Overview
Effective management of A1C levels at 10.5% involves adopting a balanced diet, increasing physical activity, and maintaining regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. The article supports this by emphasizing that personalized strategies, such as tailored meal planning and consistent exercise, have shown to significantly lower A1C values and reduce health risks associated with elevated glucose levels.
Introduction
Understanding A1C levels is crucial for individuals managing diabetes, as these figures serve as a barometer for blood sugar control over time. A reading of 10.5% signals significant challenges in glucose management, far exceeding the recommended target of below 7%. High A1C levels are not merely numbers; they reflect a heightened risk of serious health complications, including cardiovascular issues and nerve damage.
This article delves into the implications of elevated A1C levels and outlines effective strategies for improvement, emphasizing the importance of personalized care and lifestyle adjustments. With insights into nutrition, physical activity, and ongoing monitoring, individuals can take proactive steps toward achieving better health outcomes and reversing the trajectory of diabetes.
Understanding A1C Levels: What Does a 10.5 Mean?
An A1C measurement of a1c 10.5% indicates that a person’s average glucose readings have been notably raised over the prior months, greatly exceeding the advised goal of under 7% for most adults managing diabetes. Elevated A1C readings, particularly an a1c 10.5, indicate insufficient blood sugar control and present significant health hazards, including a higher chance of complications like cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, and neuropathy. Recent studies have indicated that patients with an A1C of 10.5 are at a greater risk of adverse health outcomes, reinforcing the necessity of maintaining optimal glucose control.
Transformative health solutions provided at the Integrative Wellness Center of San Diego empower patients through education and personalized care, effectively targeting A1C control. For instance, case studies show that patients who participated in customized meal planning and regular monitoring at the center lowered their A1C values by an average of 2% within six months. Significantly, the occurrence of undetected blood sugar issues in overweight adults is at 7.9%, emphasizing the urgent necessity for effective monitoring and control of glucose.
As Cheryl D. Fryar, M.S.P.H. observes, the age-adjusted prevalence of total and diagnosed conditions related to blood sugar has risen notably, emphasizing the importance of managing A1C values effectively. Case studies involving individuals who reversed type 2 conditions through the Integrative Wellness Center illustrate the varying responses to treatment based on A1C figures, particularly highlighting cases with an A1C 10.5 that emphasize the importance of personalized strategies for handling such conditions.
For example, one patient successfully reversed their condition by following a comprehensive meal plan that emphasized whole foods and regular physical activity. Comprehending A1C levels is crucial for developing an effective strategy for blood sugar regulation, as it indicates the current condition of glucose control and signals the need for timely interventions to reduce health risks. Additionally, incorporating stress management techniques and community support can further enhance patient outcomes, as highlighted in our holistic approach.
Effective Strategies to Lower Your A1C Levels
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: Emphasizing a diet rich in whole foods—such as vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains—is essential for managing Type 2 health conditions. A holistic approach starts by re-evaluating the origin of your diabetes, addressing health at the fundamental aspect. This can help alleviate the anxiety that accompanies worries about potential complications of your disease. Limiting processed foods and sugary drinks is essential for stabilizing blood sugar. Notably, a patient following an 11%-carbohydrate diet without medication experienced a significant reduction in HbA1c levels, illustrating the potential effectiveness of dietary adjustments. Furthermore, a study titled “Gene-Diet Interaction Analysis on Type 2 Diabetes Risk” found that a higher diet quality score was linked to a 9% lower risk of developing Type 2 diabetes, underscoring the importance of dietary quality in diabetes management.
- Monitor Carbohydrate Intake: Understanding the impact of carbohydrates on blood sugar is vital. Working with a dietitian can lead to a personalized meal plan that effectively manages carbohydrate intake and is crucial for individuals aiming to improve their a1c 10.5 outcomes. Research indicates that a 1-SD increment in the diet quality score correlates with a reduction of 0.050 mmol/mol in HbA, highlighting the significance of tailored dietary strategies in diabetes care.
- Increase Physical Activity: Regular physical activity significantly reduces A1C values. It is recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking or cycling. This corresponds with results from the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, which showed a clear connection between diet and exercise in regulating glucose amounts, indicating that there is a significant interaction between a Western diet and genetic risk in male health professionals.
- Stay Hydrated: Sufficient hydration is crucial in managing glucose concentrations, as drinking plenty of water helps in eliminating excess sugar through urine. This straightforward habit can assist in sustaining ideal sugar levels, aiding overall health control.
- Prioritize Sleep: Quality sleep plays a critical role in glucose regulation. Striving for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night can enhance overall health and support effective diabetes management.
- Handle Stress: Heightened stress conditions can result in elevated sugar concentrations. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can effectively assist in managing glucose concentrations.
