Overview
The article provides a comprehensive tutorial on the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator, emphasizing its role in managing diabetes through understanding and interpreting A1C test results. It supports this by detailing the significance of A1C levels in diagnosing diabetes, offering step-by-step instructions for using the calculator, and highlighting the importance of regular monitoring to enhance patient care and health outcomes.
Introduction
The A1C test stands as a cornerstone in the management of Type 2 diabetes, providing critical insights into blood sugar control over time. By measuring the percentage of glucose attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells, this test serves not only as a diagnostic tool but also as a guide for treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
With alarming statistics revealing that nearly half of U.S. adults with diabetes exhibit concerning A1C levels, understanding this test’s implications is more crucial than ever. This article delves into the significance of the A1C test, how to interpret the results, and the importance of regular monitoring, all while exploring strategies that can empower individuals to take charge of their health and mitigate the risks associated with diabetes.
Through a comprehensive approach that includes personalized care and education, patients can navigate their diabetes management journey with greater confidence and clarity.
Understanding the A1C Test: A Foundation for Diabetes Management
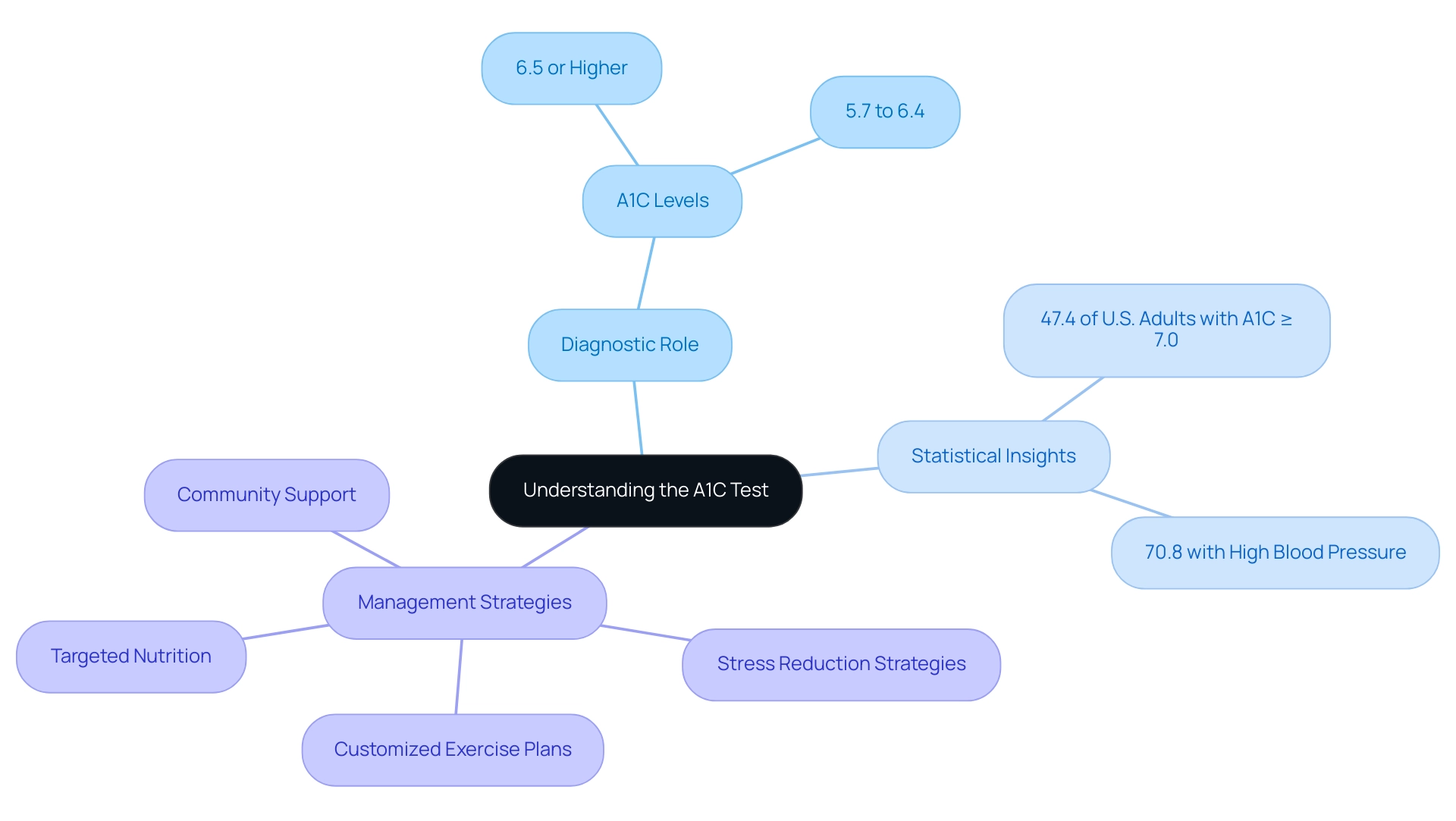
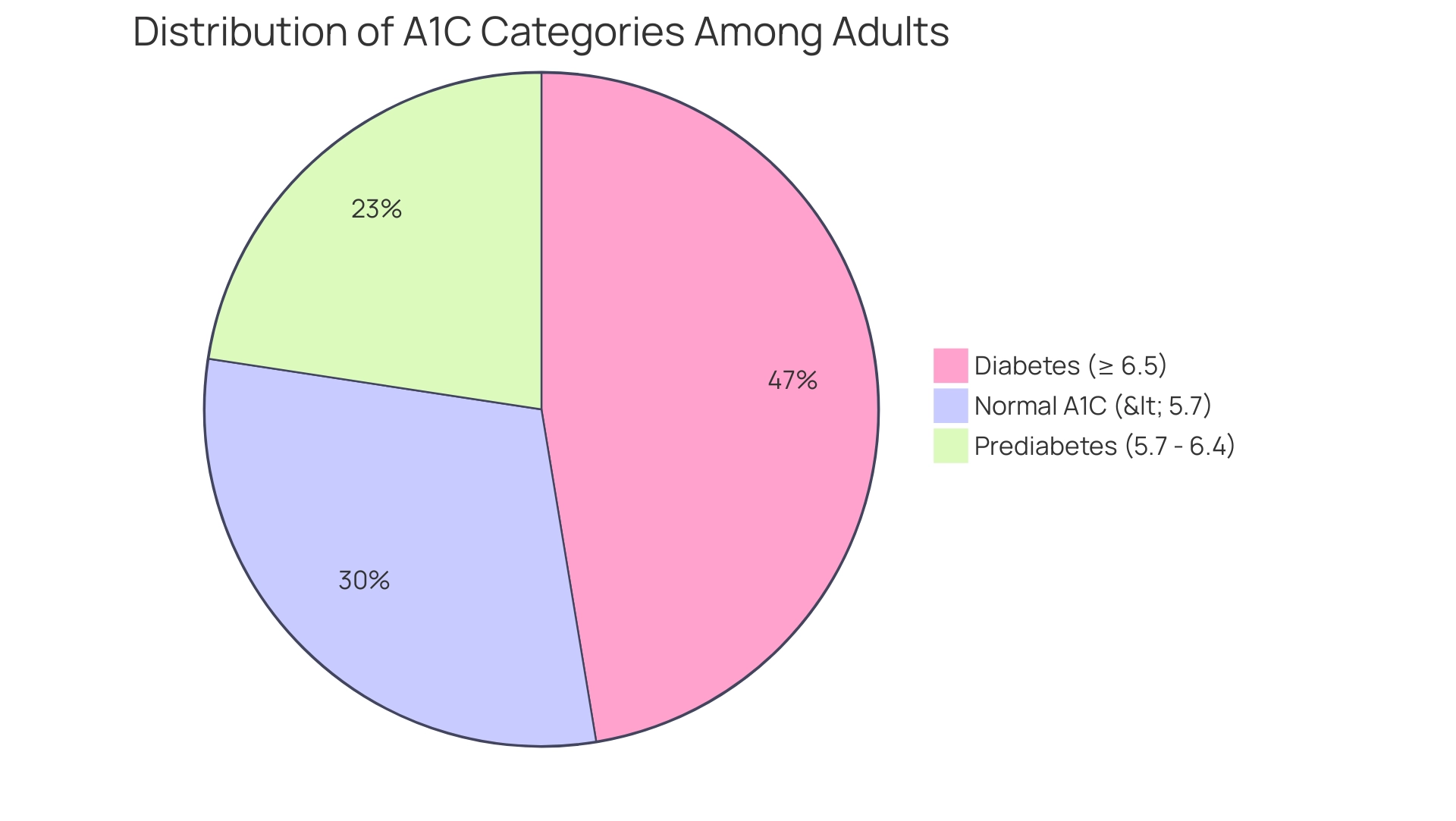
The A1C test, commonly referred to as the glycated hemoglobin test, serves as a vital diagnostic tool in managing Type 2. It measures the percentage of glucose that has bonded to hemoglobin in red blood cells, with elevated A1C percentages indicating suboptimal blood sugar control and a heightened risk of diabetes-related complications. An A1C level of 6.5% or higher typically confirms a diagnosis of a blood sugar disorder, while levels ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% suggest prediabetes.
Alarmingly, recent data shows that 47.4% of U.S. adults diagnosed with the condition exhibit A1C values of 7.0% or higher, underscoring the urgent need for enhanced management strategies. Furthermore, 70.8% of these adults have a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or a diastolic blood pressure of 90 mmHg or more, highlighting the multifaceted health challenges this population faces. Understanding the implications of the A1C test is crucial for Type 2 patients and healthcare professionals, as the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator informs treatment decisions and lifestyle modifications.
