Overview
Managing diabetes can feel overwhelming, especially when striving for a fasting sugar level of 131 mg/dL. It’s important to recognize that consistent monitoring of blood glucose, dietary changes, regular physical activity, and proper medication use are crucial steps in this journey. Many patients find that tracking glucose levels can provide valuable insights into their health. Embracing a whole foods diet not only nourishes the body but also supports overall well-being.
Incorporating regular exercise into your routine is another empowering choice. It’s not just about physical activity; it’s about finding joy in movement, whether it’s a brisk walk, dancing, or yoga. Adhering to prescribed treatments can sometimes feel challenging, but remember, you’re not alone in this. These strategies can truly empower you to maintain your target glucose levels effectively.
By taking small, manageable steps, you can create a healthier lifestyle that feels achievable. Reflect on your experiences and consider how these changes can positively impact your daily life. You deserve support and encouragement as you navigate this path toward better health.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of diabetes management can often feel overwhelming. It’s important to recognize that understanding the nuances of blood sugar control is essential for maintaining your health and well-being. With ideal fasting blood sugar levels ranging between 80 and 130 mg/dL, many individuals find themselves needing to be vigilant in monitoring their readings. Have you ever felt uncertain about your next steps? Making informed lifestyle choices can truly empower you.
From dietary adjustments and regular physical activity to the careful use of medications, a comprehensive approach can help you take charge of your health. Many patients find that small, consistent changes lead to significant improvements. This article delves into practical strategies and insights that not only assist in achieving optimal blood sugar levels but also enhance your overall quality of life. Together, we can explore how to navigate this journey with confidence and support.
Understand Ideal Blood Sugar Levels
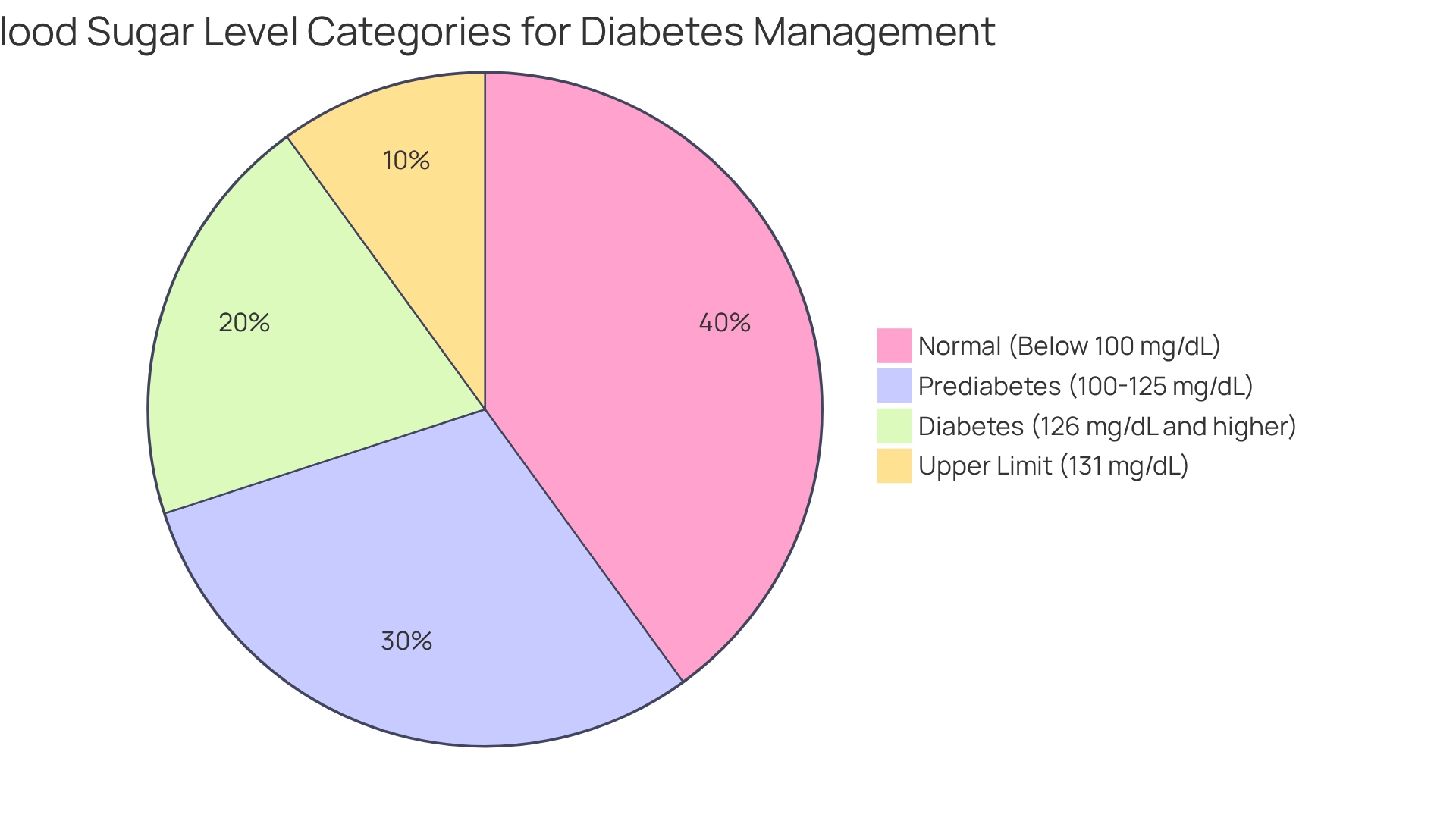
Successful control of diabetes hinges on a precise understanding of optimal glucose measurements. For individuals living with this condition, the target fasting glucose concentration typically ranges from 80 to 130 mg/dL. A reading of 131 mg/dL is at the upper limit of this range, and consistent levels above this threshold may require further intervention. It’s important to recognize that managing diabetes can be challenging, but understanding these key points can empower you:
- Normal Levels: Ideally, fasting blood sugar should be below 100 mg/dL. Levels between 100 and 125 mg/dL indicate prediabetes, while readings of 126 mg/dL or higher confirm diabetes.