- Regular Monitoring: Consistent tracking of blood sugar levels is essential for understanding how various foods and activities influence a1c 10.5. This ongoing evaluation provides valuable information that can guide adjustments in blood sugar management strategies.
- Medication Adherence: For individuals prescribed medications for blood sugar management, adherence is crucial. Discussing any concerns or side effects with healthcare providers ensures that the prescribed regimen remains effective and tailored to individual needs.
- Engage in Support Groups: Participating in support groups for those with blood sugar management issues can provide emotional support and practical strategies for overcoming challenges, fostering a sense of community.
- Consult Healthcare Professionals: Regular consultations with healthcare providers are important for modifying plans as necessary. These check-ups ensure that individuals remain on track to achieve lower A1C readings, particularly in light of recent research that highlights the effectiveness of dietary changes in managing a1c 10.5.
The Role of Nutrition in A1C Management
Nutrition is essential in effectively managing A1C values, including maintaining an A1C 10.5. Here are several dietary practices that can contribute to better sugar control:
- Incorporate Fiber-Rich Foods: Foods high in fiber, such as legumes, whole grains, and vegetables, are essential as they help slow glucose absorption and improve overall sugar regulation. Recent studies indicate that increased fiber intake can lead to significant reductions in A1C levels, with findings suggesting that a daily intake of 25-30 grams of fiber can lower levels such as A1C 10.5 by approximately 0.5-1%. This makes fiber a critical component of diabetes management.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Selecting sources of healthy fats, including avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular health, which is particularly important for individuals with diabetes.
- Limit Added Sugars: Reducing the consumption of added sugars can significantly lower sugar spikes. It is essential to consistently review food labels to recognize and prevent concealed sugars that can disrupt glucose control strategies.
- Plan Balanced Meals: Aim for meals that include an even proportion of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Such meals assist in sustaining consistent glucose measurements and avert sudden spikes that can negatively influence health.
- Practice Portion Control: Being aware of portion sizes is essential for regulating calorie consumption and avoiding excessive eating, which is crucial for preserving healthy glucose measurements. Andrew Reynolds, Senior Research Fellow at the University of Otago, emphasizes that diet and lifestyle recommendations are foundational for managing blood sugar conditions, although barriers to implementing these changes—such as lack of access to healthy foods and knowledge—exist. Moreover, a case study involving a Very Low Carbohydrate Meal Pattern demonstrates that significant reductions in carbohydrate intake can lead to improved A1C values, including those reaching an A1C 10.5, lower blood pressure, and enhanced overall health. It is also important to consider that T2D patients with advanced CKD may experience ‘burnt-out health issues,’ necessitating tailored nutritional guidelines to effectively manage their condition.
The Importance of Regular Physical Activity
Participating in consistent physical exercise is crucial for reducing a1c 10.5 levels and improving overall health in individuals with Type 2. Research indicates that the crude rate of emergency department visits for hypoglycemia was 8.6 per 1,000 adults, underscoring the critical need for effective A1C control through physical activity. To achieve optimal results and support a holistic approach to reversing this condition at the Integrative Wellness Center, consider the following recommendations:
- Aim for Consistency: Establish a routine that encompasses at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly. This degree of activity is essential for weight control and enhancing cardiovascular well-being, which are key components of comprehensive metabolic disorder management.
- Incorporate Strength Training: Integrate resistance exercises at least twice weekly. Increasing muscle mass through strength training improves insulin sensitivity, a crucial factor in managing this condition effectively.
- Find Enjoyable Activities: Choose exercises you find enjoyable, such as dancing, swimming, or cycling. Enjoyment increases the likelihood of maintaining a consistent exercise routine over time, aligning with a patient-centered approach to health.
- Set Realistic Goals: Begin with achievable objectives and progressively increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. This gradual approach helps prevent injuries and burnout, facilitating sustained engagement in physical activity.
- Stay Active Throughout the Day: Look for opportunities to incorporate movement into your daily routine. Simple actions like choosing stairs instead of elevators or taking short walks during breaks can greatly enhance your overall level of physical activity.
