Overview
The 1500 calorie diabetic diet is designed to help individuals with type 2 diabetes manage blood sugar levels and support weight loss through balanced nutrition and portion control. The article emphasizes that this diet incorporates various food groups, promotes mindful eating, and has been supported by studies showing its effectiveness in stabilizing glucose levels and improving overall health outcomes.
Introduction
In managing type 2 diabetes, the 1500 calorie diet emerges as a strategic approach that not only aids in blood sugar control but also supports weight management. This dietary plan emphasizes a balanced intake of nutrients derived from various food groups, ensuring that individuals can enjoy meals while adhering to caloric restrictions.
By focusing on:
- Portion control
- Inclusion of lean proteins
- Whole grains
- An abundance of fruits and vegetables
This regimen addresses the critical aspects of diabetes management.
Recent studies highlight the effectiveness of structured meal plans in promoting significant health improvements, reinforcing the importance of tailored dietary interventions. As individuals embark on this journey, understanding the foods to include and avoid, alongside potential challenges, becomes essential for achieving optimal health outcomes.
Understanding the 1500 Calorie Diabetic Diet
The systematic and holistic approach of the 1500 calorie diabetic diet is designed to assist individuals with type 2 conditions in effectively managing their blood sugar levels while facilitating weight loss or maintenance. By capping daily caloric intake at 1500 calories, this plan emphasizes a 1500 calorie diabetic diet that focuses on balanced nutrition derived from diverse food groups, aligning with our commitment to addressing the root causes of health issues at the Integrative Wellness Center. This method not only aims to stabilize blood glucose levels through controlled carbohydrate intake—a critical aspect of managing the condition—but also seeks to alleviate the anxiety that accompanies the worry surrounding potential complications of the illness.
We begin by re-evaluating the origin of your condition, ensuring that this dietary regimen is tailored to meet individual needs, considering factors such as age, physical activity, and overall health status. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is highly recommended prior to initiating any new dietary regimen. Recent studies indicate that such structured meal plans can lead to significant health improvements; for instance, Parker et al. observed a weight reduction of 5.2 kg ± 1.8 kg over 12 weeks in individuals with obesity and type 2, regardless of whether the diet was high or low in protein. This finding underscores the effectiveness of dietary interventions, which can vary across guidelines and healthcare systems.
Furthermore, a study titled ‘Impact of Small Rice Bowls on Dietary Intake’ demonstrated that using smaller rice bowls led to a decrease in total energy intake among women with type 2 conditions, illustrating a practical application of portion control in dietary management.
Additionally, recent findings from the Cleveland Clinic highlight the importance of achieving sufficient sleep levels in relation to personal glucose targets, further emphasizing the multifaceted approach needed for effective management of the condition. A focus on caloric restriction has also been shown to positively impact blood sugar levels, reinforcing the effectiveness of the 1500 calorie diabetic diet as part of a holistic strategy for diabetes reversal.
Effective Meal Planning for a 1500 Calorie Diet
Creating an effective meal plan requires a balanced approach that includes a variety of groups while maintaining vigilant portion control for a 1500 calorie diabetic diet. Individuals are encouraged to include:
- Lean proteins
- Whole grains
- Healthy fats
- An abundance of fruits and vegetables
in their daily menus. For instance, a well-structured sample meal plan might feature:
- Oatmeal topped with berries for breakfast
- A vibrant salad with grilled chicken for lunch
- Baked salmon with steamed broccoli for dinner
Nutritional snacks can consist of nuts or yogurt, providing additional protein without excess carbohydrates. Recent studies indicate that those who engage in meal planning tend to consume more protein and fewer starchy foods, supporting better management of blood glucose levels. Notably, the DIRECT trial revealed that at 12 months, almost half of participants achieved T2D remission off all glucose-lowering medications, underscoring the effectiveness of dietary management.
By employing meal prep techniques—such as preparing meals in advance and portioning them—individuals can enhance their adherence to caloric limits, effectively mitigate impulsive eating decisions, and promote overall dietary compliance. It is essential to consider dietary sodium restrictions, as excessive limitations may inadvertently reduce insulin sensitivity. Furthermore, people with specific health conditions, such as cirrhosis, may encounter unique challenges in nutritional treatment; therefore, tailored nutritional programs focusing on frequent meals and adequate protein intake are recommended.