As noted by Elizabeth Selvin, the corresponding author of a recent study, ‘This study highlights a weakness in the literature related to the diagnosis of diabetes-related conditions: the lack of confirmatory glucose testing to replicate the typical clinical scenario in which multiple tests are conducted before a diagnosis is made.’ This highlights the necessity for A1C testing to be integrated within a holistic framework for blood sugar control, which should also utilize the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator along with individualized care and education to empower patients. Moreover, investigating four lesser-known power-plays—such as:
- Targeted nutrition
- Customized exercise plans
- Stress reduction strategies
- Community support
can greatly improve health results and assist in reversing blood sugar issues.
A case study examining A1C values in adults with blood sugar issues reveals variation across different age groups, further illustrating the necessity for customized care strategies.
How to Use the A1C Calculator: Step-by-Step Instructions
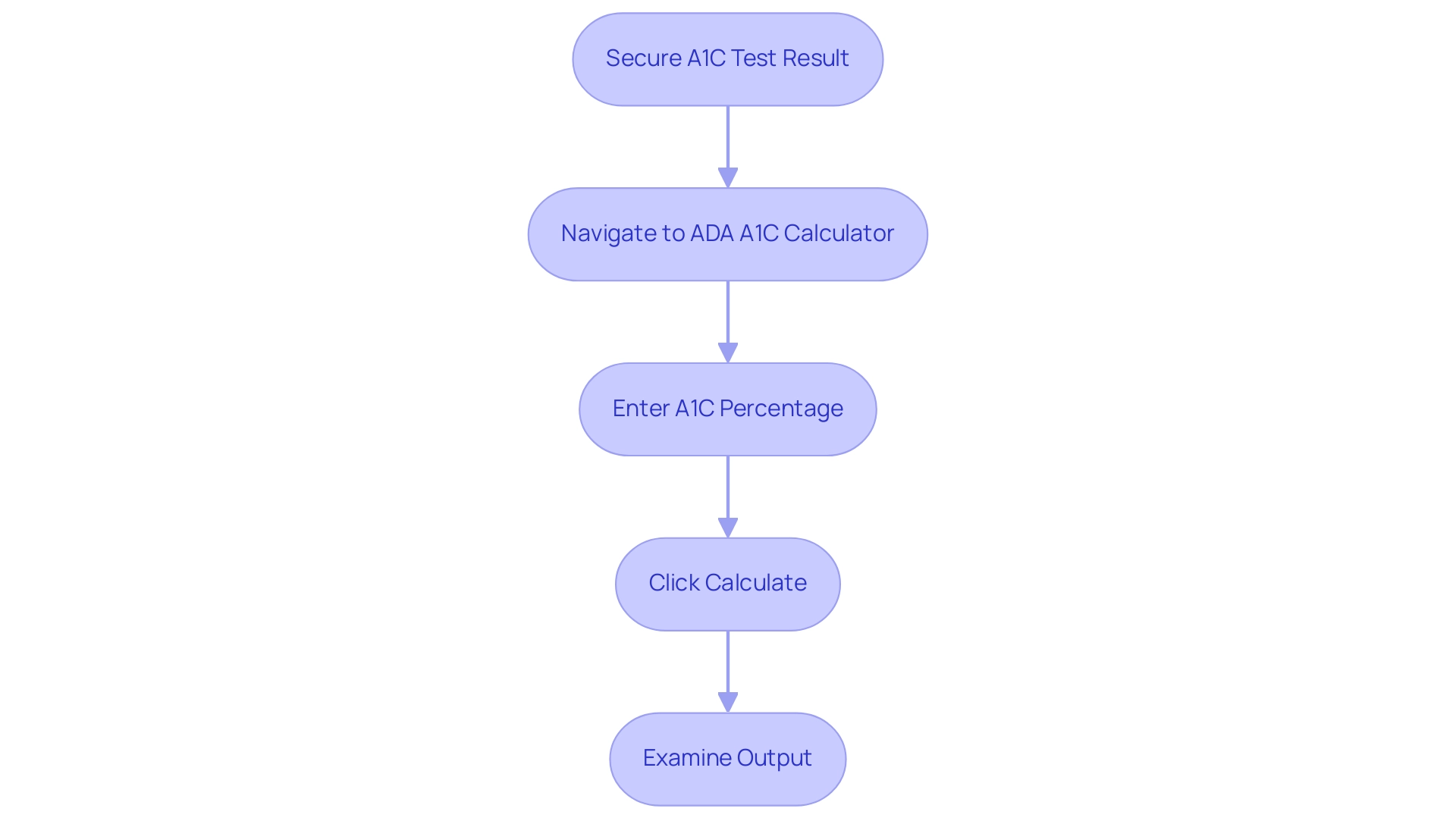
To utilize the A1C calculator effectively and empower yourself in managing diabetes, adhere to the following systematic steps:
- Secure your most recent A1C test result from your healthcare provider, as this serves as the foundational data for your calculation.
- Navigate to the official website of the American Diabetes Association to locate the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator.
- Enter your A1C percentage into the specified field on the calculator.
- Click ‘Calculate’ to acquire your estimated average glucose (eAG) reading, which is essential for comprehending your blood sugar control.
- Examine the output closely; it translates your A1C percentage into an estimated average glucose measurement, providing vital insight into your blood sugar control over time.
This understanding is crucial for effective control of blood sugar levels at the Integrative Wellness Center, where we emphasize a holistic approach to addressing root causes and empowering patient health. Sustaining an A1C of 7% or lower greatly decreases the risk of issues related to blood sugar conditions, easing concerns about acquiring severe and incapacitating complications.
As emphasized by Vivian Fonseca’s statement that ‘Translating the hemoglobin A1C assay is essential for effective control of the condition,’ understanding your A1C can help determine your status, as detailed in the case study ‘A1C as a Diagnostic Tool,’ highlighting the vital role of A1C test results in diagnosing and overseeing the illness. Furthermore, being conscious of your A1C values can assist in reducing the financial strains linked to health care for chronic conditions, emphasizing the significance of thorough treatment and education.
