Overview
The article focuses on the conversion of HbA1c levels to blood sugar readings and its significance in managing diabetes. It explains that understanding this conversion is crucial for personalized diabetes management, as it allows individuals to monitor their long-term glucose control and adjust their treatment plans accordingly, supported by evidence of improved health outcomes from regular testing and tailored strategies.
Introduction
The management of diabetes hinges on a fundamental understanding of HbA1c, a critical marker that reflects average blood sugar levels over a period of two to three months. This test not only serves as a benchmark for assessing glycemic control but also plays a pivotal role in guiding treatment decisions.
As diabetes prevalence continues to rise, with millions affected across various demographics, the importance of regular HbA1c monitoring cannot be overstated. From interpreting test results to implementing personalized nutrition strategies, the journey towards effective diabetes management is multifaceted.
This article delves into the significance of HbA1c, offers insights on converting these values to average blood glucose levels, and emphasizes the necessity of regular testing and self-monitoring to empower individuals in their health management journey.
Understanding HbA1c: The Key to Blood Sugar Monitoring
Glycated hemoglobin, often referred to as A1c, is an essential blood test that assesses the hba1c conversion to blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It is presented as a percentage, reflecting the proportion of hemoglobin molecules that have glucose attached. Increased blood sugar readings indicate insufficient glucose regulation, emphasizing the significance of this measure in managing health.
Dr. Jason Shumard emphasizes a personalized functional medicine approach, recognizing that each individual’s nutritional needs vary significantly. The American Diabetes Association advises that most adults with the condition strive for a blood sugar measurement of under 7%; however, personal goals may vary depending on particular health circumstances and the advice of healthcare professionals. Recent studies indicate that maintaining appropriate blood sugar levels can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
The economic burden of managing this condition is substantial, with estimated direct and indirect costs reaching $413 billion in the United States in 2022. Furthermore, the occurrence of prediabetes is concerning, with 97.6 million Americans aged 18 and older impacted, highlighting the essential requirement for efficient blood sugar monitoring to avert progression to the disease. Furthermore, during 2017-2018, an estimated 18,169 children and adolescents under 20 years were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, and 5,293 with type 2 diabetes in the U.S., particularly among non-Hispanic Black and Asian or Pacific Islander groups.
