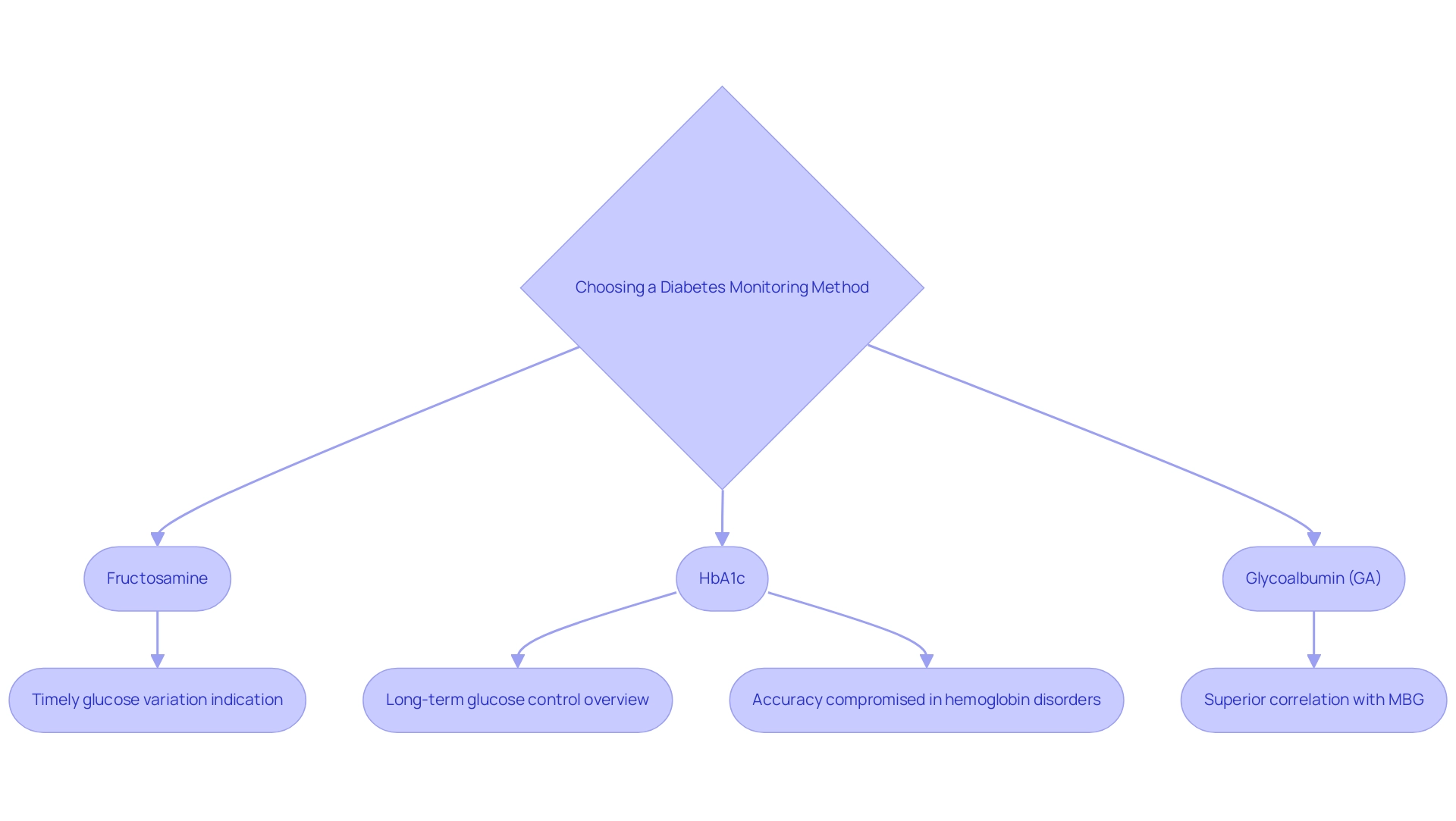
Comparative Analysis: Advantages and Limitations of Fructosamine and HbA1c
Fructosamine to A1C testing provides a timely indication of blood glucose variations, making it especially beneficial for patients who need immediate changes to their strategies. In contrast, HbA1c testing remains the standard for long-term monitoring, delivering a comprehensive overview of glucose control over time. However, HbA1c has its limitations; for example, its accuracy can be compromised in certain populations, such as individuals with hemoglobin disorders, thereby necessitating caution in interpretation, which may be addressed by comparing fructosamine to A1C.