For further guidance, individuals can explore resources like the Find a Diabetes Education Program in Your Area locator for Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support (DSMES) services tailored to their needs.
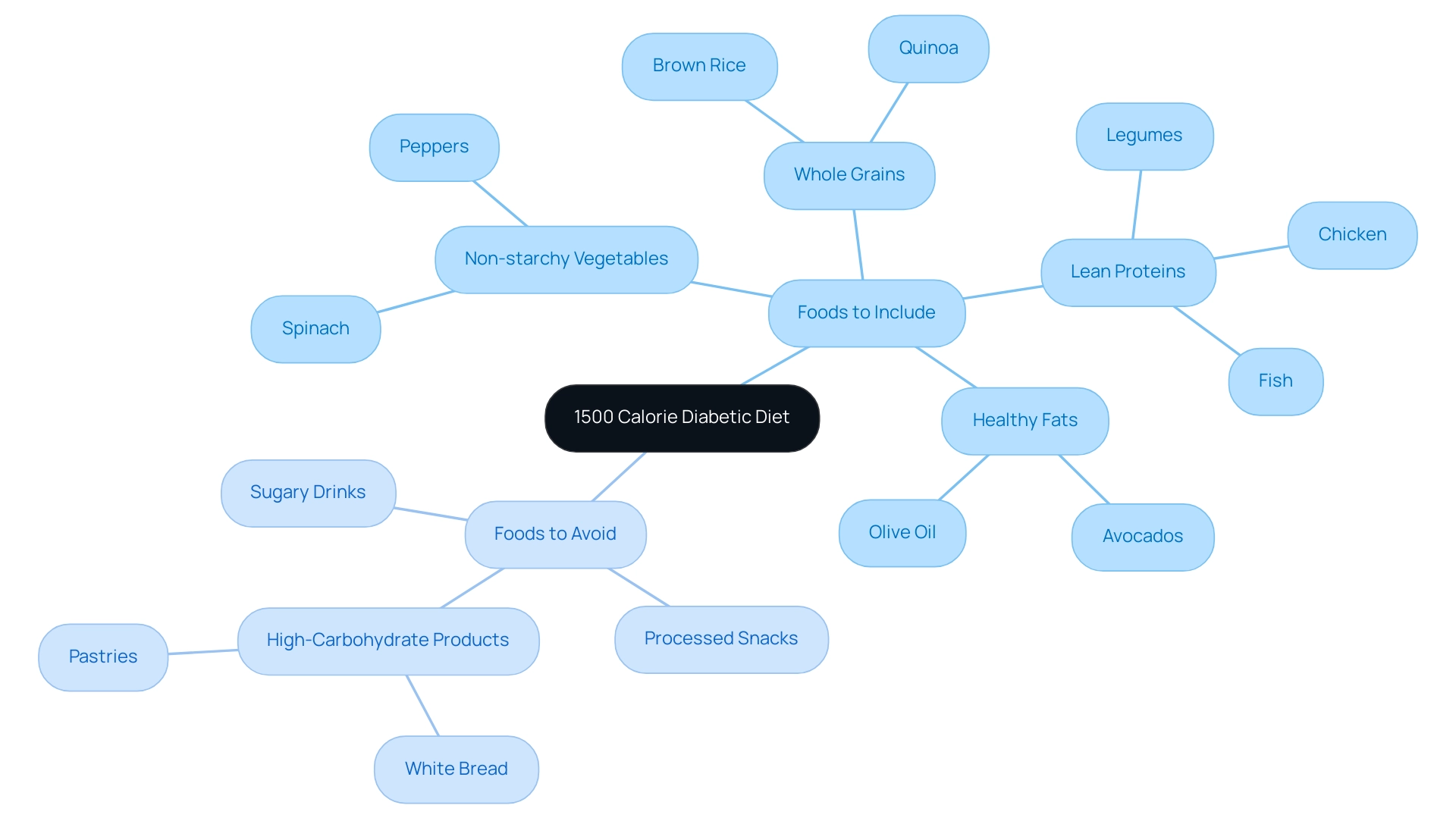
Foods to Include and Avoid in a 1500 Calorie Diabetic Diet
In crafting a 1500 calorie diabetic diet for managing blood sugar, it is essential to prioritize foods that are low in added sugars and rich in fiber. Recommended options include a variety of non-starchy vegetables, such as spinach and peppers, which provide essential nutrients and help regulate blood sugar levels due to their low carbohydrate content. Additionally, whole grains like quinoa and brown rice should be included for their high fiber content, which aids in slowing glucose absorption and maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
These healthier grains are increasingly highlighted in San Marcos eateries, making them accessible choices for those aiming to manage their condition while enjoying flavorful meals. Lean proteins, such as fish, chicken, and legumes, contribute to satiety and muscle maintenance, while healthy fats from sources like avocados and olive oil promote overall heart health. In fact, regular consumption of fatty fish, which provide Omega-3 fatty acids, may help reduce triglycerides and improve heart health, as noted in a case study discussing the benefits of these fats.