- Post-Meal Measurements: Blood glucose concentrations should remain under 180 mg/dL two hours after eating. This is vital for effective management, highlighting the importance of tracking your glucose measurements to understand how your body reacts to different foods and activities.
- Monitoring: Regular observation is essential, as it provides valuable insights into how your body responds to various foods and activities, facilitating better management of your condition.
Many individuals with elevated glucose levels find it difficult to reach these target fasting values, underscoring the need for personalized care and guidance. For instance, a case study from Dr. Shumard’s center highlighted a patient who, after joining the 30-Day Diabetes Reset program, successfully lowered their fasting glucose levels from 145 mg/dL to 120 mg/dL within three months. This transformative experience illustrates how a holistic approach, emphasizing tailored nutrition and lifestyle changes, can empower individuals to reclaim their health, leading to improved quality of life and reduced reliance on conventional medical interventions.
As Dr. Jason Shumard states, “By providing patients with actionable insights and practical tools, the center fosters an environment where individuals can reclaim their health and well-being.” By understanding and following these guidelines, you can take proactive steps toward effectively managing your condition. Moreover, consulting with educators specializing in metabolic conditions or endocrinologists can offer additional expert perspectives on achieving optimal fasting glucose targets.
Monitor Your Blood Sugar Regularly
To attain and uphold a 131 sugar level, consistent monitoring is essential. Here’s how to do it effectively:
-
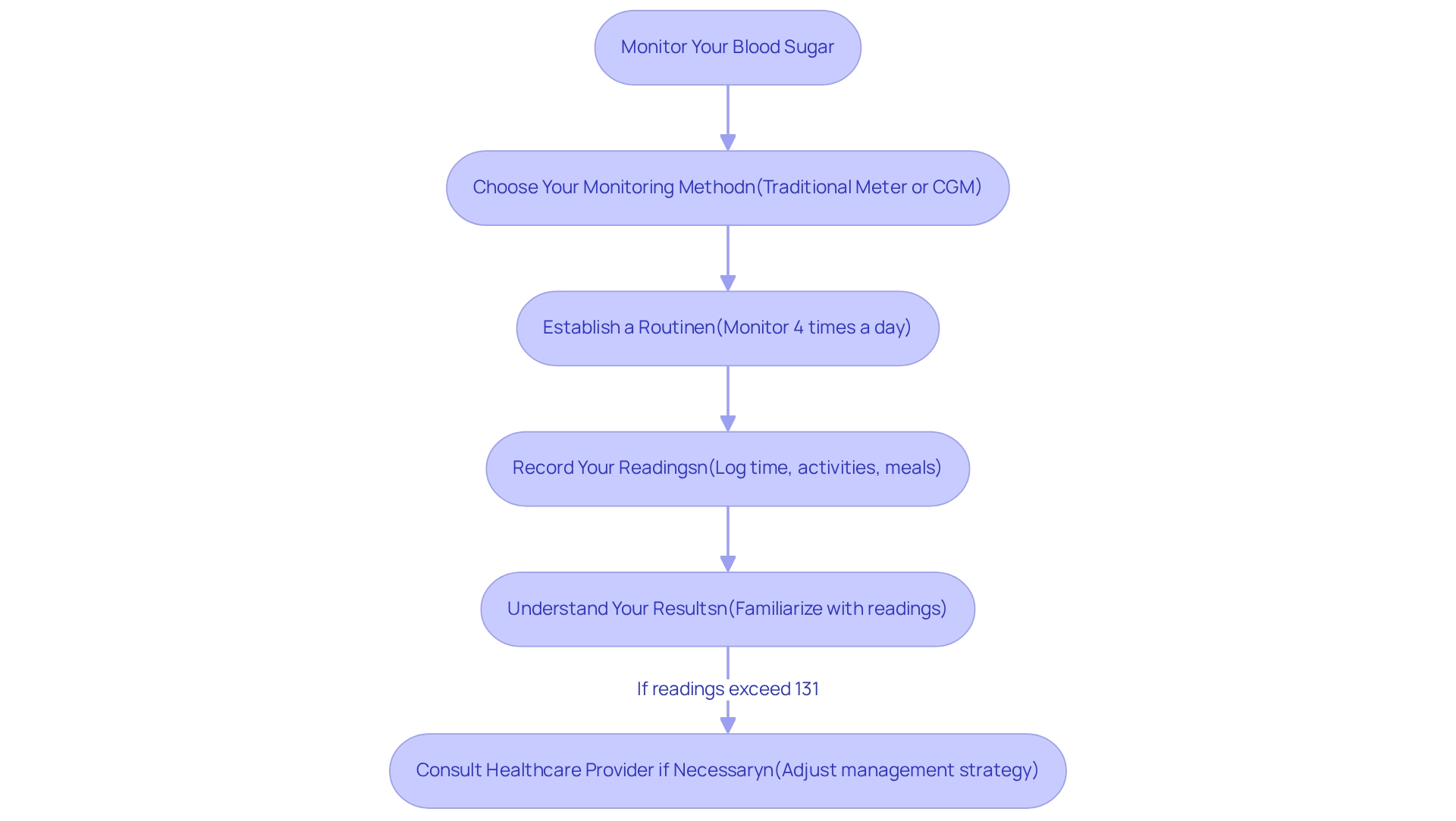
Choose Your Monitoring Method: You have options! You can select between a traditional glucose meter or a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). A systematic review of 12 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving 1248 participants with type 2 diabetes found that CGM may offer improved management compared to standard glucose monitoring (SMBG). While a CGM provides real-time data and insights into glucose trends, a traditional meter is often more budget-friendly and still effective for daily use.