A recent study illustrated that the primary endpoint was the mean Pearson correlation coefficient across various study visits, affirming that glycoalbumin (GA) demonstrated a superior correlation with mean blood glucose (MBG) compared to both A1c and fructosamine. This study confirmed that GA had a significantly better correlation with MBG, supporting its potential as a more reliable metric for glycemic control. Moreover, out of 313 comparisons of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and 7-day self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG), the estimated difference was 0.16 mmol/L (2.9 mg/dL; 95% CI 0.04–0.28 mmol/L), highlighting the importance of accurate glucose monitoring.
Patients are encouraged to engage in discussions with their healthcare providers, like Dr. Jason Shumard in San Marcos, CA, to ascertain which biomarker aligns best with their individual circumstances. This collaborative strategy, combined with customized lifestyle adjustments centered on balanced diets, regular exercise, and stress control, guarantees personalized care and optimal oversight of the condition. Remember, gradual and consistent changes are key to long-term success in managing your condition and enhancing your overall well-being.
For personalized guidance and support, consider scheduling a consultation with Dr. Shumard to empower your diabetes management journey.
Step-by-Step Conversion: From Fructosamine to HbA1c
To transform these compounds’ concentrations to HbA1c, you can apply the following formula:
HbA1c (%) = (Concentration µmol/L – 2.5) / 1.5.
For instance, if your fructosamine concentration is measured at 250 µmol/L, the calculation would be performed as follows:
(250 – 2.5) / 1.5, which yields an HbA1c equivalent of approximately 10.4%.
This conversion acts as a helpful approximation, particularly since a serum ferritin value exceeding 3325 μg/L is linked to metabolic disorders, emphasizing the significance of observing glucose concentrations in managing such conditions.
Furthermore, implementing effective progress tracking methods, such as using fitness apps or journals, can empower Type 2 individuals to set and achieve SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—in their health journey.
A case study examining laboratory data from 1,227 individuals with a blood sugar condition discovered that for every 1.0 µmol/L rise in a specific biomarker, there was a corresponding 0.5 mg/dL increase in average glucose concentrations. As noted by Luis Jesuino de Oliveira,
‘Linear regression analysis between fructosamine to A1C levels and average glucose levels showed that for each 1.0 µmol/L increase in fructosamine to A1C level, there was a 0.5 mg/dL increase in average glucose level.’
This underscores the practical application of the conversion formula. It’s essential to recognize that this estimate should supplement regular HbA1c testing to ensure thorough control of blood sugar.
Regular goal-setting persistence scores have shown to positively impact performance, with scores improving from 3.4 (SD = 2.0) to 3.8 (SD = 1.9) under specific conditions, emphasizing the effectiveness of structured goal-setting.
Always engage with your healthcare provider when interpreting these results, as they can provide tailored insights that account for your overall health status and help set achievable health goals.
Practical Implications of Fructosamine to HbA1c Conversion in Diabetes Care
The transformation of a specific sugar compound to HbA1c, as well as the conversion from fructosamine to A1C, is a pivotal aspect of diabetes care, especially for those in San Marcos, CA, seeking immediate adjustments in their management strategies. Increased amounts of specific proteins may indicate the necessity for dietary modifications or medication alterations, allowing swift steps that align with the long-term view given by HbA1c measurements. For instance, a notable case involved a patient exhibiting weight loss and polyuria, with a blood glucose level of 303 mg/dL, an HbA1c of 11.5%, and a fructosamine to A1C ratio indicated by a fructosamine level of 586 µmol/L.
The patient’s condition, worsened by an infection, prompted the introduction of insulin therapy to improve treatment. This case illustrates how personalized functional medicine strategies can revolutionize the control of blood sugar levels. Moreover, individuals undergoing significant lifestyle changes—such as increased physical activity through San Marcos’ scenic parks or weight loss supported by local farmers’ markets—often benefit from testing as a means to effectively monitor short-term blood sugar control.