These figures emphasize the increasing need for effective strategies for HbA1c conversion to blood sugar monitoring and management, especially in high-risk populations. To learn more about how personalized nutrition plans can help stabilize your blood sugar and improve your overall health, contact Dr. Shumard today! Also, discover the top 3 secrets that can help you reverse diabetes symptoms and reclaim your health.
Converting HbA1c to Blood Sugar: A Step-by-Step Guide
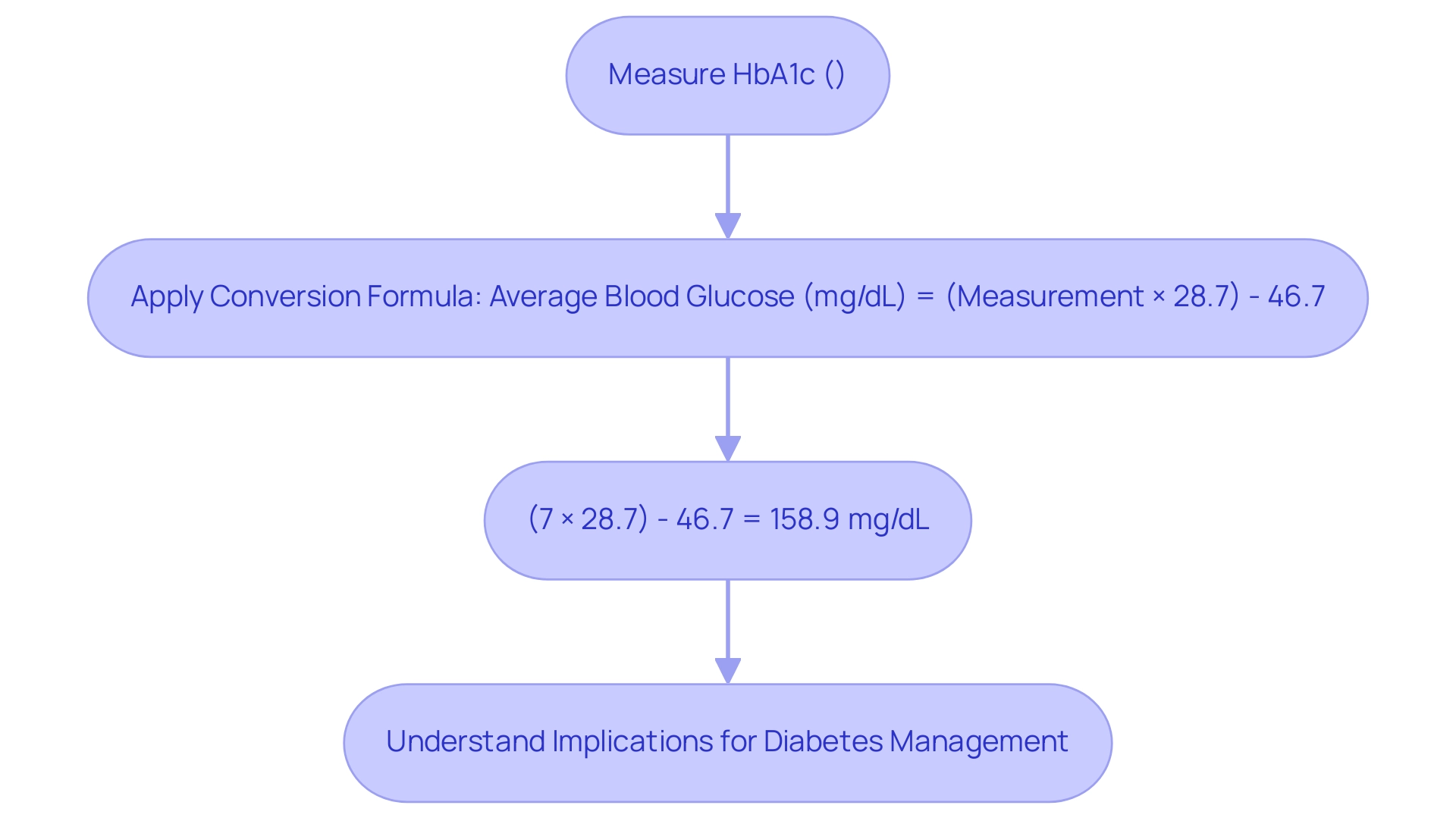
To transform the measurement into average blood glucose readings, the subsequent formula is applied:
Average Blood Glucose (mg/dL) = (Measurement × 28.7) – 46.7.
For instance, if your HbA1c is measured at 7%, the calculation would be as follows:
(7 × 28.7) – 46.7 = 158.9 mg/dL.
This transformation is essential as it enables individuals to understand their blood glucose readings through the HbA1c conversion to blood sugar in a more relatable format, thereby improving the control of their condition.
Comprehending these values can greatly aid in personalized diabetes management strategies, as studies show that tailored models can result in enhanced estimations of average glucose readings, ultimately promoting better outcomes for patients.
For broader context, the HbA1c conversion to blood sugar shows that an A1C of 8% corresponds to an estimated average glucose (eAG) of 183 mg/dL, illustrating the range of blood sugar levels that can be managed. Additionally, conversion charts and online calculators are available to assist individuals in quickly determining the HbA1c conversion to blood sugar from A1C values.
Christina M Parrinello, MPH, emphasizes that these markers can overcome limitations of HbA1c in certain patients, providing additional information on shorter-term glycemic control. Moreover, there is a recognized need for additional research on nontraditional glycemic markers, as emphasized in recent studies, which highlights the significance of ongoing investigations in blood sugar regulation and risk assessment for complications.
In light of these developments, the significance of the HbA1c conversion to blood sugar cannot be overstated, as it provides essential insights into glycemic control, empowering patients to engage in their health management actively through personalized strategies and functional medicine approaches.
The Importance of Regular HbA1c Testing and Self-Monitoring
Regular testing of HbA1c conversion to blood sugar, suggested every three to six months, is essential for individuals managing their condition as it provides insight into long-term glucose control. This testing allows healthcare providers to assess how well a patient’s treatment plan is working and make necessary adjustments. Moreover, daily self-monitoring of blood glucose values is equally essential, as it allows patients to understand how their diet, physical activity, and medications affect the HbA1c conversion to blood sugar.