Interpreting A1C Results: What Do the Numbers Mean for Your Health
Understanding A1C results is crucial for effective management of the condition, and the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator helps empower patients to take control of their health. An A1C measurement below 5.7% is deemed normal, while readings between 5.7% and 6.4% signify prediabetes, and a diagnosis of the condition is confirmed with an A1C of 6.5% or greater. For individuals diagnosed with this condition, the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator suggests aiming for an A1C level of under 7% to reduce the risk of complications like cardiovascular disease and neuropathy.
This understanding is crucial, particularly considering that a recent study revealed 47.4% of adults with the condition had an A1C of 7.0% or higher, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced management strategies, including the use of the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator. Furthermore, the National Center for Health Statistics reports a rise in undiagnosed blood sugar conditions prevalence, underscoring the necessity of regular A1C monitoring with the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator. As the prevalence of this condition continues to rise, particularly among children and adolescents, utilizing the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator for an informed interpretation of A1C results becomes essential for enhancing health outcomes.
By adopting a holistic approach that addresses the root causes of the condition, patients can alleviate the anxiety associated with potential complications, leading to more effective management. Including patient success stories can further demonstrate how a comprehensive regimen not only enhances A1C results but also empowers individuals to challenge conventional treatment myths.
The Importance of Regular A1C Monitoring in Diabetes Control
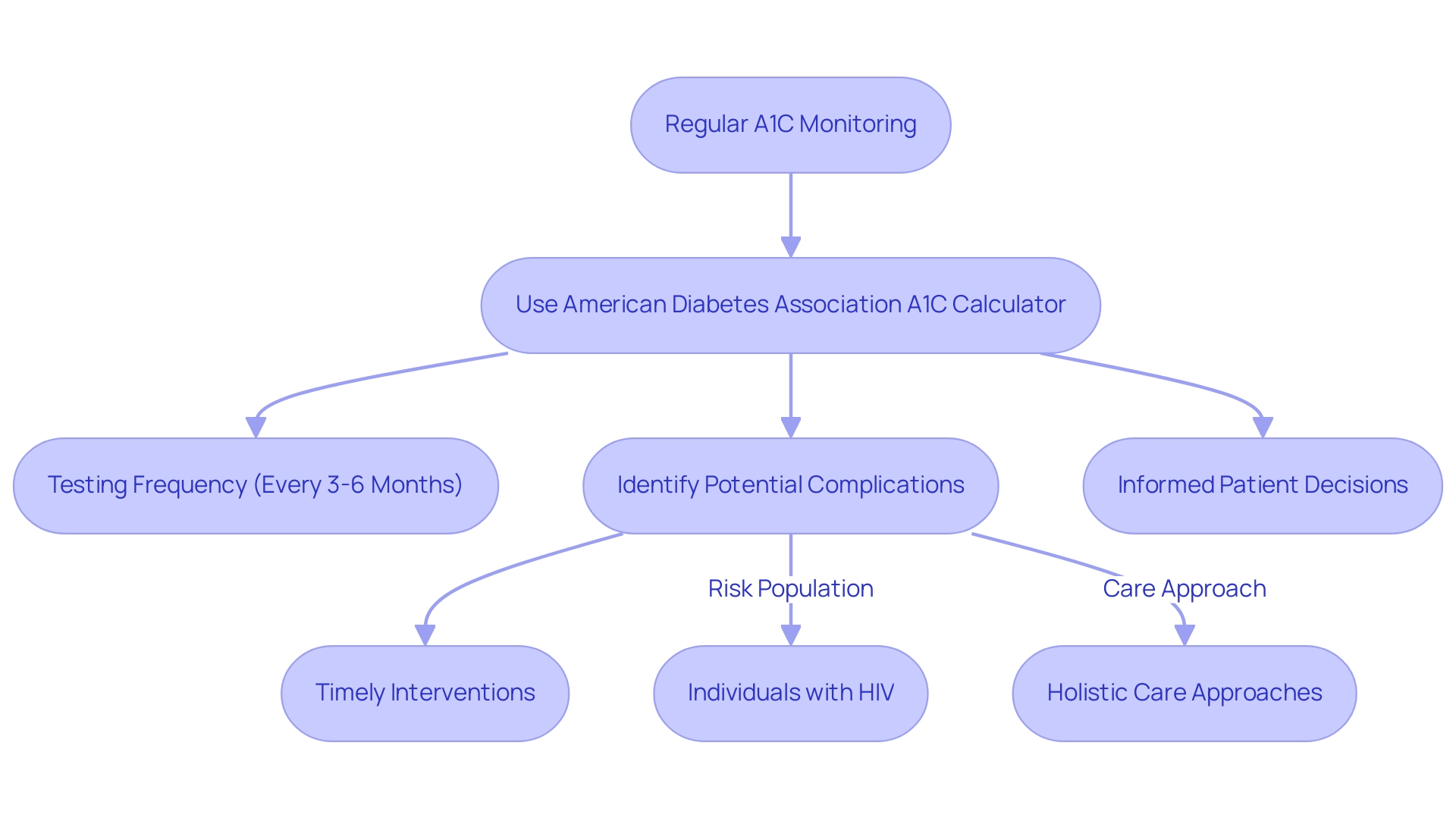
Regular monitoring of A1C levels is essential for individuals managing their condition, and the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator provides a clear picture of long-term glucose control. This practice allows for the early identification of potential complications, enabling timely intervention. Healthcare professionals typically recommend the use of the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator for testing every three to six months, a guideline supported by recent systematic reviews that emphasize the necessity of adapting testing frequency based on individual health status and risk factors.