Additionally, findings from a recent case study indicated variations in physical activity associations based on demographic and clinical factors, particularly showing that normal-weight individuals with the condition were no more likely to be active than those who were overweight or obese. This highlights the significance of individualized methods to exercise and the necessity to confront prevalent misconceptions regarding the condition’s care. It’s also important to note that, as Byrkjeland et al. observed, variability in outcomes related to aerobic training programs was evident, as their study did not find significant changes in HbA1c values after a 52-week program among patients with Type 2. Nevertheless, studies show that consistent physical activity can result in significant enhancements in A1C values, particularly for individuals with a1c 10.5, highlighting its essential function in overseeing health conditions. Furthermore, integrating effective meal planning with these physical activity strategies can enhance overall health outcomes, addressing the root causes of blood sugar issues and empowering patients through a comprehensive, holistic lens.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Diabetes Management Plan
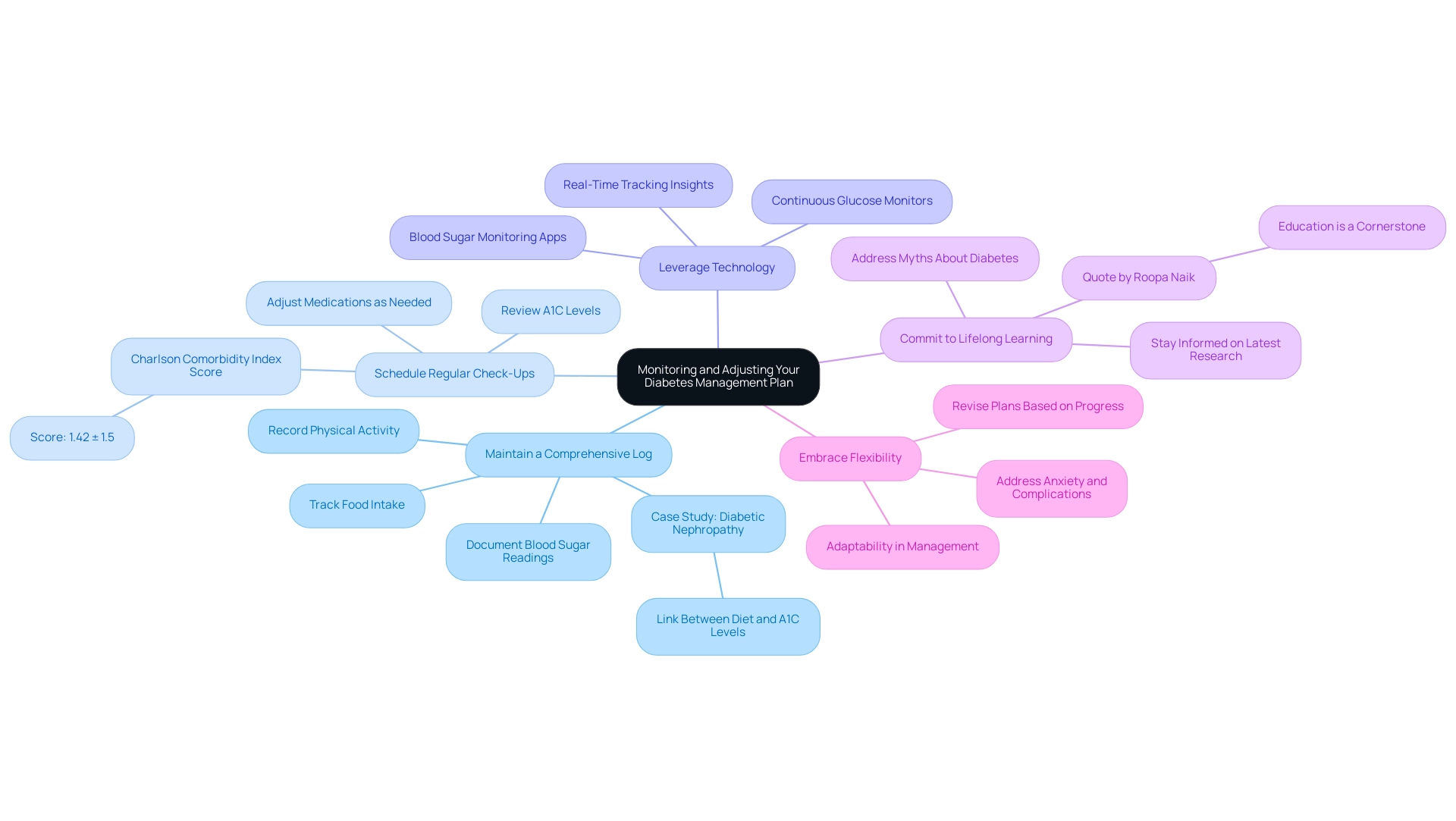
Efficient oversight of your glucose management strategy is essential for attaining and maintaining an A1C 10.5 and reduced A1C values. Here are essential strategies to consider:
- Maintain a Comprehensive Log: Documenting blood sugar readings, food intake, and physical activity can help identify patterns and potential triggers affecting your glucose levels. A holistic approach begins by re-examining the source of your diabetes, allowing you to understand how your lifestyle choices contribute to your condition. For example, a case study on diabetic nephropathy demonstrates how regular documentation enabled patients to observe links between their dietary choices and variations in A1C 10.5 levels, ultimately resulting in improved outcomes.