-
Establish a Routine: Aim to monitor your glucose levels at least four times each day—before meals and at bedtime. This consistent routine helps you recognize patterns in your glucose readings, allowing for timely adjustments to your diet or medication. Consider setting SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—to enhance your focus and motivation in managing your diabetes.
-
Record Your Readings: Keeping a comprehensive log of your blood sugar readings, along with the time of day and any relevant activities or meals, can be invaluable. This information aids both you and your healthcare provider in making informed decisions about your blood sugar management plan. Regularly reviewing your progress not only fosters accountability but also allows for adapting goals in response to changing fitness levels.
-
Understand Your Results: It’s important to familiarize yourself with what your readings indicate. If your readings consistently exceed the 131 sugar level, consulting with your healthcare provider is essential to reassess and adjust your management strategy. Participating in community wellness initiatives can also offer assistance and tools designed for effectively managing blood sugar levels.
Regular blood sugar monitoring is not merely a routine; it’s an essential element of efficient management. Many patients find that engaging in consistent monitoring leads to better control over their glucose levels, resulting in improved health outcomes. By adopting these best practices and prioritizing goal-setting, you empower yourself to take charge of your health and make informed decisions. As emphasized by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, understanding disparities in diabetes risk factors is essential for successful management, highlighting the importance of regular monitoring in addressing the rising prevalence of diabetes worldwide.
Implement Dietary Changes for Blood Sugar Control
Making educated dietary decisions is essential for effective glucose management, particularly to maintain a 131 sugar level. It’s important to recognize that many individuals face challenges in this area. Here are several strategies to consider that can truly make a difference:
-
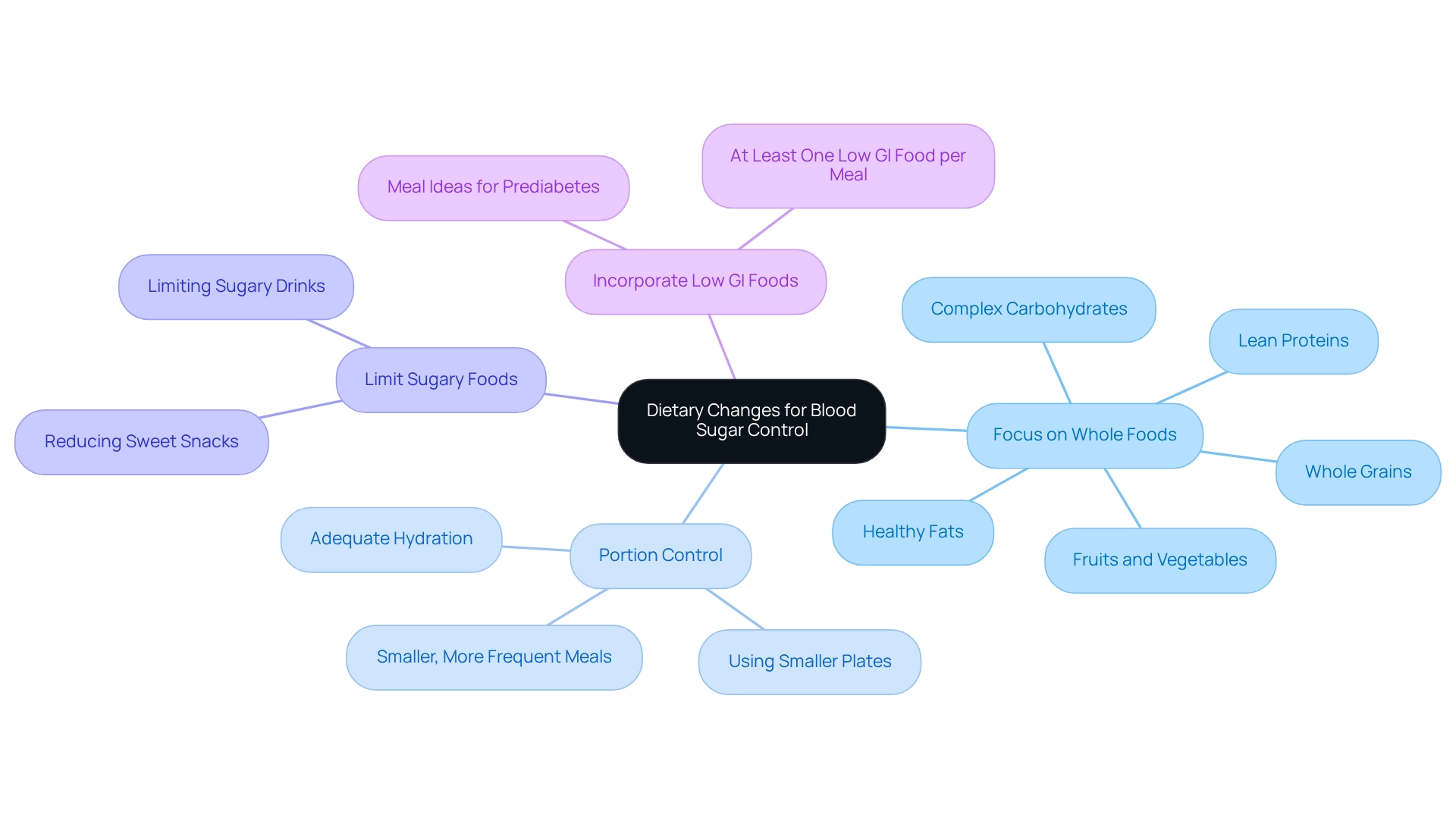