This integrated approach not only permits personalized adjustments but also promotes a more thorough health oversight plan overall. As noted by experts Mohammed Iqbal Tanveer Ashraf and Adam J. Buckley:
- “We aimed to establish clinically useful treatment targets for glycation levels in a population with a high prevalence of conditions affecting erythrocyte survival, including variant hemoglobin and G6PD deficiency.”
Regular assessment of fructosamine to A1C is essential in different populations, highlighting the significance of personalized approaches for effective health control.
Furthermore, participating in community wellness initiatives available in San Marcos, such as health education classes and nutrition workshops, can offer invaluable support. These programs often emphasize hydration strategies, encouraging individuals to opt for water and herbal teas over sugary drinks, which is essential for blood sugar control. Moreover, incorporating stress management techniques like yoga and meditation can further enhance overall well-being and diabetes management.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of both fructosamine and HbA1c in diabetes management highlights the importance of a comprehensive approach to blood sugar monitoring. While HbA1c provides essential insights into long-term glucose control, fructosamine offers a valuable perspective on short-term fluctuations, allowing for timely adjustments in treatment. This dual approach is particularly beneficial for individuals navigating the complexities of type 2 diabetes, enabling personalized strategies tailored to their unique health profiles.
Incorporating these markers into diabetes care, especially within supportive communities like San Marcos, CA, empowers patients to take charge of their health. Engaging in local wellness initiatives, outdoor activities, and healthy eating can significantly enhance blood sugar regulation and overall well-being. By understanding and utilizing these blood sugar indicators, individuals can improve their management strategies, reduce the risk of complications, and ultimately elevate their quality of life.
As the prevalence of type 2 diabetes continues to increase, the integration of fructosamine and HbA1c monitoring into personalized care plans becomes increasingly vital. This approach not only fosters better health outcomes but also encourages a proactive stance toward diabetes management, ensuring that individuals are equipped with the knowledge and resources necessary for success on their health journeys.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are fructosamine and HbA1c, and why are they important?
Fructosamine and HbA1c are critical indicators for evaluating blood glucose control. HbA1c measures average blood glucose concentrations over the past 2-3 months, providing a long-term view, while fructosamine reflects glucose concentrations over the last 2-3 weeks, making it useful for short-term monitoring.
In what situations might HbA1c not accurately reflect glycemic control?
HbA1c may not accurately reflect glycemic control in patients with hemoglobin variants or those who have experienced recent blood loss.
How can understanding fructosamine and HbA1c benefit diabetes management?
Understanding these markers empowers patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding diabetes care and to tailor management strategies based on individual needs and lifestyle factors.
What lifestyle activities can influence blood sugar levels?
Engaging in outdoor activities, such as hiking at Lake San Marcos or walking at Discovery Lake, can positively influence blood sugar levels and enhance the knowledge gained from HbA1c measurements.
What is the significance of glycated albumin in diabetes care?
Glycated albumin has associations with complications like retinopathy and chronic kidney disease, similar to those seen with HbA1c, highlighting its complementary role in risk stratification for diabetes-related issues.
How can personalized management strategies improve diabetes care?
Incorporating fructosamine and HbA1c into personalized management strategies can lead to more effective care that considers individual lifestyle factors, nutrition, and community support.
What are the testing procedures for fructosamine and HbA1c?
Both tests involve drawing a blood sample, either from a vein or through a finger prick, which is then analyzed in a laboratory. Fructosamine provides data on average blood glucose over the past 2-3 weeks, while HbA1c reflects levels over the past 2-3 months.
Why is it important to consult a healthcare provider regarding these tests?
Consulting with a healthcare provider is advisable to determine the most appropriate test for individual health profiles, allowing for personalized functional medicine approaches tailored to each patient’s needs.
How do these tests help in predicting diabetes progression?
These tests can predict which pre-diabetic patients may progress to clinical conditions, potentially leading to lifestyle and pharmacological interventions to prevent the onset of diabetes and its complications.
What are some recommended lifestyle modifications for managing type 2 conditions?
Recommended lifestyle modifications include balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and community support, as well as utilizing tools like fitness apps and journals to monitor daily activities and set specific health goals.