Conversely, people should avoid sugary drinks, processed snacks, and high-carbohydrate products, such as white bread and pastries, which can cause spikes in blood sugar. Monitoring carbohydrate intake is critical, as it directly influences glucose levels. The National Institutes of Health highlights that dietary modifications advantageous for managing blood sugar, such as a 1500 calorie diabetic diet, include:
- Regular meals
- Mindful portion sizes
- A variety of items throughout the day
Furthermore, it is vital to read nutrition labels and practice portion control, as these strategies can significantly impact overall health and blood sugar regulation.
Health Benefits and Considerations of a 1500 Calorie Diet
Following a 1500 calorie diabetic diet presents numerous health benefits for individuals managing diabetes, particularly in the context of the transformative approaches offered at the Integrative Wellness Center. The 1500 calorie diabetic diet is associated with enhanced blood sugar control, significant weight loss, and a diminished risk of complications such as heart disease and neuropathy. A structured eating plan fosters healthier eating habits, contributing to improved overall well-being.
Health experts emphasize,
The first step is to read food labels carefully,
underscoring the importance of informed food choices. A typical daily total for this 1500 calorie diabetic diet includes:
- 1,513 calories
- 111 g of protein
- 151 g of carbohydrates
- 30 g of fiber
- 59 g of fat
- 14 g of saturated fat
- 1,309 mg of sodium
Research indicates that a regimen abundant in fresh produce, protein, and fiber not only aids in weight management but also helps in minimizing diabetes-related complications.
For instance, one patient shared, “After following the meal plan, my blood sugar levels stabilized, and I lost 20 pounds within three months!” It is also crucial to address common misconceptions, such as the belief that people with blood sugar issues must avoid sugar completely or require specific diabetic meals. The Integrative Wellness Center demonstrates through case studies that individuals can enjoy treats while maintaining a balanced nutritional approach without needing special items, as healthy eating principles remain consistent for everyone.
Another success story highlights a patient who stated, “I thought I had to give up all my favorite dishes, but now I can enjoy them in moderation and still manage my diabetes effectively.” In contrast, recent trends like the ice hack plan, which promotes consuming cold foods to enhance metabolism, may not be effective and should be approached with caution. It is crucial for individuals to consider their unique health conditions and seek guidance from healthcare professionals to customize their nutrition according to their specific needs and lifestyle.
Consistent tracking of blood glucose levels is crucial to assess the effectiveness of the nutritional plan and make necessary adjustments for optimal health outcomes.
Overcoming Challenges in Maintaining a 1500 Calorie Diabetic Diet
Following a 1500 calorie diabetic diet can present various challenges, such as:
- Dealing with cravings for high-calorie items
- Navigating social situations that involve meals
- Managing time constraints for meal preparation
To effectively address these challenges, individuals can adopt several strategies:
- Keeping healthy snacks readily available helps mitigate cravings and provides nutritious options when hunger strikes.
- Practicing mindful eating encourages awareness of portion sizes and food choices, enhancing the overall dining experience. In fact, a meta-analysis found that increasing fruit and vegetable consumption by just 0.8 servings daily is associated with significant reductions in BMI and HbA, underscoring the importance of healthy eating in managing this condition.
- Careful meal planning is essential; by preparing meals in advance, people can avoid impulsive decisions that may lead to unhealthy eating patterns.