Focus on Whole Foods: Emphasize whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables. These nutrient-rich foods not only supply vital vitamins and minerals but also assist in stabilizing glucose concentrations, contributing to a 131 sugar level. Many patients participating in Dr. Jason Shumard’s 30-Day Diabetes Reset program have reported transformative outcomes by adopting a whole foods approach, which has helped them achieve a 131 sugar level, highlighting the effectiveness of dietary interventions in managing diabetes. Select intricate carbohydrates, such as whole grains and legumes, which break down more gradually and have a milder effect on glucose amounts, helping to maintain a 131 sugar level.
-
Portion Control: Utilizing smaller plates can help regulate portion sizes. Consuming smaller, more frequent meals can also help maintain a stable glucose concentration, ideally around the 131 sugar level, throughout the day. Adequate hydration promotes kidney performance, assisting in the removal of surplus glucose through urine, which is essential for maintaining a 131 sugar level.
-
Limit Sugary Foods: Reducing the consumption of sweet snacks and drinks is crucial, as these can cause quick increases in glucose levels, potentially leading to a rise above the 131 sugar level.
Integrating these dietary adjustments can greatly improve glucose regulation and help maintain a healthy 131 sugar level. As highlighted by nutrition specialists, incorporating at least one low glycemic index (GI) food into every meal can enhance glucose stability, which is especially important for maintaining a 131 sugar level. Kathy W. Warwick, RDN, CDCES, notes that ‘individuals with prediabetes may struggle to discover appealing meal concepts to assist in reducing their glucose concentrations.’ By combining these dietary strategies with exercise, weight management, and medications, individuals can take proactive steps toward achieving a 131 sugar level, leading to better health and an improved quality of life. If you’re concerned about your glucose levels, particularly if they are around a 131 sugar level, it’s advisable to consult a physician for tailored advice. Join our community at the Integrative Wellness Center to discover real solutions and receive free resources, including Dr. Jason Shumard’s insightful book, when you attend our next event.