These practices not only enable individuals to take charge of their health but also significantly lower the risk of complications related to blood sugar issues. In conjunction with advanced diagnostic testing utilized by functional medicine in San Marcos, which explores a variety of biomarkers such as inflammation levels, insulin resistance, and gut health, patients can receive a more holistic and personalized approach to their condition. These services are designed to help eliminate dependency on insulin and other diabetes-related drug therapies, focusing on comprehensive care that addresses interconnected health factors.
Studies indicate that individuals with high monitoring adherence have a probability of achieving glycaemic control of 0.5, which rises to 0.53 for patients with an index blood glucose level ≥ 7%. As emphasized in conversations among educators in the field, effective self-monitoring can result in improved health outcomes, reinforcing the idea that regular testing for HbA1c conversion to blood sugar is a fundamental aspect of care. Additionally, sensitivity analyses have explored alternative cut-offs for optimal and suboptimal control, particularly based on guidelines from South Africa, suggesting that personalized approaches to monitoring can further enhance patient outcomes.
The increasing occurrence of the condition, with over 7.2 million cases reported in Germany as of 2014, highlights the necessity for such monitoring practices. Hee-Chung Kang from the Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs emphasizes, “It is crucial to narrow this gap in patient management in the future,” underscoring the need for enhanced adherence to self-monitoring and regular testing protocols among patients. The effectiveness of the A1c test as a diagnostic tool is especially significant in low-resource environments, as it not only assists in diagnosis but also promotes improved patient care, particularly concerning HbA1c conversion to blood sugar issues that are rising worldwide.
Interpreting Your HbA1c Results: What Do They Mean?
Glycated hemoglobin results are categorized into distinct groups that indicate a person’s glycemic control:
- Normal: Less than 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher.
For individuals diagnosed with diabetes, the main goal is usually to keep an A1c value under 7%. This target is crucial as it significantly reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular disease and neuropathy. Transformative success stories from Dr. Jason Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset Program illustrate how individuals, like M.L., have achieved remarkable improvements in their health, including weight loss and significant reductions in both blood sugar and fasting glucose. M.L. noted, ‘I have lost 55 lbs. My A1C started at 9.1 after 8 months it is now 5.7.’
Increased blood sugar levels indicate inadequate glucose control, which may necessitate modifications in diet, physical activity, or pharmacological interventions. Customized functional medicine approaches are crucial, as they offer individualized nutrition strategies that take into account each patient’s distinct health requirements, enabling them to take charge of their condition. Regular consultations with healthcare providers, as emphasized in our clinic, ensure that individuals receive personalized guidance tailored to their unique situations.
Moreover, a case study titled ‘Combining CGM and A1c for Improved Accuracy’ emphasizes that integrating CGM data with A1c measurements can enhance the precision of glycemia estimates, thereby improving blood sugar management through hba1c conversion to blood sugar. As the incidence of the condition continues to increase, especially among young people—with 5,293 newly diagnosed cases of type 2 among those aged 10 to 19 in 2017-2018—comprehending and efficiently controlling the hba1c conversion to blood sugar levels is essential for long-term health results.
If you have this condition, you’ve probably tried most of the fad diets or headlining approaches to nutrition that promise lasting results. The choice is yours… but if we can learn anything from grains, it’s that you reap what you sow.