- Schedule Regular Check-Ups: Regular consultations with your healthcare provider are vital for reviewing A1C levels, especially if they reach A1C 10.5, and making necessary adjustments to medications. These evaluations assist in guaranteeing that your strategy stays aligned with your health needs. Research has indicated that patients with a Charlson comorbidity index score of 1.42 ± 1.5 often gain from more regular check-ups to manage their condition effectively.
- Leverage Technology: Utilizing blood sugar monitoring applications or continuous glucose monitors can offer real-time tracking of your progress, providing valuable insights into daily fluctuations in glucose levels. This technology can empower you to make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle choices, aligning with an integrative approach to health that challenges traditional treatment methods.
- Commit to Lifelong Learning: Staying informed about the latest research and strategies for handling the condition is essential. Knowledge enables you to make informed choices regarding your health and addresses prevalent myths associated with the condition. As Roopa Naik highlights, “Education is a cornerstone of effective control of the disease; comprehending your condition can result in improved outcomes.”
- Embrace Flexibility: Be prepared to revise your plan in response to your progress or any changes in your health status. Adaptability is essential to effective management of the condition, ensuring that you address the root causes while empowering your journey towards better health. Additionally, recognizing and addressing the anxiety that accompanies the worry of potential complications can enhance your overall well-being, allowing you to approach your diabetes management with a clearer mindset.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing A1C levels is vital for individuals with diabetes, particularly when faced with a reading of 10.5%. This level signifies a serious challenge in blood glucose control and a heightened risk of complications. Through a combination of personalized care, dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, and effective monitoring, individuals can significantly improve their A1C levels and overall health outcomes.
Implementing a balanced diet rich in whole foods, along with consistent physical activity and stress management, forms the cornerstone of effective diabetes management. Monitoring carbohydrate intake and prioritizing hydration and sleep can further enhance blood sugar control. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals and engagement in support groups provide essential guidance and community support, fostering an environment conducive to better health.
In summary, achieving optimal A1C levels requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the complexities of diabetes management. By taking proactive steps and making informed lifestyle changes, individuals can reverse the trajectory of their condition and significantly reduce the risk of severe health complications. Empowerment through education, personalized strategies, and ongoing commitment to health will pave the way for improved well-being and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does an A1C measurement of 10.5% indicate?
An A1C measurement of 10.5% indicates that a person’s average glucose readings have been significantly elevated over the past months, exceeding the recommended goal of under 7% for most adults managing diabetes.
What are the health risks associated with an A1C of 10.5%?
Elevated A1C readings, such as 10.5%, indicate poor blood sugar control and increase the risk of serious health complications, including cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, and neuropathy.
How can patients lower their A1C levels?
Patients can lower their A1C levels through personalized care strategies, such as customized meal planning and regular monitoring, which have been shown to reduce A1C values by an average of 2% within six months.
What is the prevalence of undetected blood sugar issues in overweight adults?
The occurrence of undetected blood sugar issues in overweight adults is approximately 7.9%, highlighting the importance of effective monitoring and glucose control.
How does age-adjusted prevalence relate to blood sugar conditions?
The age-adjusted prevalence of total and diagnosed blood sugar-related conditions has notably increased, underscoring the need for effective management of A1C values.
What role does a balanced diet play in managing A1C levels?
A balanced diet rich in whole foods, such as vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, is essential for managing Type 2 diabetes and can significantly impact A1C levels.
Why is monitoring carbohydrate intake important?
Understanding and managing carbohydrate intake is vital for blood sugar control, and working with a dietitian can help create an effective meal plan tailored to individual needs.
How does physical activity influence A1C levels?
Regular physical activity is linked to reduced A1C values, with a recommendation of at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week.
What is the significance of hydration in glucose management?
Staying hydrated helps eliminate excess sugar through urine, which can assist in maintaining ideal blood sugar levels.
How does stress affect blood sugar levels?
Increased stress can elevate blood sugar concentrations, so incorporating stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness and yoga can help manage glucose levels.
Why is regular monitoring of blood sugar levels essential?
Consistent tracking of blood sugar levels provides valuable insights into how different foods and activities affect A1C, guiding necessary adjustments in management strategies.
What is the importance of medication adherence?
For those prescribed medications for blood sugar management, adhering to the regimen is crucial for effectiveness, and discussing any concerns with healthcare providers is essential.
How can support groups benefit individuals managing blood sugar issues?
Participating in support groups offers emotional support and practical strategies for overcoming challenges, fostering a sense of community among individuals facing similar issues.
Why should individuals consult healthcare professionals regularly?
Regular consultations with healthcare providers are important for modifying management plans as needed and ensuring progress towards achieving lower A1C readings.