- Assistance from friends, family, or support groups can also be essential in offering encouragement and responsibility as people work to meet their dietary objectives.
- Tracking food intake via mobile applications or journals allows people to monitor their consumption, ensuring they remain within their caloric limits while making necessary adjustments for optimal health management.
It is also important to be aware of the risks linked to certain dietary choices; for instance, a meta-analysis reported that consumption of at least one serving of sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs) per day heightened the risk of type 2 conditions in adults with prediabetes by 26%.
By implementing these strategies and being mindful of dietary risks, individuals can more effectively navigate the complexities associated with a 1500 calorie diabetic diet. Furthermore, case studies have shown that replacing SSBs with water can reduce diabetes risk by 7-8%, providing a real-world example of how dietary choices can impact health outcomes.
Conclusion
Adopting a 1500 calorie diet can serve as an effective strategy for individuals managing type 2 diabetes, addressing both blood sugar control and weight management. By emphasizing balanced nutrition through the inclusion of:
- Lean proteins
- Whole grains
- A variety of fruits and vegetables
this dietary approach not only stabilizes glucose levels but also promotes overall well-being. The evidence supporting structured meal plans further illustrates the potential for significant health improvements, making it crucial for individuals to understand the foods that support their goals while avoiding those that hinder progress.
Challenges may arise while maintaining this dietary regimen, yet practical strategies such as:
- Meal planning
- Mindful eating
- Seeking support
can help overcome obstacles. The importance of portion control and informed food choices cannot be overstated, as they play a vital role in achieving optimal health outcomes. Each individual’s journey is unique, and personalized guidance from healthcare professionals can enhance the effectiveness of this diet, ensuring it aligns with specific health needs.
Ultimately, the 1500 calorie diet represents a holistic approach to diabetes management that empowers individuals to take control of their health. By fostering healthier eating habits and encouraging mindful choices, individuals can enjoy a fulfilling lifestyle while effectively managing their condition. Embracing this structured dietary plan not only aids in the immediate management of diabetes but also contributes to long-term health and vitality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the 1500 calorie diabetic diet?
The 1500 calorie diabetic diet is designed to help individuals with type 2 diabetes manage their blood sugar levels while facilitating weight loss or maintenance through balanced nutrition and controlled caloric intake.
How does the 1500 calorie diabetic diet stabilize blood glucose levels?
This diet stabilizes blood glucose levels by controlling carbohydrate intake, which is a critical aspect of managing diabetes.
Why is it important to consult a healthcare professional before starting this diet?
Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended to ensure the dietary regimen is tailored to individual needs, considering factors such as age, physical activity, and overall health status.
What have studies shown about the effectiveness of structured meal plans for individuals with type 2 diabetes?
Recent studies indicate that structured meal plans can lead to significant health improvements, such as a weight reduction of 5.2 kg over 12 weeks in individuals with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
What role does portion control play in the 1500 calorie diabetic diet?
Portion control is crucial in dietary management, as demonstrated by a study showing that using smaller rice bowls led to a decrease in total energy intake among women with type 2 diabetes.
How does sleep affect blood glucose targets in individuals with diabetes?
Recent findings highlight the importance of achieving sufficient sleep levels in relation to personal glucose targets, emphasizing a multifaceted approach for effective diabetes management.
What types of foods should be included in a 1500 calorie diabetic diet?
The diet should include lean proteins, whole grains, healthy fats, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables.
Can you provide an example of a meal plan for the 1500 calorie diabetic diet?
A sample meal plan could feature oatmeal topped with berries for breakfast, a vibrant salad with grilled chicken for lunch, and baked salmon with steamed broccoli for dinner.
What are some benefits of meal planning for individuals with diabetes?
Meal planning can lead to higher protein consumption and fewer starchy foods, supporting better management of blood glucose levels.
What should individuals with specific health conditions consider when following the 1500 calorie diabetic diet?
Individuals with specific health conditions, such as cirrhosis, may face unique challenges and should consider tailored nutritional programs focusing on frequent meals and adequate protein intake.
Where can individuals find additional resources for diabetes management?
Individuals can explore resources like the Find a Diabetes Education Program in Your Area locator for Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support (DSMES) services tailored to their needs.