Common Questions About HbA1c Testing and Conversion
-
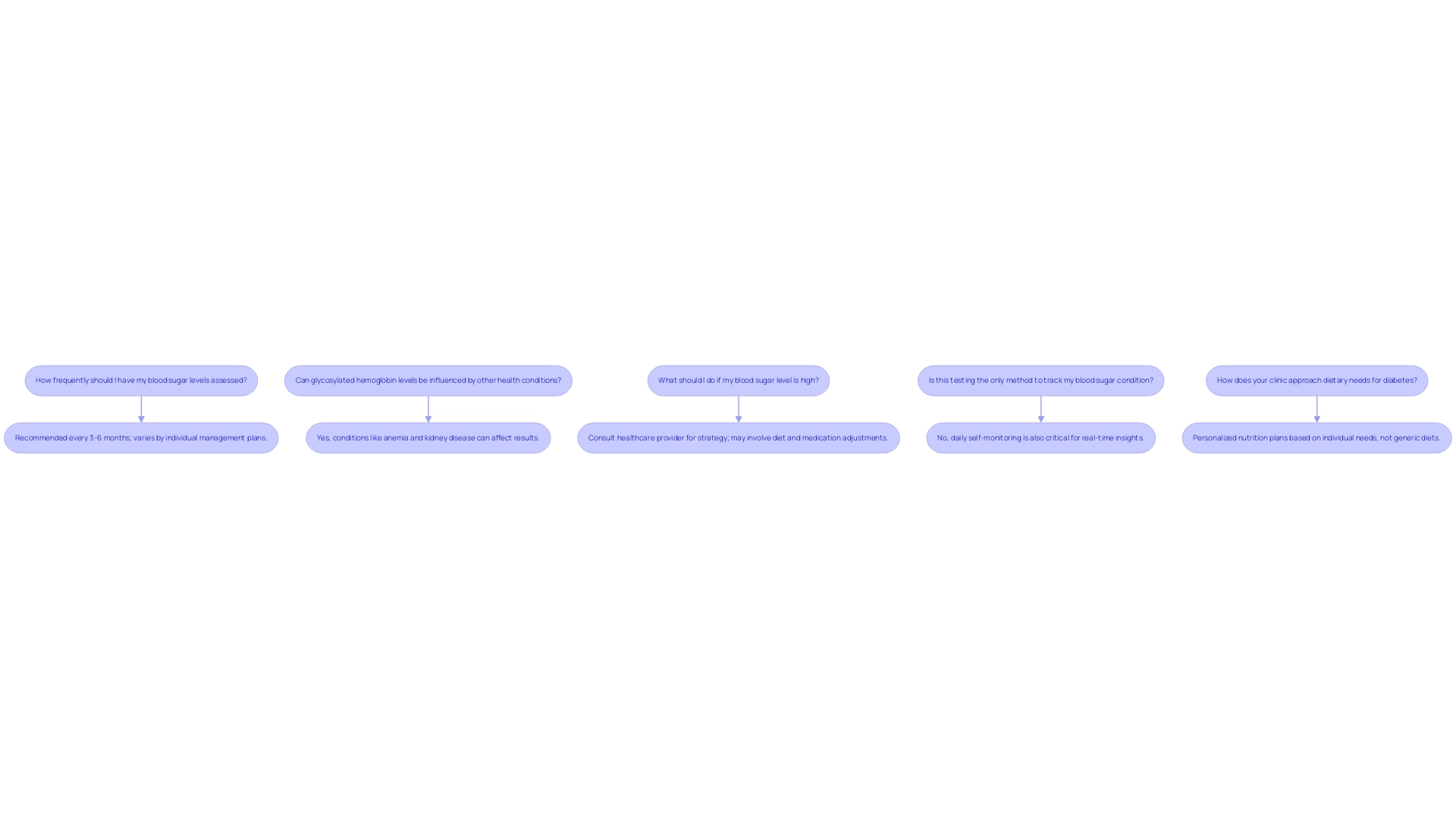
How frequently should I have my blood sugar levels assessed?
- For most adults living with diabetes, it is recommended to have HbA1c levels tested every three to six months. This interval may vary based on individual management plans and treatment goals. Regular testing is crucial for monitoring long-term blood sugar control, particularly as understanding your A1C results and the hba1c conversion to blood sugar can lead to more personalized functional medicine solutions tailored to your unique nutritional needs. Some people with diabetes can achieve an A1C below 6.5%, which is considered a target for effective diabetes management.
-
Can glycosylated hemoglobin levels be influenced by other health conditions?
- Indeed, several health conditions can significantly impact HbA1c results. Factors such as anemia, kidney disease, and even pregnancy can result in inaccurately low or high blood sugar levels over time. Falsely low values may occur at high altitudes or during pregnancy, while falsely high values can be caused by iron deficiency anemia and hemoglobinopathies. It is essential to keep your healthcare provider informed about any changes in your health status, as this information can influence your diabetes management strategy and inform the development of a tailored treatment plan.