The Integrative Wellness Center acknowledges that understanding insulin resistance and addressing root causes can empower patients to eliminate anxiety over complications related to blood sugar through holistic care and education. As one patient shared, ‘Since starting my journey at the Integrative Wellness Center, I feel more in control of my condition and less worried about complications.’ For instance, the TEDDY study demonstrated that type 1 condition developed in 21% of subjects with at least one autoantibody by age 3, highlighting the importance of early screening.
Additionally, individuals with HIV are at an increased risk of prediabetes and other metabolic disorders, particularly if they are on certain antiretroviral therapies. This necessitates tailored screening protocols, as preventive healthcare and lifestyle modifications are crucial for managing risk in such populations. Furthermore, consistent tracking of A1C levels with the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator empowers patients to make informed decisions about their dietary choices, physical activity, and medication adjustments.
This proactive approach can lead to significantly improved health outcomes and an enhanced quality of life. As Roopa Naik states, ‘Regular A1C monitoring, including the use of the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator, is vital for effective management of the condition.’ Transformative patient experiences at the Integrative Wellness Center demonstrate that with the right support, patients can reverse Type 2 and address related health issues like hypothyroidism.
Another patient remarked, ‘I never thought I could feel this good again; the support here has truly changed my life.’ As we approach recommendations for 2024, the impact of regular A1C monitoring, utilizing the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator, on health outcomes cannot be overstated, offering not just health benefits but also peace of mind for patients navigating their condition journey.