Incorporate Regular Physical Activity
Consistent exercise is essential for controlling diabetes and achieving a glucose measurement of 131 sugar level. It’s important to recognize that incorporating exercise into your daily routine can be a transformative journey. Here’s how to effectively make it a part of your life:
-
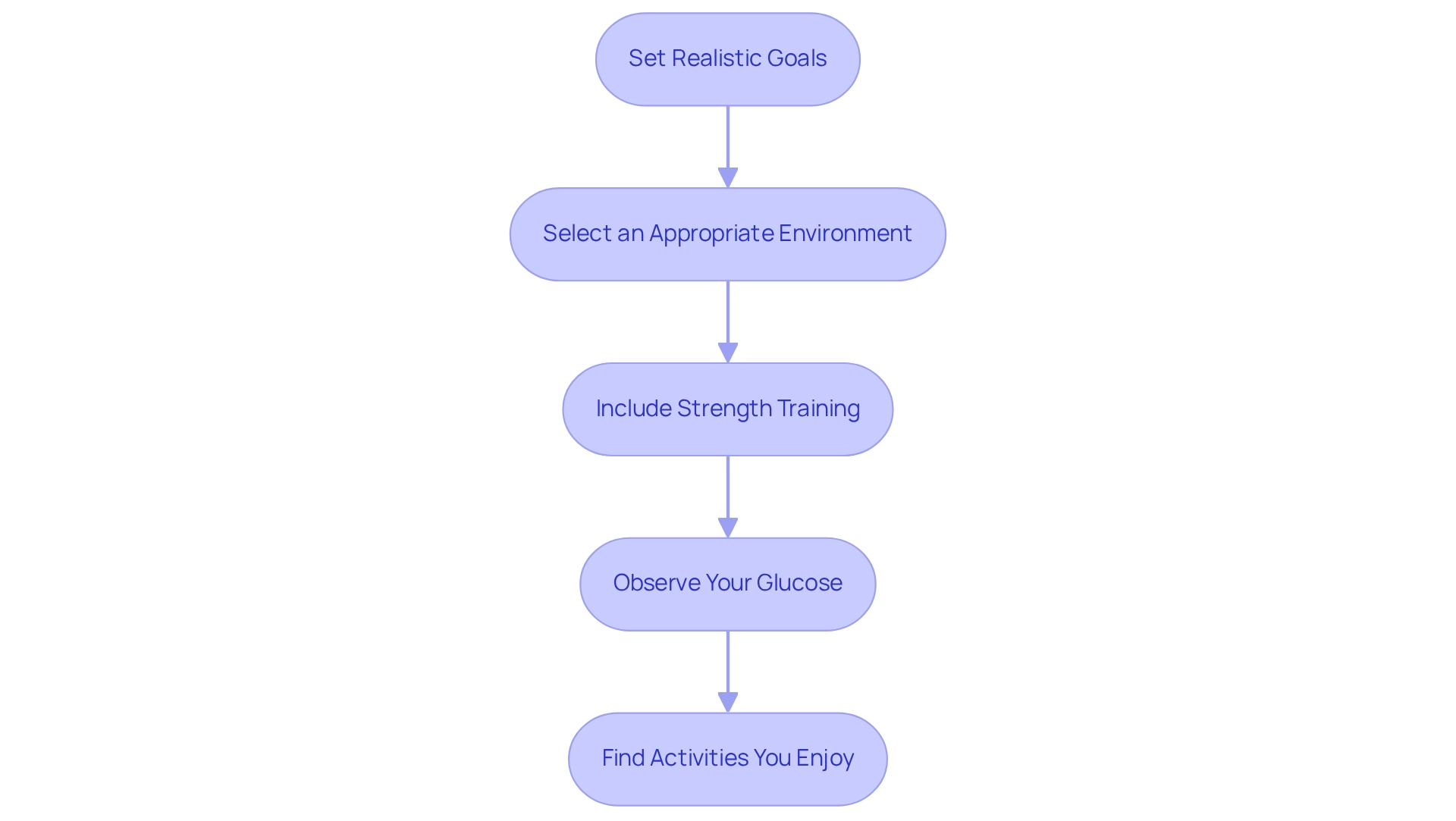
Set Realistic Goals: Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise each week. Begin by assessing your current fitness level and setting attainable objectives, such as dedicating 10-15 minutes to a daily walk. Activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming can significantly enhance your overall health.
-
Select an Appropriate Environment: Choose a safe and comfortable space for your walks, whether indoors or outdoors. This ensures you can exercise without distractions or hazards, making the experience more enjoyable.
-
Include Strength Training: Engage in strength training exercises at least twice a week. Increasing muscle mass improves insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for managing glucose levels. Stay Active Throughout the Day: Look for opportunities to boost your activity, like using the stairs instead of the elevator or taking brief walks during breaks. Remember, small changes can lead to significant benefits. Consider joining a hiking group or partnering with a friend to enhance accountability and enjoyment.
-
Observe Your Glucose: Consistently check your glucose levels, especially when monitoring for a 131 sugar level, before and after exercise to understand how different activities affect your readings. This awareness allows you to adjust your food intake or medication accordingly. Tracking your progress with a journal or an app can help maintain motivation and celebrate your achievements.
-
Find Activities You Enjoy: Choose exercises that you genuinely enjoy, whether it’s dancing, hiking, or joining a sports team. Engaging in enjoyable activities makes it easier to maintain a consistent routine. Research shows that organized walking initiatives can lead to substantial health improvements, making it easier to stick to your exercise plan.
Research indicates that physical activity not only helps in managing blood sugar levels but also enhances overall health. For instance, a meta-analysis of various exercise interventions underscores the importance of regular activity in managing blood sugar levels. Additionally, the American College of Sports Medicine highlights the benefits of both aerobic and resistance training for individuals with diabetes, especially during challenging times like the COVID-19 pandemic. Notably, 33% of participants in the DIADEM-I trial went into remission after one year, showcasing the potential impact of lifestyle changes. Furthermore, older age, ongoing health issues, and lack of physical activity before social isolation were linked to an increased risk of reduced physical activity during the pandemic, emphasizing the importance of maintaining physical exercise. By adhering to these guidelines, you can take proactive steps toward better health and improved glucose control.