-
What should I do if my blood sugar level is high?
- If your HbA1c levels are elevated, it is vital to consult with your healthcare provider. They can assist you in creating a strategy to reduce your amounts, which may involve dietary changes, increased physical activity, or adjustments to your medication regimen. Tackling elevated blood sugar indicators swiftly can assist in averting complications related to the condition. Understanding the hba1c conversion to blood sugar can also empower you to manage your condition more effectively.
-
Is this testing the only method to track my blood sugar condition?
- While HbA1c testing is an essential component of diabetes management, it is not the sole method of monitoring blood sugar levels. Daily self-monitoring of blood glucose is also critical, as it offers real-time insights into your blood sugar fluctuations, enabling more effective day-to-day management of your condition and enhancing your overall wellness.
-
How does your clinic approach dietary needs for diabetes?
- Our clinic utilizes state-of-the-art testing to identify your specific dietary needs, allowing us to design a personalized nutrition plan tailored to you—not just the disease. Unlike generic online diets, our approach recognizes that each individual is unique. You can choose to continue searching for one-size-fits-all solutions or schedule a consultation with a functional medicine practitioner who will consider your individual experiences and health goals.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing HbA1c levels is crucial for anyone living with diabetes. This important marker not only reflects average blood glucose levels over two to three months but also serves as a key indicator for assessing overall glycemic control. Regular testing and self-monitoring empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health, ensuring that treatment plans can be adjusted as necessary to achieve optimal outcomes.
The article outlines the conversion of HbA1c to average blood glucose levels, providing a practical tool for individuals to better understand their results. By interpreting these values accurately, patients can tailor their dietary and lifestyle choices to effectively manage their condition. Furthermore, the significance of personalized nutrition plans and functional medicine approaches is emphasized, highlighting how individualized care can lead to successful diabetes management.
In summary, maintaining an HbA1c level below the recommended threshold is essential for reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. The alarming increase in diabetes prevalence, particularly among high-risk populations, underscores the urgency of effective monitoring and management strategies. By prioritizing regular HbA1c testing and embracing a personalized approach to health, individuals can take significant strides towards better diabetes control and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is glycated hemoglobin (A1c) and why is it important?
Glycated hemoglobin, or A1c, is a blood test that measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It is expressed as a percentage, indicating the proportion of hemoglobin molecules with glucose attached. This measure is crucial for assessing glucose regulation and managing health.
What does the American Diabetes Association recommend for blood sugar levels in adults?
The American Diabetes Association recommends that most adults with diabetes aim for a blood sugar measurement of under 7%. However, personal goals may vary based on individual health circumstances and healthcare provider advice.
What is the economic impact of diabetes management in the United States?
The economic burden of managing diabetes is significant, with estimated direct and indirect costs reaching $413 billion in the United States in 2022.
How prevalent is prediabetes in the United States?
Prediabetes affects approximately 97.6 million Americans aged 18 and older, highlighting the need for effective blood sugar monitoring to prevent progression to diabetes.
What is the formula to convert HbA1c to average blood glucose readings?
The formula to convert HbA1c to average blood glucose is: Average Blood Glucose (mg/dL) = (Measurement × 28.7) – 46.7. For example, an HbA1c of 7% corresponds to an average blood glucose of 158.9 mg/dL.
How does understanding HbA1c values help in diabetes management?
Understanding HbA1c values allows individuals to relate their blood glucose readings to a more familiar format, aiding in personalized diabetes management strategies and improving health outcomes.
What are the implications of having an A1c of 8%?
An A1c of 8% corresponds to an estimated average glucose (eAG) of 183 mg/dL, indicating the range of blood sugar levels that can be managed.
Why is there a need for research on nontraditional glycemic markers?
Research on nontraditional glycemic markers is necessary to provide additional information on shorter-term glycemic control and improve risk assessment for diabetes-related complications.
How can personalized nutrition plans help individuals with diabetes?
Personalized nutrition plans can help stabilize blood sugar levels and improve overall health, empowering patients to engage actively in their health management.
Where can individuals find tools to assist with HbA1c conversion to blood sugar?
Conversion charts and online calculators are available to help individuals quickly determine the HbA1c conversion to blood sugar from A1c values.