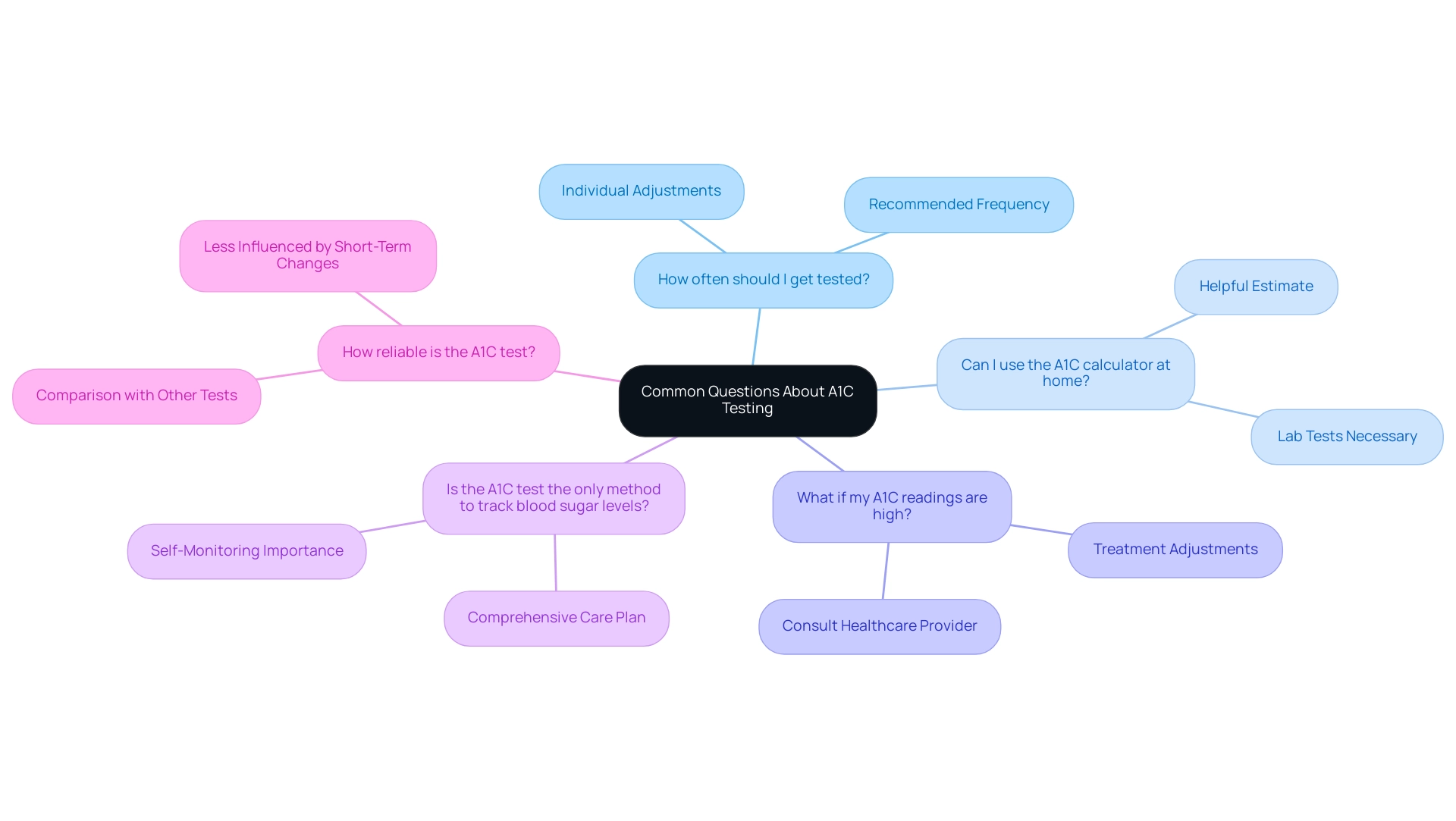
Common Questions About A1C Testing and Calculators
Frequently asked questions regarding A1C testing, including the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator, are crucial for effective management of the condition, especially in the context of a holistic approach that seeks to address root causes and alleviate the anxiety surrounding potential complications of your illness. Here are some key inquiries:
-
How often should I get tested?
While the recommended frequency is typically every three months, your healthcare provider may adjust this based on your specific health needs and holistic treatment plan.
-
Can I use the A1C calculator at home?
While the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator can provide a helpful estimate, it cannot replace lab tests, which are necessary for obtaining accurate A1C measurements essential for evaluating your overall health.
-
What if my A1C readings are high?
It is essential to consult your healthcare provider to evaluate potential treatment adjustments and lifestyle modifications that align with an integrative wellness approach.
-
Is the A1C test the only method to track blood sugar levels?
No, self-monitoring of blood glucose readings remains vital for daily management and should be integrated into your comprehensive care plan.
-
How reliable is the A1C test?
A1C tests are less influenced by short-term changes in blood glucose compared to fasting plasma glucose (FPG) or oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT), making them a more stable measure over time.