Utilize Medication and Supplements Wisely
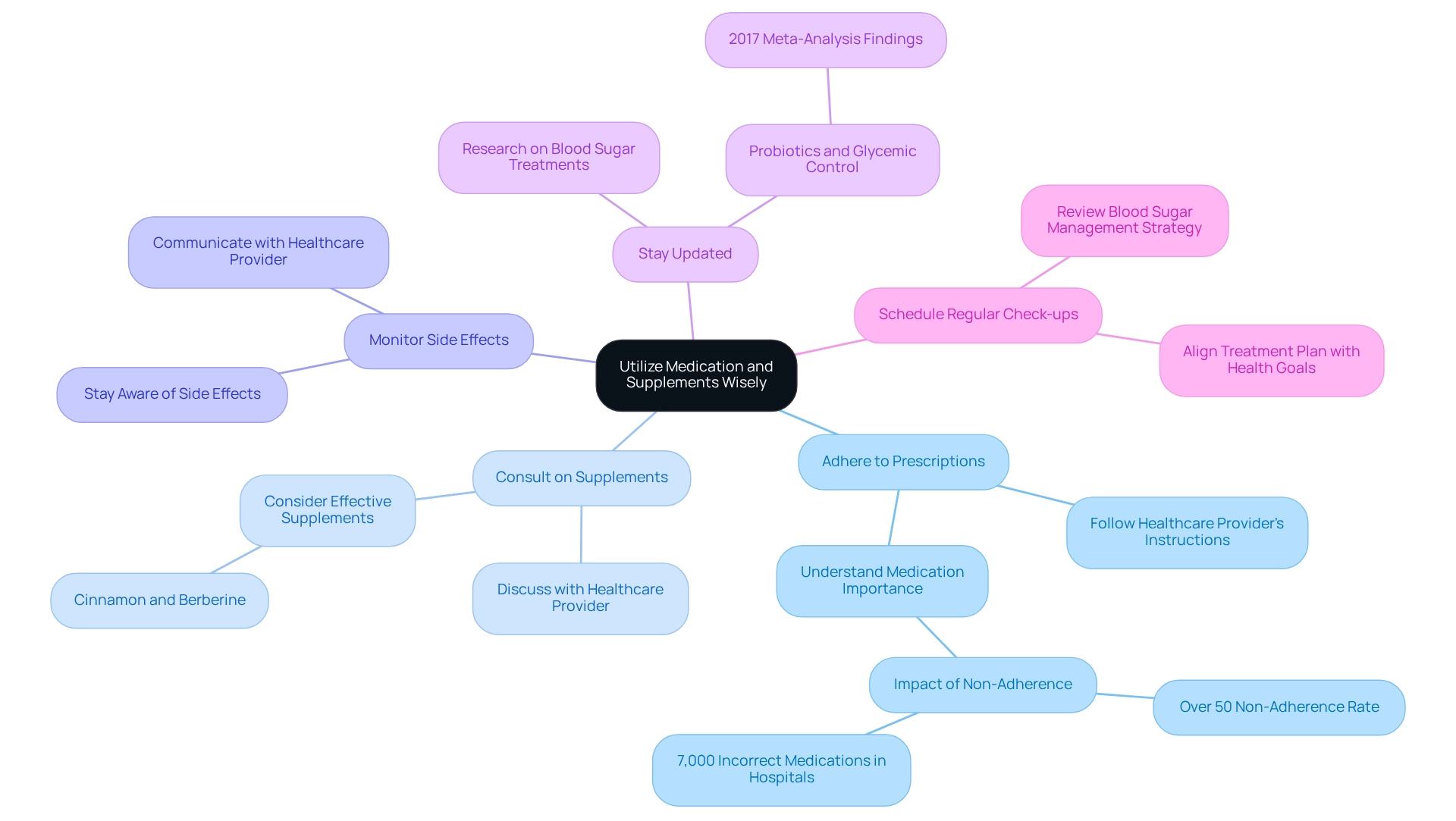
Managing glucose concentrations is essential for your health, especially when considering safety in hospital settings. Here’s how you can make the most of medications and supplements in your journey:
-
Adhere to Prescriptions: It’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding medications, including any oral drugs and insulin prescribed. Research indicates that over 50% of patients with diabetes-related conditions may not adhere to their medication schedules, which can significantly impact health outcomes (source: American Diabetes Association). With alarming statistics showing 7,000 incorrect medications and 80,000 infections acquired in hospitals, ensuring correct medication use is vital for your safety.
-
Consult on Supplements: Before adding any supplements to your routine, have a conversation with your healthcare provider. Some supplements, like cinnamon and berberine, show promise in lowering the 131 sugar level. However, they should complement, not replace, prescribed medications. Personalized guidance from your healthcare team can help you find the right balance for your needs.
-
Monitor Side Effects: Stay aware of any potential side effects from your medications. Regularly share your concerns with your healthcare provider, as adjustments may be necessary to optimize your treatment plan. This vigilance is particularly important in a healthcare environment focused on safety.
-
Stay Updated: Keeping informed about the latest research on blood sugar treatments and supplements can empower your health decisions. For instance, a 2017 meta-analysis highlighted the potential of probiotics in lowering fasting blood glucose levels, underscoring their role in managing diabetes-related conditions. Understanding these developments can help you feel more in control of your health.
-
Schedule Regular Check-ups: Regular appointments with your healthcare provider are essential for reviewing your blood sugar management strategy, including the effectiveness of your medications and supplements. This ongoing dialogue ensures your treatment plan aligns with your health goals, especially as personalized functional medicine approaches become increasingly important.
Incorporating dietary fiber into your daily regimen is also beneficial. The American Diabetes Association recommends a daily intake of 25-35 grams of dietary fiber for optimal health. Fiber supplementation can enhance glucose control in individuals with type 2 diabetes, which is essential for maintaining a 131 sugar level as part of your overall management plan. By providing you with actionable insights and practical tools, the Integrative Wellness Center creates a nurturing environment where you can reclaim your health and well-being, even amidst the challenges posed by hospital safety concerns.
Troubleshoot Common Blood Sugar Management Issues
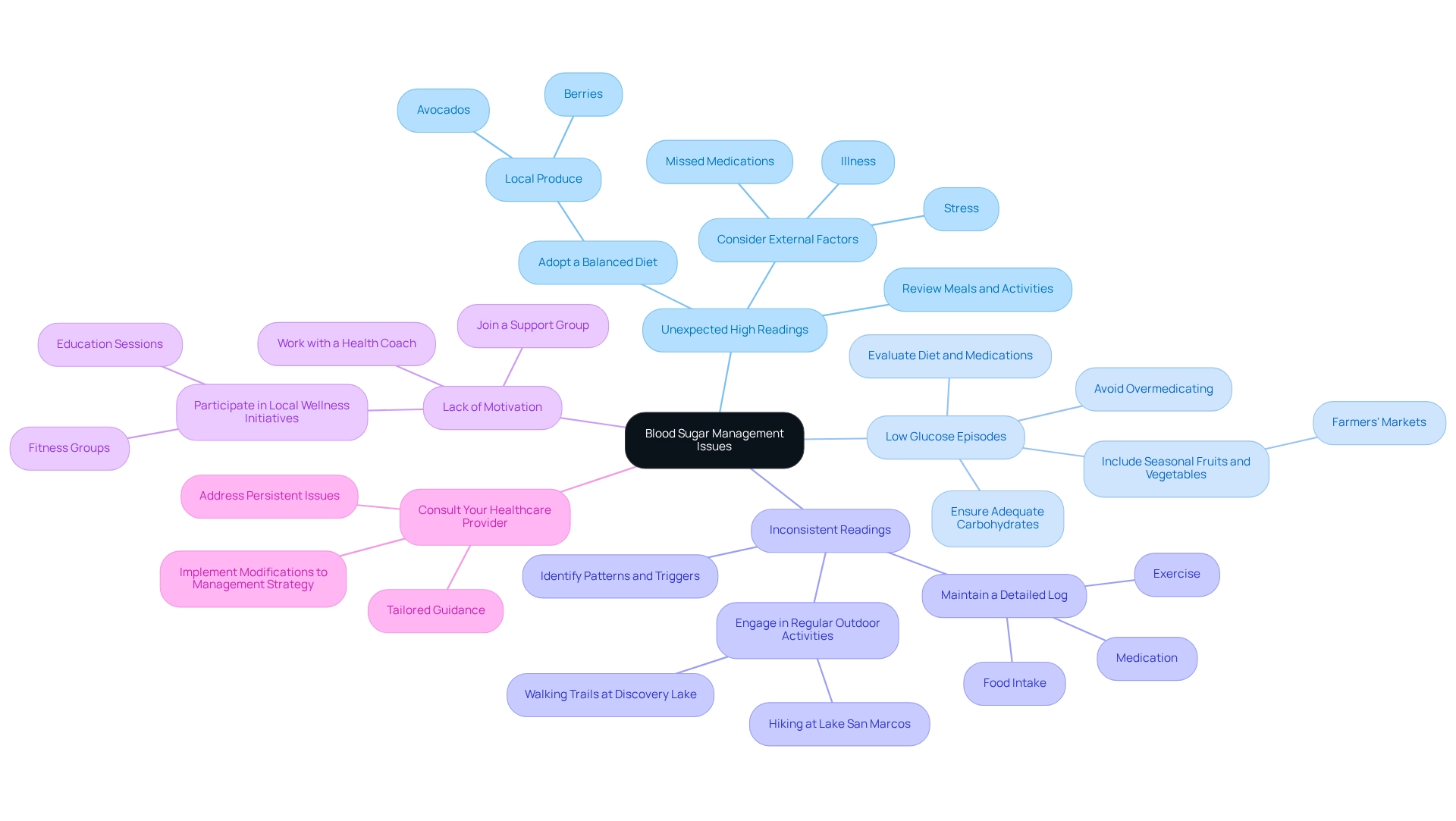
Controlling glucose concentrations can pose different difficulties, and it’s important to recognize that you’re not alone in this journey. Here are some common issues and effective strategies to troubleshoot them:
-
Unexpected High Readings: A sudden increase in glucose levels can be alarming. Have you recently reviewed your meals and activities? Consider external factors such as stress, illness, or missed medications that may have contributed to the increase. Adopting a balanced diet abundant in local produce, such as avocados and berries, can assist in stabilizing your values.