By understanding these elements, individuals can effectively manage their condition by utilizing the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator. Understanding the nuances of A1C testing is essential, especially given that studies indicate 50–60% of patients with fasting plasma glucose levels of ≥7 mmol/L may have an A1C score below 6.5%, highlighting the risk of underdiagnosis.
Additionally, as noted by expert Robert Cohen,
There is substantial variability in erythrocyte life span among individuals without hematological illness,
which further complicates A1C interpretation. Furthermore, it is critical to recognize that the A1C test should not be the sole method for diagnosing the condition; relying solely on it could lead to misdiagnosis and inadequate treatment. Staying informed about these factors, including the emotional aspects of diabetes management, can significantly enhance diabetes care, encouraging patients to adopt a holistic perspective in their journey towards better health.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is fundamental for effective management of Type 2 diabetes. This test not only serves as a diagnostic tool but also plays a crucial role in informing treatment decisions and lifestyle modifications. With a significant percentage of adults with diabetes exhibiting concerning A1C levels, the need for regular monitoring and personalized care is more pressing than ever. By interpreting A1C results accurately, patients can gain insights into their blood sugar control and take proactive steps to mitigate the risk of complications.
Regular A1C monitoring empowers individuals to make informed choices regarding their health, enabling early identification of potential complications and timely interventions. The integration of holistic strategies, including targeted nutrition, exercise, and stress management, can greatly enhance overall health outcomes. Moreover, understanding the nuances of A1C testing and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers are essential components of a comprehensive diabetes management plan.
Ultimately, the journey toward effective diabetes management hinges on education, personalized care, and consistent monitoring of A1C levels. By embracing these principles, individuals can take control of their health, alleviate anxiety about complications, and work towards reversing Type 2 diabetes, leading to improved quality of life and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test?
The A1C test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, measures the percentage of glucose that has bonded to hemoglobin in red blood cells. It is a vital diagnostic tool for managing Type 2 diabetes.
What do A1C percentages indicate?
Elevated A1C percentages indicate suboptimal blood sugar control and a heightened risk of diabetes-related complications. An A1C level of 6.5% or higher typically confirms a diagnosis of a blood sugar disorder, while levels from 5.7% to 6.4% suggest prediabetes.
What percentage of U.S. adults with diabetes have A1C values of 7.0% or higher?
Recent data shows that 47.4% of U.S. adults diagnosed with diabetes exhibit A1C values of 7.0% or higher.
What additional health challenges do adults with diabetes face?
Among adults diagnosed with diabetes, 70.8% have a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or a diastolic blood pressure of 90 mmHg or more, indicating multifaceted health challenges.
How can the A1C test influence treatment decisions?
The A1C test results inform treatment decisions and lifestyle modifications for Type 2 diabetes patients, as guided by the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator.
What does the recent study by Elizabeth Selvin highlight regarding diabetes diagnosis?
The study points out a weakness in the literature related to diabetes diagnosis, specifically the lack of confirmatory glucose testing, emphasizing the need for A1C testing to be part of a comprehensive approach to blood sugar control.
What are some strategies to improve health outcomes for diabetes patients?
Targeted nutrition, customized exercise plans, stress reduction strategies, and community support are four lesser-known approaches that can significantly improve health outcomes and help reverse blood sugar issues.
How should one utilize the American Diabetes Association A1C calculator?
To use the A1C calculator: 1. Secure your most recent A1C test result from your healthcare provider. 2. Visit the American Diabetes Association’s website to find the A1C calculator. 3. Enter your A1C percentage into the calculator. 4. Click ‘Calculate’ to receive your estimated average glucose (eAG) reading. 5. Examine the output, which translates your A1C percentage into an estimated average glucose measurement.
Why is maintaining an A1C of 7% or lower important?
Sustaining an A1C of 7% or lower significantly decreases the risk of complications related to blood sugar conditions, reducing concerns about severe health issues.
How does understanding A1C values impact healthcare costs?
Being aware of your A1C values can help reduce the financial strains associated with healthcare for chronic conditions, underscoring the importance of thorough treatment and education.