-
Low Glucose Episodes: Frequent low glucose levels can be worrying. It’s essential to evaluate your diet and the timing of your medications. Are you consuming adequate carbohydrates? Ensure you’re not overmedicating, as both can lead to these episodes. Including seasonal fruits and vegetables from nearby farmers’ markets can offer the essential nutrients to maintain stable glucose amounts.
-
Inconsistent Readings: If your blood sugar levels fluctuate significantly, maintaining a detailed log of your food intake, exercise, and medication can be invaluable. Many patients find that this practice helps identify patterns and triggers, allowing for more informed adjustments to their management plan. Regular outdoor activities, such as hiking at Lake San Marcos or walking the trails at Discovery Lake, can enhance insulin sensitivity and improve overall health.
-
Lack of Motivation: Staying motivated can be challenging. Have you considered joining a support group or working with a health coach? Engaging with a community can provide essential encouragement and accountability, making the journey more manageable. Local wellness initiatives in San Marcos, including education sessions and fitness groups, offer resources designed for managing blood sugar levels, fostering an environment conducive to reclaiming health. As highlighted in the case study “Patient Empowerment through Education,” Dr. Shumard emphasizes patient education and empowerment.
-
Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Persistent issues warrant a conversation with your healthcare provider. They can provide tailored guidance and implement essential modifications to your management strategy, ensuring you have the assistance required to manage your condition effectively. As Dr. Elizabeth Selvin noted, “There has been a real decline in glycemic control from a decade ago,” underscoring the importance of effective management strategies.
By addressing these common challenges with practical solutions, individuals can take proactive steps toward better blood sugar management. Remember, this condition is not curable; it is manageable, and continuous oversight is essential for better health results. For personalized guidance and support tailored to your unique needs, consider reaching out to Dr. Jason Shumard in San Marcos, CA, or participating in local wellness programs to enhance your diabetes management journey.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes can feel overwhelming, but it’s a journey that many navigate with success. Understanding blood sugar levels is a crucial step, as is regular monitoring, making dietary changes, exercising, and using medications wisely. By recognizing that the ideal fasting blood sugar range is between 80 to 130 mg/dL, you can gain valuable insights into your health. Consistently checking your levels empowers you to make informed decisions about your well-being.
It’s essential to focus on dietary strategies that emphasize whole foods, control carbohydrate intake, and maintain proper hydration. These steps are key to stabilizing blood sugar levels. Incorporating regular physical activity not only helps with blood sugar control but also boosts your overall well-being. Have you considered setting realistic fitness goals or finding activities you enjoy? These can foster a sustainable exercise routine that feels less like a chore and more like a rewarding part of your day.
Moreover, using medications and supplements wisely, while staying informed about the latest research, can significantly enhance your blood sugar management. It’s important to address common challenges, such as unexpected high or low readings, with a proactive approach and the support of your healthcare providers. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey.
Ultimately, managing diabetes is about empowerment through knowledge and action. By embracing a comprehensive strategy that includes education, lifestyle modifications, and community support, you can truly enhance your quality of life. With the right tools and determination, navigating the complexities of diabetes can become not just manageable but also an opportunity for personal growth and well-being. You have the power to take charge of your health and create a fulfilling life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the target fasting glucose concentration for individuals with diabetes?
The target fasting glucose concentration typically ranges from 80 to 130 mg/dL. A reading of 131 mg/dL is at the upper limit of this range.
What do different fasting blood sugar levels indicate?
Ideally, fasting blood sugar should be below 100 mg/dL. Levels between 100 and 125 mg/dL indicate prediabetes, while readings of 126 mg/dL or higher confirm diabetes.
What should post-meal blood glucose levels be?
Blood glucose concentrations should remain under 180 mg/dL two hours after eating for effective management.
Why is regular monitoring of blood glucose important?
Regular monitoring provides valuable insights into how your body responds to various foods and activities, facilitating better management of diabetes.
Can personalized care help individuals with elevated glucose levels?
Yes, personalized care and guidance can help individuals lower their fasting glucose levels, as illustrated by a case study where a patient reduced their fasting glucose from 145 mg/dL to 120 mg/dL within three months.
What are some methods for monitoring blood glucose levels?
Individuals can choose between a traditional glucose meter or a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). CGMs may offer improved management compared to standard glucose monitoring.
How often should blood glucose levels be monitored?
It is recommended to monitor glucose levels at least four times each day—before meals and at bedtime.
What should be done with the recorded blood sugar readings?
Keeping a comprehensive log of blood sugar readings, along with the time of day and relevant activities or meals, can help both you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your management plan.
What should you do if your readings consistently exceed the target level?
If readings consistently exceed the target level, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider to reassess and adjust your management strategy.
How does regular blood sugar monitoring impact health outcomes?
Engaging in consistent monitoring often leads to better control over glucose levels, resulting in improved health outcomes for individuals with diabetes.